We can see uncountable things in this universe. Just take a peek at the surroundings; surely, you will be able to see at least ten different things just lying around or walking in front of you, be it a cat, a book, a table, a laptop, etc.
We can filter all the things based on one major criterion – whether a thing can breathe or not. If it can, it is called a living thing; if it does not, it is known as a non-living thing.
Therefore, that is what we will discuss in this blog. Let us talk about both things of the universe elaborately.
Classification of things
As seen earlier, there are two different things in this world. They are:
-
Living things:
These are the things that can breathe, sleep, eat, play, walk, talk, etc. They have a soul, brain, and all the other body parts. They do all kinds of activities that non-living things cannot.
-
Non-living things:
These things do not breathe or do any activities mentioned above. They do not have a soul or a heart. They exist.
In the following passages, let us see more about them.
Living things
They are made of microscopic structures. They are capable of existing and living. They show significant growth or movement in their lives when they are alive. And finally, they will all die one day, and they can’t be immortal. No living thing has ever existed for centuries. Maybe some trees exist longer, but they will still die after a certain period.
In addition, they experience metabolism. They have blood flow from their heart to other body parts through blood vessels. However, the blood colour may vary depending on the creature. For example, human beings’ blood colour is red, while for sea creatures like octopuses, it is blue.
Furthermore, living things can reproduce. They are capable of introducing new lives to this planet, and those new lives can create more new lives. So, it is like an endless loop; it goes on and on.
Living creatures’ life cycle is as follows:
Born →Live and Grow →Reproduce →Die
Characteristics of Living Organisms
some of the important and common characteristics are:
-
Movement:
They are capable of showing locomotory motion. For example, humans and animals move by walking, and worms move by crawling through the soil. All of them are given the privilege of moving from one place to another except for trees and plants.
-
Touch-sensitive:
They are touch-sensitive. They can feel things as long as they do not go numb. For instance, if you touch dogs on their heads, they would feel that touch and get attached easily because they love to be petted. It goes the same for other organisms, and almost all are sensitive to touch.
-
Respiration:
To release the energy acquired from food and water, the respiration process takes place. We breathe to survive, and living would not be possible without respiration. In respiration, there are two forms. One is inhalation; it means inhaling the air into our lungs through respiratory tubes. Meanwhile, the other one is exhalation; it indicates exhaling the already inhaled air through respiratory tubes to the surrounding.
-
Growth:
These creatures grow every second, but we cannot see their results, as the growth is very minute. As lengthier as we get, our maturity increases, and that helps us make better decisions in our lives.
-
Consumption and Digestion:
Scientifically speaking, These things acquire adequate energy through food. The food type varies vastly depending on the creature. For example, humans eat fruits, vegetables, or meats to obtain energy for the day. Then, they spend that energy on various daily activities such as playing, singing, walking, talking, etc. The food they consume gets digested and disposed of the next day in the form of waste. This elimination process is termed excretion.
-
Reproduction:
They can reproduce either sexually or asexually. Sexual reproduction involves two parents, a father and a mother, to produce new offspring. On the other hand, asexual reproduction involves only one parent. Few plants do this type of reproduction.
Examples of Living things
There are numerous examples. They are:
- Animals
- Plants
- Trees
- Human beings
- Sea creatures
- Insects
- Reptiles
- Mosses
- Mammals
- Bacteria
Non-living things
They are the things that do not live. They do not have the same features as living things. They are literal things that exist in the world. These things do not possess life. The immortality of the non-living things purely depends on the type of the thing. Some things, such as mountains and rivers, have existed for thousands of years.
In addition, they do not require energy to survive. They have a whole different purpose. Some serve their life as living things.
Interestingly enough, non-living things can be categorised into two:
- Natural things
- Man Made or Artificial things
-
Natural things
Natural non-living things have been existing by themselves since the start of the universe. They can be anything from stars and planets to mountains, rivers and other natural resources. Living things consume natural resources daily, such as water, fire, coal, and fuel. Most of these resources are infinite. Therefore, these resources play a vital part in everyone’s life.
Given below are a few examples of natural things:
- Mountains and hills
- Rivers
- Seas and oceans
- Stones and rocks
- Coal
- Fuels such as petrol, diesel
- Planets and stars
-
Artificial (or manmade) things
Humans or other creatures create these types of non-living things. The objectives of such kinds of things are to serve mankind. For instance, we can use smartphones to do various tasks such as calling, texting, surfing the internet, etc. These things have a limited lifespan but vary from one thing to another. Although short-lived, they are very helpful in serving our daily needs.
Let us have a look at some of the artificial non-living things:
- Smartphones, laptops, televisions, AC, and other electronic gadgets
- Cars, bikes and other automobiles
- Blender, refrigerator, oven, and other domestic appliances
- Chairs, benches, doors, sofa, table, cot and other furniture
- Clothes, dresses, blankets, towels and other similar items
- Bags, purses and wallets
- Toys, dolls
- Books, pencils, pens, papers and other stationery items
- Sunglasses, watches, shoes and other accessories
- Preserved food items
Characteristics of Non-living things:
- They do not have cells, so they are lifeless. Also, there is no protoplasm present in them.
- Because of the lack of protoplasm, they cannot do any metabolic activities.
- These things do not have their definite size. In many cases, they take up the shape of the element or the substance they are contained in. A good example of that would be liquid substances such as water and oil. In addition, rocks and stones are generally mounted by switching the surroundings or environment. So, from that, we can understand that non-living things’ states change depending on external influence.
- These things mostly grow by accretion. In other words, we can grow non-living things by adding more material or substance. Some ideal examples include welding metals, rainfall in water resources that can cause increased water levels, adding more snow to make a snowball bigger, etc.
- One great thing about non-living things is that they never die, as they never live. However, they have their lifespan. For example, a smartphone will stop working after 3 or 4 years of usage; a table might break after ten years, etc.
- Essential things in life, namely breathing, reproduction, respiration, and movement, are all absent in non-living things.
Differentiation Table – Living things and Non-living things
Now that we have understood every concept related to both of them, let us have a look at the tabulation which distinguishes them:
Living things |
Non-living things |
| Living things possess life. | Non-living things do not possess life. |
| To survive, they need food and water. | No such requirements. |
| They can reproduce and keep the community growing. | They do not reproduce. |
| They respond to stimuli and are sensitive. | They do not respond to stimuli and are not sensitive. |
| They can move from one position to another independently. | They require external help to move from one place to another. |
| They are not immortal and have a lifespan. | They are immortal. |
| Most of them have feelings. | They do not have feelings. |
| Examples: plants, humans, animals, etc. | Examples: water, gadgets, paper, etc. |
Conclusion
In conclusion, both play a special part in each other’s life. Therefore, they coexist without any trouble. It is a beautiful part of nature that brings all such things together.
In this article, we have provided a comprehensive idea of both living & non-living things, which can help the readers obtain knowledge. In addition, we have also seen what their differences are.
Frequently Asked Questions.
1. Mention the criteria we use to distinguish both living and non-living things.
A.The following are some of the criteria for identifying them:
- Living things are capable of growing and developing.
- Non-living things are immortal and have an immortal lifespan.
- Living things (except plants and trees) can move independently from one place to another.
- Mainly, living things can reproduce and grow their family while non-living things cannot.
2. Why is studying living and nonliving things important?
A. Obtaining knowledge about living and non-living things helps us understand how this world works. Moreover, it is fundamental to know this concept at a young age because many future topics will be related to that.
3. Mention some of the examples of non-living things.
A. The following are a few examples of non-living things:
- Hills
- Water resources
- Natural resources
- Accessories
- Clothing and bedding
- All the home furniture
- Electronic gadgets
- Planets and stars in the solar system

Relevant Articles
Structural Organisation & Different Levels
Structural Organisation The most extensive, in-depth studies begin with the …
Structural Organisation & Different Levels Read More »
Read More >>Polysaccharides – Structure, Types, Characteristics and Functions
What is a Polysaccharide? Polysaccharides are a major group of …
Polysaccharides – Structure, Types, Characteristics and Functions Read More »
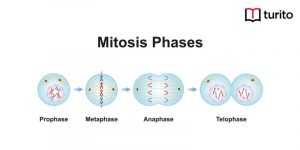
Read More >>What is Mitosis? Phases of Mitosis, Diagrams, Cytokinesis
Mitosis phase Have you ever wondered what the yeast in …
What is Mitosis? Phases of Mitosis, Diagrams, Cytokinesis Read More »
Read More >>What is Cell Division? Process, Cell Cycle, Mitosis
What is cell division? Each day, every hour, every second, …
What is Cell Division? Process, Cell Cycle, Mitosis Read More »
Read More >>

















Comments: