Physics-
General
Easy
Question
Two identical beads are attached to free ends of two identical springs of spring constant  Initially both springs make an angle of
Initially both springs make an angle of  at the fixed point N. Normal length of each spring is 2R. Where R is the radius of smooth ring over which bead is sliding. Ring is placed on vertical plane and beads are at symmetry with respect to vertical line as diameter Choose the correct statement
at the fixed point N. Normal length of each spring is 2R. Where R is the radius of smooth ring over which bead is sliding. Ring is placed on vertical plane and beads are at symmetry with respect to vertical line as diameter Choose the correct statement

- Maximum angle made by spring after collision is same as that of initial moment
- If the collision is perfectly inelastic, the total energy is conserved
- If the collision is perfectly elastic, each bead undergoes SHM
- Both Linear momentum and angular momentum with respect to centre of smooth ring are conserved only at the instant of collision
The correct answer is: Both Linear momentum and angular momentum with respect to centre of smooth ring are conserved only at the instant of collision
Related Questions to study
physics-
Two identical beads are attached to free ends of two identical springs of spring constant  Initially both springs make an angle of
Initially both springs make an angle of  at the fixed point N. Normal length of each spring is 2R. Where R is the radius of smooth ring over which bead is sliding. Ring is placed on vertical plane and beads are at symmetry with respect to vertical line as diameter The speed of bead when spring is at normal length
at the fixed point N. Normal length of each spring is 2R. Where R is the radius of smooth ring over which bead is sliding. Ring is placed on vertical plane and beads are at symmetry with respect to vertical line as diameter The speed of bead when spring is at normal length

Two identical beads are attached to free ends of two identical springs of spring constant  Initially both springs make an angle of
Initially both springs make an angle of  at the fixed point N. Normal length of each spring is 2R. Where R is the radius of smooth ring over which bead is sliding. Ring is placed on vertical plane and beads are at symmetry with respect to vertical line as diameter The speed of bead when spring is at normal length
at the fixed point N. Normal length of each spring is 2R. Where R is the radius of smooth ring over which bead is sliding. Ring is placed on vertical plane and beads are at symmetry with respect to vertical line as diameter The speed of bead when spring is at normal length

physics-General
physics-
Two identical beads are attached to free ends of two identical springs of spring constant  Initially both springs make an angle of
Initially both springs make an angle of  at the fixed point N. Normal length of each spring is 2R. Where R is the radius of smooth ring over which bead is sliding. Ring is placed on vertical plane and beads are at symmetry with respect to vertical line as diameter Relative acceleration between two beads at the initial moment
at the fixed point N. Normal length of each spring is 2R. Where R is the radius of smooth ring over which bead is sliding. Ring is placed on vertical plane and beads are at symmetry with respect to vertical line as diameter Relative acceleration between two beads at the initial moment

Two identical beads are attached to free ends of two identical springs of spring constant  Initially both springs make an angle of
Initially both springs make an angle of  at the fixed point N. Normal length of each spring is 2R. Where R is the radius of smooth ring over which bead is sliding. Ring is placed on vertical plane and beads are at symmetry with respect to vertical line as diameter Relative acceleration between two beads at the initial moment
at the fixed point N. Normal length of each spring is 2R. Where R is the radius of smooth ring over which bead is sliding. Ring is placed on vertical plane and beads are at symmetry with respect to vertical line as diameter Relative acceleration between two beads at the initial moment

physics-General
physics-
Two identical beads are attached to free ends of two identical springs of spring constant  Initially both springs make an angle of
Initially both springs make an angle of  at the fixed point N. Normal length of each spring is 2R. Where R is the radius of smooth ring over which bead is sliding. Ring is placed on vertical plane and beads are at symmetry with respect to vertical line as diameter. Normal reaction on one of the bead at initial moment due to ring is
at the fixed point N. Normal length of each spring is 2R. Where R is the radius of smooth ring over which bead is sliding. Ring is placed on vertical plane and beads are at symmetry with respect to vertical line as diameter. Normal reaction on one of the bead at initial moment due to ring is

Two identical beads are attached to free ends of two identical springs of spring constant  Initially both springs make an angle of
Initially both springs make an angle of  at the fixed point N. Normal length of each spring is 2R. Where R is the radius of smooth ring over which bead is sliding. Ring is placed on vertical plane and beads are at symmetry with respect to vertical line as diameter. Normal reaction on one of the bead at initial moment due to ring is
at the fixed point N. Normal length of each spring is 2R. Where R is the radius of smooth ring over which bead is sliding. Ring is placed on vertical plane and beads are at symmetry with respect to vertical line as diameter. Normal reaction on one of the bead at initial moment due to ring is

physics-General
maths-
If sec4A = cosec(A –  ) where 4A is an acute angle, find the value of A
) where 4A is an acute angle, find the value of A
If sec4A = cosec(A –  ) where 4A is an acute angle, find the value of A
) where 4A is an acute angle, find the value of A
maths-General
maths-
 right angled a
right angled a
 right angled a
right angled a
maths-General
chemistry-
The reaction, Is called
The reaction, Is called
chemistry-General
physics-
Statement - I One end of ideal massless spring is connected to fixed vertical wall and other end to a block of mass m initially at rest on smooth horizontal surface. The spring is initially in natural length. Now a horizontal force F acts on block as shown. Then the maximum extension in spring is equal to maximum compression in spring.

Statement - II To compress or to expand an ideal unstretched spring by equal amount, same work is to done on spring.
Statement - I One end of ideal massless spring is connected to fixed vertical wall and other end to a block of mass m initially at rest on smooth horizontal surface. The spring is initially in natural length. Now a horizontal force F acts on block as shown. Then the maximum extension in spring is equal to maximum compression in spring.

Statement - II To compress or to expand an ideal unstretched spring by equal amount, same work is to done on spring.
physics-General
physics-
A hollow vertical cylinder of radius r and height h has a smooth internal surface. A small particle is placed in contact with the inner side of the upper rim, at point A, and given a horizontal speed u, tangential to the rim. It leaves the lower rim at point B, vertically below A. If n is an integer, then–

A hollow vertical cylinder of radius r and height h has a smooth internal surface. A small particle is placed in contact with the inner side of the upper rim, at point A, and given a horizontal speed u, tangential to the rim. It leaves the lower rim at point B, vertically below A. If n is an integer, then–

physics-General
physics-
A machine, in an amusement park, consists of a cage of the end of one arm, hinged at O. The cage revolves along a vertical circle of radius r (ABCDEFGH) about its hinge O, at constant linear speed v=  . The cage is so attached that the man of weight 'W' standing on a weighing machine, inside the cage, is always vertical. Then which of the following is correct
. The cage is so attached that the man of weight 'W' standing on a weighing machine, inside the cage, is always vertical. Then which of the following is correct

A machine, in an amusement park, consists of a cage of the end of one arm, hinged at O. The cage revolves along a vertical circle of radius r (ABCDEFGH) about its hinge O, at constant linear speed v=  . The cage is so attached that the man of weight 'W' standing on a weighing machine, inside the cage, is always vertical. Then which of the following is correct
. The cage is so attached that the man of weight 'W' standing on a weighing machine, inside the cage, is always vertical. Then which of the following is correct

physics-General
physics-
Acceleration versus time graph of a particle moving in a straight line is as shown in adjoining figure. If initially particle was at rest then corresponding kinetic energy versus time graph will be:

Acceleration versus time graph of a particle moving in a straight line is as shown in adjoining figure. If initially particle was at rest then corresponding kinetic energy versus time graph will be:

physics-General
physics-
Volt/meter is the unit of
Volt/meter is the unit of
physics-General
chemistry-
From methyl alcohol we get:
From methyl alcohol we get:
chemistry-General
chemistry-
Which of the following is oxidised by 
Which of the following is oxidised by 
chemistry-General
maths-
Calculate the median from the following data:
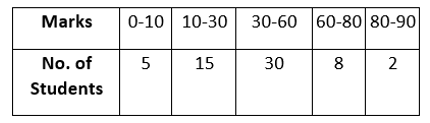
Calculate the median from the following data:

maths-General
Maths-
Find the mean of the following distribution

Mean = 55
Find the mean of the following distribution

Maths-General
Mean = 55





