Chemistry-
General
Easy
Question
For the reaction

 predominates
predominates
 predominates
predominates
- Both are formed in equal amounts
- The product ratio depends on the halogen
The correct answer is: The product ratio depends on the halogen
Related Questions to study
chemistry-
Alcohols undergo acid catalysed elimination reactions to produce alkenes. Because water is lost in the elimination, this reaction is called dehydration reaction. Secondary and tertiary alcohols always give E1 reaction in dehydration. Primary alcohols whose b-carbon is branched also give E1 reaction. The reactivity of alcohol for elimination reaction is tertiary alcohol > Secondary alcohol > Primary alcoholc
Identify the product in the given reaction

Alcohols undergo acid catalysed elimination reactions to produce alkenes. Because water is lost in the elimination, this reaction is called dehydration reaction. Secondary and tertiary alcohols always give E1 reaction in dehydration. Primary alcohols whose b-carbon is branched also give E1 reaction. The reactivity of alcohol for elimination reaction is tertiary alcohol > Secondary alcohol > Primary alcoholc
Identify the product in the given reaction

chemistry-General
chemistry-
What are the products of the following reaction ?

What are the products of the following reaction ?

chemistry-General
chemistry-
Write the product of the following reaction

Write the product of the following reaction

chemistry-General
chemistry-
Which of the following is not expected to be intermediate of the following reaction ?

Which of the following is not expected to be intermediate of the following reaction ?

chemistry-General
chemistry-
The products formed in the reaction are :

The products formed in the reaction are :

chemistry-General
chemistry-
The final product (IV) in the sequence of reactions is :

The final product (IV) in the sequence of reactions is :

chemistry-General
chemistry-
The product of the reaction given below is :

The product of the reaction given below is :

chemistry-General
physics-
In the figure shown the potential drop across the series resistor is

In the figure shown the potential drop across the series resistor is

physics-General
physics-
The maximum and minimum values of zener diode current are

The maximum and minimum values of zener diode current are

physics-General
physics-
The resistance of the diode in forward bias and infinity in the reverse  condition is 20 biased condition. The current in the circuit is
condition is 20 biased condition. The current in the circuit is

The resistance of the diode in forward bias and infinity in the reverse  condition is 20 biased condition. The current in the circuit is
condition is 20 biased condition. The current in the circuit is

physics-General
physics-
In the figure shown, current passing through the diode is .

In the figure shown, current passing through the diode is .

physics-General
General
Find the value of p. Leave your answer in simplest radical form.

For such questions, we should know the properties of different triangles.
Find the value of p. Leave your answer in simplest radical form.

GeneralGeneral
For such questions, we should know the properties of different triangles.
chemistry-
The decreasing order of nucleophilicity among the nucleophiles :
A) 
B) 
C) 
D) 
The decreasing order of nucleophilicity among the nucleophiles :
A) 
B) 
C) 
D) 
chemistry-General
chemistry-
Phenols are converted into their salts by aqueous NaOH but not by aqueous bicarbonates. The salts are converted into the free phenols by aqueous mineral acids, carboxylic acid or carbonic acids. Most phenols have Ka value of about 10–10, and are tremendously more acidic than alcohols. The difference in acidity are due to difference in stabilities of reactants and products. Phenol and phenoxide ions contain benzene ring and therefore must be hybrid of Kekuley structures
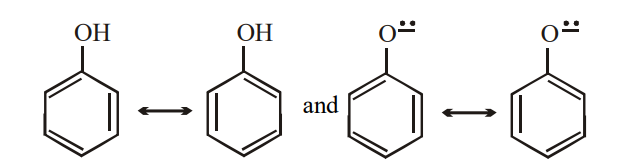
Being basic, oxygen can share more than a pair of electron with the ring

Since energy must be supplied to separate opposite charge, the structure of phenols should contain more energy. The net effect of resonance is therefore to stabilise the phenoxide ion to a greater extent than the phenol and thus to shift the equilibrium towards ionization and make Ka larger than for an alcohol.
Consider the following curves :

Phenols are converted into their salts by aqueous NaOH but not by aqueous bicarbonates. The salts are converted into the free phenols by aqueous mineral acids, carboxylic acid or carbonic acids. Most phenols have Ka value of about 10–10, and are tremendously more acidic than alcohols. The difference in acidity are due to difference in stabilities of reactants and products. Phenol and phenoxide ions contain benzene ring and therefore must be hybrid of Kekuley structures

Being basic, oxygen can share more than a pair of electron with the ring

Since energy must be supplied to separate opposite charge, the structure of phenols should contain more energy. The net effect of resonance is therefore to stabilise the phenoxide ion to a greater extent than the phenol and thus to shift the equilibrium towards ionization and make Ka larger than for an alcohol.
Consider the following curves :

chemistry-General
chemistry-
Symmetrically substituted epoxides give the same products in both the acid catalysed and base catalyzed ring opening. An unsymmetrical epoxide gives different products under acid catalysed and base catalysed conditions. Under basic conditions, the alkoxide ion simply attacks the less hindered carbon atom in an  2 displacement. Under acidic conditions, the alcohol, attacks the protonated epoxide
2 displacement. Under acidic conditions, the alcohol, attacks the protonated epoxide

Structure II and III show that the oxirane carbon share part of positive charge. The tertiary carbon bear a larger part of positive charge and it is more strongly electrophilic. The bond between tertiary carbon and oxygen is weaker implying a lower transition state energy for attack at the tertiary carbon. Attack by the weak nucleophilic is sensitive to the strength of electrophilic is sensitive to the strength of electrophile. Centre attack takes place at more electrophilic carbon which is usually the more substituted carbon because it can better support the positive charge

Symmetrically substituted epoxides give the same products in both the acid catalysed and base catalyzed ring opening. An unsymmetrical epoxide gives different products under acid catalysed and base catalysed conditions. Under basic conditions, the alkoxide ion simply attacks the less hindered carbon atom in an  2 displacement. Under acidic conditions, the alcohol, attacks the protonated epoxide
2 displacement. Under acidic conditions, the alcohol, attacks the protonated epoxide

Structure II and III show that the oxirane carbon share part of positive charge. The tertiary carbon bear a larger part of positive charge and it is more strongly electrophilic. The bond between tertiary carbon and oxygen is weaker implying a lower transition state energy for attack at the tertiary carbon. Attack by the weak nucleophilic is sensitive to the strength of electrophilic is sensitive to the strength of electrophile. Centre attack takes place at more electrophilic carbon which is usually the more substituted carbon because it can better support the positive charge

chemistry-General





