Carbon Dioxide Definition
Carbon dioxide is an element found in the atmosphere in its gaseous state at room temperature. It is made up of two oxygen atoms and one carbon atom. Carbon dioxide gas is released when animals and humans exhale. It is one of the greenhouse gases found in the Earth’s atmosphere in low concentrations. In its solid form, carbon dioxide is found in the form of dry ice.
The carbon dioxide in the atmosphere increases due to human activities as it is produced when hydrocarbon fuels like coal, gasoline, wood, natural gas, and oil burn. Burning fossil fuels releases carbon that reacts with oxygen in the atmosphere to give carbon dioxide and water vapour.
One molecule of carbon dioxide comprises one carbon atom and two oxygen atoms. That is why the carbon dioxide molecular formula is CO2. The molecular weight of CO2 is around 44 g/mol.
The molecular structure of carbon dioxide

The Properties of Carbon dioxide
- Carbon dioxide is a colourless and odourless gas soluble in water, acetone, and ethanol. Below are some general properties of carbon dioxide:
| The carbon dioxide molecular formula and molecular weight of CO2 | CO2 and 44 g/mol |
| The Molar mass and molecular structure of carbon dioxide | 44.0095(14) g/mol |
| Density | 1,600 g/L – solid 771 g/L – liquid 1.98 g/L – gas |
| Boiling point | −78.5 °C |
| Melting point | −56.6 °C |
| Synonyms | Carbonic anhydride |
| Specific gravity | 1.53 at 21oC |
| Water solubility | 0.9 vol/vol at 20oC |
| Henry constant for the solubility | 298.15 mol/ kg * bar |
Chemical Properties of Carbon dioxide
- On dissolution in water to a small extent, carbon dioxide forms a weak acid called carbonic acid, whose chemical formula is HCO3.
CO2 ( carbon dioxide molecular formula) + H2O → H2CO3
- After carbonic acid reacts in water slightly and reversibly, the bicarbonate ion HCO3– and hydronium cation, H3O+, is formed.
H2CO3 + H2O → HCO3– + H3O+
- During photosynthesis, plants take in water and carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. In the plant cell, water is oxidised; that is, it loses electrons. On the other hand, carbon dioxide is reduced, meaning that it gains electrons. This results in the conversion of water to oxygen and carbon dioxide to glucose. The oxygen is then released into the atmosphere by the plant while energy is stored in the molecules of glucose.
- The process of conversion of light energy into chemical energy by green plants is called photosynthesis. During the process, light energy is absorbed and used up by green plants to convert water, minerals, and carbon dioxide into oxygen and oxygen-rich organic compounds.
Main Function of Carbon dioxide
Carbon is the primary component of lipids, proteins, carbohydrates, and nucleic acids. The molecular weight of CO2and the molecular structure of carbon dioxide let it bond with a diverse range of elements in many ways. The carbon cycle shows how carbon passes through the living and nonliving components of the environment.
There are two main plant and animal processes—respiration and photosynthesis, both of which require carbon dioxide. Through photosynthesis, green plants convert water and carbon dioxide into food compounds like oxygen and glucose. Following is the reaction involved:
6CO2 (molecular formula of carbon dioxide) + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2
Carbon dioxide is one of the main gases involved in human processes. It is the only gas that almost every human tissue releases and works on almost every organ. The CO2 molecule has a variety of roles to play in the human body, including the supply of oxygen to the cells and the regulation of blood pH.
Environmental Problems – Carbon Dioxide
An increase in CO2molecule levels in the atmosphere results in an increase in the abundance of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, trapping more heat. This results in melting ice caps and rising sea levels, causing flooding in nearby habitations. Our clean atmosphere is contaminated with carbon dioxide emissions, which form an impenetrable layer across the globe. The heat is trapped inside the plant by this sheet, which gives rise to the phenomenon of global warming. Another name for this phenomenon is the greenhouse effect.
Burning fossil fuels releases carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, which results in the release of chemicals into the atmosphere, decreased forest cover, and the growth of production, cultivation, and industrial activities at an alarming rate. Both of these changes the equilibrium of the climate system. A balance between the incoming solar energy and the energy reflected into the atmosphere determines the temperature of the Earth. The heat that was supposed to be lost in space is taken up by carbon dioxide. When this energy is released into the Earth, the atmosphere becomes even hotter.
What are Greenhouse Gases?
The CO2 molecule is one of the commonest greenhouse gases and accounts for about 76% of the total greenhouse gases. After carbon dioxide, methane is the main greenhouse gas, followed by NO2 and other fluorinated gases that are produced as a result of industrial processes. Almost 90% of carbon dioxide is produced due to the burning of fossil fuels like oil, coal, and natural gas. Electricity is generated by the power plants fired by natural gas and coal. Oil-based products like diesel, gasoline, and aviation fuel provide most of the energy required for transportation. Fossil fuels also provide the power and heat required by industrial processes. Electricity is also used in commercial and residential areas for air-conditioning and lighting, while oil and natural gas are used for heating.

One more source of carbon dioxide is the changes caused by land use, especially the destruction of forests to make way for crops, animals, and human habitation. Trees and other plant materials absorb carbon dioxide as a part of the photosynthesis process. They also remove carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. Due to deforestation, more carbon dioxide remains in the atmosphere or is taken up by the oceans.
Wondering why CO2 (molecular formula of carbon dioxide) is suddenly a problem? For a very long time (around 100 years), only a few people thought about the fact that now humans are burning an increasing amount of coal, oil, and natural gas. Humans were too busy enjoying the perks of abundant, low-cost fuel. A young scientist in 1958 started observing the top of the Mauna Loa in Hawaii. This spot was selected because this site was in the middle of the Pacific Ocean, and the degree of air pollution was extremely low. Scientists observed that the carbon dioxide level in the atmosphere was steadily increasing. Subsequently, he devoted his life to carrying on with this research, as a result of which we know that the carbon dioxide in the atmosphere is on the rise at an alarming rate. Rising carbon dioxide in the atmosphere is equivalent to adding more glass layers to a greenhouse, which is causing the temperature of the Earth to rise.
Conclusion
Currently, mankind is in the process of changing the chemistry of the global atmosphere. As discussed above, atmospheric CO2 (molecular formula of carbon dioxide) concentrations have been on the rise due to human activities like burning fossil fuels such as coal and oil and deforestation. The concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere has increased by as much as 30% over the past 150 years. As a result of this, the global mean surface temperature has increased between 0.4 and 0.8°C. Over the last 20,000 years, the present rate of carbon dioxide increase has been unprecedented.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the function of carbon dioxide in the body?
Carbon dioxide is odourless and colourless, that the human body releases as a waste product. The blood carries this gas to the lungs. We exhale carbon dioxide and inhale oxygen by the process of breathing all day without even thinking about it. A CO2 blood test can be used to measure carbon dioxide levels in the blood.
What are the advantages of carbon dioxide?
Increased carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere result in increased photosynthetic activity by plants. This promotes the growth of plants. Even though increased levels of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere are good for plants, they lead to global warming and are detrimental to humans.
What are three uses for carbon?
1. Carbon is used as a fuel in the form of coal.
2. Carbon in the form of graphite is used to make high-temperature crucibles, pencil tips, electrodes, dry cells, and lubricants.
3. Diamond is a form of carbon that apart from being used in jewellery, is used in industries for drilling, cutting, polishing, and grinding of substances owing to its exceptional hardness.
Why is carbon dioxide important for us?
Carbon dioxide is an essential gas required for internal respiration in the human body. It is a mechanism responsible for transporting oxygen to different body tissues while also carrying carbon dioxide away from them. It also balances the blood pH, acting as an essential gas for our bodies.
What are the physical properties of carbon dioxide?
1. Carbon dioxide is a colourless and odourless gas at low concentrations, but it has a strong acidic smell at higher concentrations.
2. Its density is about 1.97 kg/m3 at room temperature and normal pressure conditions, which is about 1.52 times that of normal air.

Relevant Articles
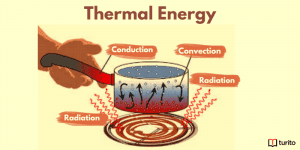
Understanding Thermal Energy: What It Is and How It Works
Thermal energy is essential to our daily lives, from warming …
Understanding Thermal Energy: What It Is and How It Works Read More »
Read More >>Avogadro’s Number: Meaning, Importance, and More
Introduction The concept of measuring the microscopic particles that make …
Avogadro’s Number: Meaning, Importance, and More Read More »
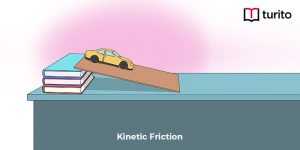
Read More >>Kinetic Friction – Definition, Laws, Types
Kinetic Friction Kinetic force is a force acting between two …
Kinetic Friction – Definition, Laws, Types Read More »
Read More >>

















Comments: