Trade winds have been used by sailors and merchants to sail their ships in the right direction. The trade winds allowed sailors to sail to North or South America from Europe or Africa. Like flying eastward can be shortened by using the jet stream’s wind boost, sailing westward can be shortened by using the trade winds.
Several winds on earth are relatively predictable. For instance, the jet streams that generally sweep across the earth in the upper atmosphere flow from west to east. Near the equator, east-to-west air currents called the trade winds to flow closer to the earth’s surface.
What Are Trade Winds?
| The Quick Response:
What are trade winds? Winds that consistently flow from east to west between the northern and southern hemispheres are known as the trade winds. The winds assist ships in moving westward and can also direct storms like hurricanes. |
Trade winds east is characterised as winds that originate from the northeast of the northern hemisphere or the southeast of the southern hemisphere and move towards the equator. These are also referred to as tropical easterlies, distinguished by their constancy of force and direction.
These northeast trade winds or southeast trade winds are created when the hot air rises or floats to the equator, where it is driven in the direction of the poles, making them cool.
| Did You Know?
Christopher Columbus was the first renowned person to locate America with the help of trade winds. |
Different Types of Wind
Following are the different types of winds based on multiple criteria:
Trade Winds
Trade winds are also referred to as tropical easterlies because they flow from rightwards in the northern hemisphere to leftwards in the southern hemisphere of the earth due to Ferrel’s law and the Coriolis effect. They begin flowing in the direction of the equatorial low-pressure zone from the subtropical high-pressure zones. They flow as northeast trade winds in the northern hemisphere and as southeast trade winds in the southern hemisphere.
The Westerlies
Other names for these winds include the Furious Fifties, Roaring Forties, and Shrieking Sixties. The westerlies and trade winds flow in both the northern and southern hemispheres. They move from the west to the east at midlatitudes between 30° and 60° latitude. These winds are named westerlies because of the direction from where they come. These are carried to the poles by the wind from the horse latitudes. These come primarily from the southwest in the northern hemisphere and the northwest in the southern hemisphere. The wind patterns in US and Canada are because of the westerly winds.
The Easterlies
The Polar Easterlies are dry, cold, and year-round winds that flow from the north of the northern hemispheres to the south and from the south of the southern hemispheres to the north. The easterlies, also known as polar easterlies, originate from the high-pressure polar regions, called for the direction they come from and occur between 60° and 90° latitude in both the northern and southern hemispheres. These winds are formed when the cool breeze from the poles descends and travels in the direction of the equator. The Coriolis effect causes the winds to curl westward. These breezes are crucial for the sailors.
Monsoon Winds
A monsoon is a wind that occasionally changes its direction between winter and summer in low-latitude areas. Monsoons typically flow from land to water in winter and from water to land in the summer, causing a significant change in the region’s precipitation and temperature patterns.
Land Breeze and Sea Breeze
Land breezes are local wind patterns characterised by dry winds that flow from land to sea. These are warm and dry winds. On the other hand, sea breezes are winds that flow from the sea to the land and carry some humidity.
Valley and Mountain Breeze
During the daytime, the slopes get heated up in the mountain areas, and air moves upslope to close the ensuing gap, forming a valley breeze. During the nighttime, the mountain slopes get cooled, and the dense air flows into the valley as a mountain breeze.
Local Winds
Local variations in pressure and temperature create local winds. Only the lowest troposphere levels experience such winds. Zonda, loo, chinook, and bora are common examples of local winds.
Coriolis Effect
The Coriolis effect is an imaginary or inertial force that causes winds in the northern hemisphere to be deflected to the right and in the southern hemisphere to be deflected to the left.
Ferrel’s law is derived using the Coriolis effect. A moving object tends to diverge to the right in the Northern and the left in the Southern hemispheres. This natural wind phenomenon is known as the Coriolis effect. One of the best examples of the application of the Coriolis effect is how hurricane winds in the Northern Hemisphere turn left.
There is no Coriolis effect below a horizontally travelling object at the equator since there is no rotation of the earth’s surface (a sense of turning), and no curving in the path for the object as we evaluate the object’s path, thus, resulting in no Coriolis effect.
Let’s examine the mathematically expressed Coriolis effect using Ferrel’s Law.
The object’s inertial reference’s motion equation:
F = ma
Where,
m = mass of the object
a = acceleration of the object (relative to the inertial reference frame)
F = sum of all vector physical forces applying to the object
To create a non-inertial reference frame for the equation as mentioned above:
F − m dΩ / dt × r − 2mΩ × v− mΩ × (Ω × r) = ma
Where,
Ω = rotational vector
r = position vector of the object
v = velocity relative to the rotating reference frame
a = acceleration relative to the rotating reference frame
| Did You Know?
Anemometers: Anemometer is used frequently in weather stations to measure wind speed. The various types of anemometers include windmill anemometers, cup anemometers, hot wire anemometers, laser doppler anemometers and sound anemometers. |
What are trade winds, and why do they flow from east to west?
The way the earth revolves on its axis and other factors contribute to the trade winds blowing westward. As cooler air nearer the poles descends, warm, humid air rises from the equator, forming trade winds.
Why not all winds blow north and south if the air rotates from the equator to the poles? That is where the earth’s rotation alters the situation. Since the earth rotates as the air flows, the northern hemisphere winds turn to the right and leftwards in the southern hemisphere.
This natural wind phenomenon is known as the Coriolis effect, and because of this effect, the trade winds in both the northern and southern hemispheres blow toward the west. Trade winds are present between 30 degrees north and south of the equator. The region near the equator, the doldrums, has essentially no wind at all.
Conclusion
Trade winds or easterlies are the persistent east-to-west prevailing breezes found in the earth’s tropical regions (between 30°N and 30°S latitudes). Throughout the year’s colder months, the trade winds strengthen as they blow transversely from the southeast direction in the southern hemisphere and from the northeast direction in the northern hemisphere.
Cruise ship captains have depended heavily on trade winds to navigate the oceans across the globe. It permits the entry of pilgrims into the Americas and the establishment of shipping corridors over the Pacific and Atlantic oceans. Thus, for learners to obtain higher-level information, they must comprehend the idea of trade winds.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q) Why do the trade winds flow from east to west?
A) The earth’s rotation on its axis is one of the reasons why the trade winds are directed toward the west. The trade winds are created when the warm, humid air rises upwards from the equator in the atmosphere and cools (sinks) steadily when it reaches the poles.
The trade wind does not flow from north to south, even though air cycles from the equator; the reason is, that as the earth rotates, it curves rightwards in the northern hemisphere and leftwards in the southern hemisphere. This effect is called the Coriolis effect. Because of this, the trade winds flow toward the west in the southern and northern hemispheres.
Q) How are trade winds produced?
A) The trade winds are produced by intense heat and evaporation in the stratosphere around the equator, where the warm air rises while holding a lot of moisture. The dominant winds known as the trade winds, which travel from east to west on both sides of the equator, are caused by the Coriolis effect in combination with a high-pressure area.
Q) What weakens the trade winds?
A) The northeast trade winds or southeast trade winds are driven by the surface pressure pattern, which is higher in the eastern Pacific and lower in the west. The trade winds east begin to weaken when the pressure difference weakens, propelling the easterly trade winds.

Relevant Articles
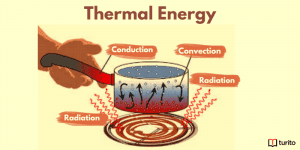
Understanding Thermal Energy: What It Is and How It Works
Thermal energy is essential to our daily lives, from warming …
Understanding Thermal Energy: What It Is and How It Works Read More »
Read More >>Avogadro’s Number: Meaning, Importance, and More
Introduction The concept of measuring the microscopic particles that make …
Avogadro’s Number: Meaning, Importance, and More Read More »
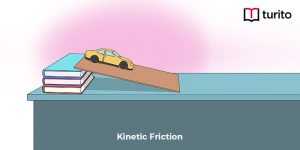
Read More >>Kinetic Friction – Definition, Laws, Types
Kinetic Friction Kinetic force is a force acting between two …
Kinetic Friction – Definition, Laws, Types Read More »
Read More >>

















Comments: