Maths-
General
Easy
Question
In  then find
then find  in the figure.
in the figure.

- 45°
- 57°
- 50°
- 51°

In a triangle ,exterior angle is equal to the sum of both opposite interior angles
The correct answer is: 51°
Related Questions to study
Maths-
if y=2x,z=3x,r=4x then find y in the given figure.

if y=2x,z=3x,r=4x then find y in the given figure.

Maths-General
Maths-
In the given figure, if  find x y z
find x y z

In the given figure, if  find x y z
find x y z

Maths-General
Maths-
Find the value of a+b in the given figure

Find the value of a+b in the given figure

Maths-General
physics-
The figure shows a ray incident at an angle . If the plot drawn shown the variation of
versus
, (r=angle of refraction
The figure shows a ray incident at an angle . If the plot drawn shown the variation of
versus
, (r=angle of refraction
physics-General
physics-
The refracting media are separated by a spherical interface as shown in the figure. PP' is the principal axis,  and
and  are the refractive indices of medium of incidence and medium of refraction respectively. Then :
are the refractive indices of medium of incidence and medium of refraction respectively. Then :

The refracting media are separated by a spherical interface as shown in the figure. PP' is the principal axis,  and
and  are the refractive indices of medium of incidence and medium of refraction respectively. Then :
are the refractive indices of medium of incidence and medium of refraction respectively. Then :

physics-General
physics-
In the figure shown a point object 0 is placed in air on the principal axis. The radius of curvature of the spherical surface is 60 cm. If is the final image formed after all the refractions and reflections.

In the figure shown a point object 0 is placed in air on the principal axis. The radius of curvature of the spherical surface is 60 cm. If is the final image formed after all the refractions and reflections.

physics-General
physics-
In the diagram shown, a ray of light is incident on the interface between 1 and 2 at angle slightly greater than critical angle. The light suffers total internal reflection at this interface. After that the light ray falls at the interface of 1 and 3, and again it suffers total internal reflection. Which of the following relations should hold true?

In the diagram shown, a ray of light is incident on the interface between 1 and 2 at angle slightly greater than critical angle. The light suffers total internal reflection at this interface. After that the light ray falls at the interface of 1 and 3, and again it suffers total internal reflection. Which of the following relations should hold true?

physics-General
physics-
A curved surface of radius  separates two medium of refractive indices
separates two medium of refractive indices  and
and  as shown in figures A and B
as shown in figures A and B
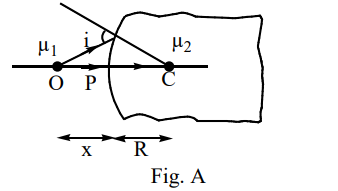
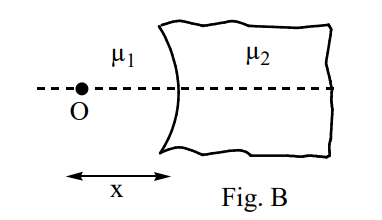
Identify the correct statement (s) related to the formation of images of a real object placed at x from the pole of the concave surface, as shown in figure B
A curved surface of radius  separates two medium of refractive indices
separates two medium of refractive indices  and
and  as shown in figures A and B
as shown in figures A and B


Identify the correct statement (s) related to the formation of images of a real object placed at x from the pole of the concave surface, as shown in figure B
physics-General
physics-
Three right angled prisms of refractive indices  and
and  are fixed together using an optical glue as shown in figure. If a ray passes through the prisms without suffering any deviation, then
are fixed together using an optical glue as shown in figure. If a ray passes through the prisms without suffering any deviation, then

Three right angled prisms of refractive indices  and
and  are fixed together using an optical glue as shown in figure. If a ray passes through the prisms without suffering any deviation, then
are fixed together using an optical glue as shown in figure. If a ray passes through the prisms without suffering any deviation, then

physics-General
physics-
In n similar thin prisms of same material and refractive index are arranged in series as shown :

In n similar thin prisms of same material and refractive index are arranged in series as shown :

physics-General
physics-
Figure shows the graph of angle of deviation  versus angle of incidence i for a light ray striking a prism. The prism angle is :
versus angle of incidence i for a light ray striking a prism. The prism angle is :

Figure shows the graph of angle of deviation  versus angle of incidence i for a light ray striking a prism. The prism angle is :
versus angle of incidence i for a light ray striking a prism. The prism angle is :

physics-General
physics-
A vertical light ray strikes a plane mirror kept inclined at an angle of 45° to the horizontal. The reflected ray is horizontal as shown in fig. A glass prism with refracting angle 6° is placed in the path of the reflected ray. In what way and by how much should the mirror be rotated, if the total deviation of the light ray is to be 90° ?

A vertical light ray strikes a plane mirror kept inclined at an angle of 45° to the horizontal. The reflected ray is horizontal as shown in fig. A glass prism with refracting angle 6° is placed in the path of the reflected ray. In what way and by how much should the mirror be rotated, if the total deviation of the light ray is to be 90° ?

physics-General
physics-
A fixed cylindrical tank of height H=4 m and area  , is filled up with a liquid. An observer through a telescope fitted at the top of the wall of the tank and inclined at
, is filled up with a liquid. An observer through a telescope fitted at the top of the wall of the tank and inclined at  with the vertical. When the tank is completely filled with liquid, he notices an insect, which is at the centre of the bottom of the tank. At t=0, he opens a cork of area a at the bottom of the tank. The insect moves in such a way that it is visible for a certain time. Find the refractive indexof the liquid
with the vertical. When the tank is completely filled with liquid, he notices an insect, which is at the centre of the bottom of the tank. At t=0, he opens a cork of area a at the bottom of the tank. The insect moves in such a way that it is visible for a certain time. Find the refractive indexof the liquid

A fixed cylindrical tank of height H=4 m and area  , is filled up with a liquid. An observer through a telescope fitted at the top of the wall of the tank and inclined at
, is filled up with a liquid. An observer through a telescope fitted at the top of the wall of the tank and inclined at  with the vertical. When the tank is completely filled with liquid, he notices an insect, which is at the centre of the bottom of the tank. At t=0, he opens a cork of area a at the bottom of the tank. The insect moves in such a way that it is visible for a certain time. Find the refractive indexof the liquid
with the vertical. When the tank is completely filled with liquid, he notices an insect, which is at the centre of the bottom of the tank. At t=0, he opens a cork of area a at the bottom of the tank. The insect moves in such a way that it is visible for a certain time. Find the refractive indexof the liquid

physics-General
physics-
A medium (M) having refractive index 2 is placed in air. Its pole is at origin. A point object at (-10 cm,0) starts moving towards the surface with velocity  at 45° with principal axis. [R=20 cm]
at 45° with principal axis. [R=20 cm]
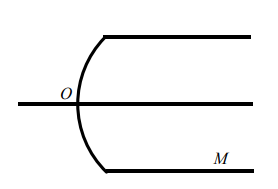
Velocity of image along '  ' direction is ___________ ms–1
' direction is ___________ ms–1
A medium (M) having refractive index 2 is placed in air. Its pole is at origin. A point object at (-10 cm,0) starts moving towards the surface with velocity  at 45° with principal axis. [R=20 cm]
at 45° with principal axis. [R=20 cm]

Velocity of image along '  ' direction is ___________ ms–1
' direction is ___________ ms–1
physics-General
physics-
The time required for the light to go from A to B, when a ray of light goes from point A in a medium where the speed of light is  to a point
to a point  in a medium where the speed of light is
in a medium where the speed of light is  as shown in figure, is:
as shown in figure, is:

The time required for the light to go from A to B, when a ray of light goes from point A in a medium where the speed of light is  to a point
to a point  in a medium where the speed of light is
in a medium where the speed of light is  as shown in figure, is:
as shown in figure, is:
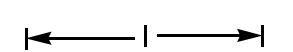

physics-General





