What is Light Energy?
The type of kinetic energy that produces forms of light visible to the human eyes is called light energy. What is light? The form of electromagnetic radiation given off by hot physical bodies or things like light bulbs, lasers, and the sun is called light.
Light carries minute clusters of energy called photons. When the temperature of the atoms of an object increases, photons are formed. The heat energy excites the electrons, and extra energy is produced. The energy that is produced is emitted as photons. More photons are emitted as the temperature of the substance increases.
When light navigates, it goes from one place to another in the form of waves. But it does not need any matter to carry energy along with it. So, light can easily navigate in the absence of air in space. Sound waves do not have this property. The propagation of light energy is faster than anything else. It travels with a speed of more than 186,281 miles per second.

Huge quantities of electromagnetic radiation are released by the sun. Only a fraction of this energy is perceived by the human eyes, which is called “visible light”. Solar energy navigates in the form of waves. Scientists calculate the quantity of energy a wave carries by quantifying its wavelength and the distance between two adjacent wave points.
Among the diverse types of electromagnetic radiation given off by the sun, visible light is one. The range of all possible radiation frequencies is called the electromagnetic spectrum. It reveals the diverse types of electromagnetic radiation the sun emits, such as X-rays and UV rays.
The electromagnetic spectrum distinguishes the different types of radiation energies from the sun. The amount of energy these waves carry corresponds to the difference in their wavelengths.
Types of Light Energy
There are various types of light energies, including:
Visible light: The only type of light energy example visible to the naked human eyes is a type of electromagnetic energy called visible light. Sun is the primary source of visible light. However, bulbs and torches also emit it.
Infrared Light: This form of electromagnetic energy also releases heat. Switching on the TV with the remote is possible because of the infrared light. This is because the infrared waves navigate from the remote to the television.
X-rays and Ultraviolet light: These light waves are employed by medical professionals to obtain photographs of the body’s interior to diagnose bone fractures and other defects. Dentists even employ X-rays to find out the extent of tooth decay.
Key Properties of Light
Intensity: The rate at which energy in the form of light is given off by the source is called intensity. Power is given in Watts. In other words, intensity is the brightness quantified by the rate at which energy in the form of light is given off per unit time per unit area.
Frequency: The number of crests that go through a specific point per second is called frequency.
Wavelength: The distance between two adjacent crests or troughs can be defined as wavelength. The speed at which light waves travel through a vacuum is the same. Wavelength and frequency are inversely related to each other. If the wavelength is more, the frequency is less.
Polarisation: The phenomenon of converting unpolarised light to polarised light energy examples is called polarization. Generally, the vibration of light waves occurs in multiple planes, so they are not polarised.
Phase: A specific point in time during the cyclic waveform is called a phase. When light waves are in a phase, they have a higher intensity.
Uses of Light Energy
Light energy is used for a diverse range of commercial and scientific applications, including:
Food: Living organisms can generate food only through light energy. All living beings depend on light for food and energy. The exceptions to this, however, are a few microorganisms like bacteria.
Vision: Because living beings possess eyes, they can visualize the objects around them. The function of the eyes is, however, of no use in the absence of light. When light falls on the eyes, the eyes receive the image of the object to be seen. This information is then conveyed to the brain, and the object is seen. Therefore, light is crucial for seeing.
Colors: The presence of colors makes the entire world look beautiful. The existence of colors is based on light. The light has lots of spectra, each spectrum corresponding to a particular color. The spectrum of light is classified as VIBGYOR.
Light energy has a speed of about 300,000 km/s. As an example of this, when you see the sun setting, in actuality, the light you are seeing has left the sun ten minutes ago. Light can be quantified in two ways:
The light energy examples of all wavelengths are quantified by radiometry, while photometry quantifies light when the wavelength is compared to a standard of brightness perception by the human eye.
Whenever we need to quantify what light energy is to be used by humans, photometry is useful. Units of photometry differ from other units of measurement as they consider how the human eye reacts to light. According to this, if two light sources form visible light of the same intensity, they might not appear equally bright.
Physical pressure is applied to objects in their path by light energy. This mechanism is understood based on the concept of particle nature of light which indicates that photons hit the light energy and transfer their momentum. The power of light divided by its speed is the pressure of light. For daily use objects, the effect of a light beam is light pressure.
Suppose a coin can be picked up with laser pointers, but you need billions of those for this task. Asteroids spin faster because of the pressure of light. This is because it works on them like wind pushes a windmill. This is the reason why certain researchers work on solar sails to try to propel interstellar flight.

We are surrounded by what is light energy on all sides. Our skins can get tanned or burned due to it, metals can melt, and food can be heated. Up to the 1950s, harnessing light energy was a big challenge for scientists. It is hoped that light energy will be used to navigate among stars in the future.
The sense of light of humans can detect light energy. It consists of electromagnetic radiation and navigates in a straight path. Humans are so used to the word “light” that they use it at least ten times daily. Do you ever think about the energy generated from light?
As light does not have mass, it can be considered “pure” energy. It is both a wave and a particle. The amount of energy in light or electromagnetic radiation depends upon the frequency of light.
Facts About Light Energy
- The electromagnetic radiation viewed by the human eye can be defined as light energy
- Light energy navigates in the form of rays that are emitted outwards from the light source.
- It navigates in a straight path and consists of electromagnetic radiation
- Most waves of light energy cannot be viewed by the human eye and occur in various wave frequencies compared to visible light.
- Light waves navigate in the form of photons.
Examples of Light Energy
The best example of light energy is sunlight. It is where light energy comes from naturally. Along with that things like stars, lightbulbs, lasers, and hot objects all emit light energy.
Conclusion
Scientists are attempting to gain more knowledge regarding how to store and utilise light energy effectively. As the light energy is available in nature abundantly, learning how to manage it is fruitful. Light energy has the capacity to enhance the speed of an asteroid in motion or alter its direction.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. What do you mean by light energy?
A. Light energy is a type of electromagnetic radiation or kinetic energy. It has a wavelength visible to the human eye.
2. How does light navigate?
A. Light energy navigates as waves. It travels very fast, probably faster than any other form of energy.
3. How is light energy produced?
A. Light is composed of photons or tiny clusters of energy. Once the atoms of an object heat up, it emits electrons as a result of movement. The number of photons produced depends on the temperature of the object.
4. What do you mean by electromagnetic radiation?
A. Electromagnetic radiation is a type of energy generated as a result of the motion of electrically charged particles that navigate in a vacuum or oscillation of magnetic and electric disturbance.
5. What is chemical potential energy?
The energy held by the chemical bonds is called chemical potential energy. It is susceptible to being absorbed and released as the particle number of the given species changes.
6. What is meant by electromagnetic spectrum?
A. The range of all forms of electromagnetic radiation is simply called the electromagnetic spectrum.
7. Where does visible light lie in the electromagnetic spectrum?
In the electromagnetic spectrum, visible light lies between infrared and ultraviolet. Frequencies of about 4 × 1014 to 8 × 1014 hertz (Hz) and wavelengths of about 740 nanometers to 380 nanometers (1.5 × 10−5 inches) belong to visible light.

Relevant Articles
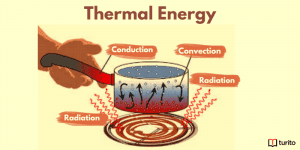
Understanding Thermal Energy: What It Is and How It Works
Thermal energy is essential to our daily lives, from warming …
Understanding Thermal Energy: What It Is and How It Works Read More »
Read More >>Avogadro’s Number: Meaning, Importance, and More
Introduction The concept of measuring the microscopic particles that make …
Avogadro’s Number: Meaning, Importance, and More Read More »
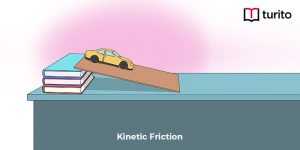
Read More >>Kinetic Friction – Definition, Laws, Types
Kinetic Friction Kinetic force is a force acting between two …
Kinetic Friction – Definition, Laws, Types Read More »
Read More >>

















Comments: