Our Solar planetary system is made up of the sun, and stars and everything are gravitationally connected to it, including the planetary system (planets listed in order), Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune, dwarf planets like Pluto, plenty of moons, and billions of asteroids, meteoroids, and comets. In addition to our solar system, thousands of celestial objects are orbiting other stars in the Milky Way.
Formation and Discovery of Solar Planetary System
About 4.5 billion years ago, a dense cloud of gas and dust started to disintegrate. According to NASA Science, the cloud straightened into a whirling disc known as a solar nebula as it shrank.
At some point, the pressure and heat reached a point where hydrogen atoms started fusing to make helium. The sun was created due to the enormous energy generated by nuclear reactions.
About 99 percent of the available energy was gathered by the sun, and the remaining energy crusted into smaller groups inside the rotating disc. Some of these aggregates collected sufficient mass to be molded into spheres by gravity, forming planets, dwarf planets, and moons. The remaining leftover parts formed our solar system’s smaller moons, asteroids, and comets.
Solar System
The solar system extends in enormous diameters—at least 100 astronomical units— (15 trillion km). It is kept together by the sun’s powerful gravitational attraction, which also keeps asteroids and planets in place. The sun, the largest body in the solar system, powers the planet through nuclear reactions at its core. It has a surface temperature of 6000°C. Along with a little helium gas, hydrogen gas makes up most of its composition.
What Does the Solar Planetary System Consist Of?
Asteroids
These large rocks or metal fragments are typically found between Mars and Jupiter’s orbits. It is assumed that these moons were once components of the asteroid belt rather than orbiting Mars. The asteroid belt is located between Mars and Jupiter. It has rock fragments that are significantly smaller than planets. These rock fragments are called asteroids or minor planets. They are not visible to the human eye from Earth, although many can be seen with a small telescope or binoculars.
Satellites
Satellites are planet-revolving spacecraft that are also members of the solar system. The moon is the only single natural satellite of the planet Earth.
A significant portion of the solar system comprises human-made artificial satellites. Compared to the moon, the Earth’s natural satellite, these satellites orbit the planet more closely.
Comets
Comets are tiny, ice-based bodies with erratic shapes. They typically originate from the Kuiper Belt, the outermost region in the solar system, beyond Neptune. It starts vaporizing as they approach the sun, creating a stunning tail. Some of these comets are seen frequently, such as Halley’s Comet, which will show up again in 2061 (after a 76-year gap).
Planets
The solar system also has eight planets, which are massive, almost circular celestial bodies travelling in oval orbits around the sun. Of all the planets in our solar system, Earth is one of the planets situated sufficiently far from the sun for life to survive without being either too hot or too cold. At least 4.6 billion years ago, the planets were formed when discs of gas and dust orbiting the sun contracted and clustered together due to gravitational pull.
Planetary Systems: Types of Planets
The innermost four planets, Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars, are frequently referred to as “terrestrial planets” because of the stony composition of their surfaces.
The four massive outermost planets—Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune—are occasionally referred to as the Jovian or “Jupiter-like” planets because of their huge size compared to the terrestrial planets. While astronomers assume some or all of them might have solid cores, they are also primarily composed of gases such as hydrogen, ammonia, and helium, rather than only solid surfaces.
| Curiously Enough:
Uranus and Neptune have also been termed the ice giants, while Jupiter and Saturn have also been termed the gas giants. According to the Planetary Society, Uranus and Neptune have much more atmospheric moisture and other ice-forming compounds, like methane, hydrogen sulfide, and phosphene, that solidify into clouds on the planet’s icy surfaces. |
Solar Planetary System: Planets List in Order
Mercury: The nearest planet
Mercury is the nearest and smallest planet in the solar system to the sun; it is just slightly bigger than Earth’s moon. Because Mercury is closest to the sun, it completes its revolution within 88 days around the sun (approximately two-fifths the distance between the sun and the Earth).
The temperature of Mercury varies greatly throughout the day and night. Mercury’s daytime temperature, which is not sufficiently warm to melt lead, can soar to a searing 840 F (450 C). During the night, though, the temperature drops to minus 290 F. (minus 180 C).
Venus: The Earth’s twin
Venus, the hottest planet in our solar system. It is second among all planets in our solar system. The planet is a prominent illustration of the greenhouse effect, consisting of a thick and exceedingly toxic atmospheric layer made up of sulfuric acid clouds.
Venus is termed Earth’s twin because of their similar sizes and the abundance of mountains and volcanoes seen in radar photos taken beneath Venus’ atmosphere. Beyond that, the planets are very distinct from one another.
Earth: Our home
Among all planets in our solar system, Earth is the only planet that has made life possible!
Earth is the third planet in the solar system. It is a water planet since water covers two-thirds of the planet’s surface. The only planet known to support life is Earth. It has nitrogen and an oxygen-rich atmosphere. At the equator, the Earth spins on its axis at a speed of 1,532 feet per second (467 meters per second), or just over 1,000 mph (1,600 kph). The planet circles the sun at a rate of more than 18 miles per second (29 km per second).
Mars: The red planet
Mars is positioned fourth among all the planets in our solar system. The iron oxide dust contributes to the planet’s distinctive red color, surrounded by the chilly, desert-like world. Mars and Earth are quite comparable. Both are rocky planets with mountains, canyons, and valleys, and storm systems ranging from small-scale tornado-like dust devils to planet-sized dust storms.
Asteroid Belt
The asteroid belt is positioned between Jupiter and Mars. As per NASA, asteroids are minor planets; there are millions of smaller asteroids in addition to between 1.1 and 1.9 million asteroids larger than 0.6 miles (1 km) in diameter in the main asteroid belt, where the 590-mile-diameter dwarf planet Ceres is located.
Jupiter: The solar system’s largest planet
The solar system’s largest planet, Jupiter, is the fifth planet from the sun. As per NASA, Jupiter is more than twice as large as all the other planets. Jupiter, the solar system’s largest planet, comprises colorful swirling clouds because of the variety of trace gases, including ammonium hydrosulfide crystals and ammonia ice.
Saturn: Planet of rings
Saturn is known for its extensive and distinctive ring system. It is the sixth planet from the sun. Along with Saturn, there are other planets with rings. Scientists are still unsure how the rings evolved, even though they are built of ice and rock. The gaseous planet is primarily made of hydrogen and helium, with many moons.
Uranus: The Tilted, Sideways Planet
Uranus is positioned seventh among all the planets in our solar system and is quite irregular. It has hydrogen sulfide clouds, the same substance that gives rotting eggs their terrible odor. Like Venus, it also rotates from east to west on its axis. Its equator, however, is almost at a right angle to its orbit, making it essentially orbit on its side.
Neptune: The huge, stormy blue planet
Neptune is positioned eighth from the sun. It is the solar system’s coldest planet. The average temperature on Neptune’s surface is minus 346 degrees Fahrenheit (minus 210 degrees Celsius).
Pluto: Earlier a planet, but now a dwarf planet!
Pluto is distinct from other planets in our solar system and was formerly considered the ninth planet from the sun. Its orbit is highly elliptical, occasionally falling inside Neptune’s orbit and most often, outside its orbit. Additionally, as per ESA, Pluto’s orbit does not fall on the same plane as the other planets; rather, it orbits 17.1 degrees above or below, taking 288 years to complete its one orbit. Pluto is smaller than Earth’s moon.
Conclusion
Although humans have been studying the solar system for hundreds of years, it wasn’t until recent centuries that scientists began to understand how things function. Exploring the solar system is quite interesting and important for students. Therefore, they must comprehend the elements of the solar system well to obtain complete knowledge about the universe, of which they are a small part!
Frequently Asked Questions
What components comprise the solar system?
There are eight massive planets in the solar system, with almost circular celestial bodies that follow oval orbits around the sun. The Earth is one of the planets and is situated far enough from the sun for life to survive without being either too hot or too cold.
How many different kinds of planets exist in the solar system?
There are two kinds of planets:
1. Rock Planets: Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars (smaller planets in the solar system) are among the rocky planets primarily composed of m etals and solid rock.
2. Gaseous Planets: Saturn, Jupiter, Uranus, and Neptune are gas giants composed of hydrogen, helium, methane, and other gases.
Explain dwarf planets.
Dwarf planets are celestial objects that orbit the sun in various locations and are smaller than planets but bigger than asteroids. Ceres is the closest dwarf planet, located in the asteroid belt.

Relevant Articles
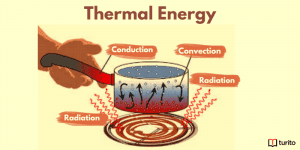
Understanding Thermal Energy: What It Is and How It Works
Thermal energy is essential to our daily lives, from warming …
Understanding Thermal Energy: What It Is and How It Works Read More »
Read More >>Avogadro’s Number: Meaning, Importance, and More
Introduction The concept of measuring the microscopic particles that make …
Avogadro’s Number: Meaning, Importance, and More Read More »
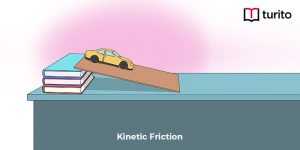
Read More >>Kinetic Friction – Definition, Laws, Types
Kinetic Friction Kinetic force is a force acting between two …
Kinetic Friction – Definition, Laws, Types Read More »
Read More >>

















Comments: