A wide variety of electrical accessories must be connected to the distribution board of the utility company to distribute electricity throughout the house. This article will teach you about the various types of wiring and the types of wiring connectors and their application.
What do you understand by the term wiring?
Wiring refers to the process of distributing electrical power through wires in such a way as to maximize the efficiency of the usage of wiring conductors within a structure or a particular room to achieve greater load control.
What is electrical wiring?
Electrical wiring is an installation of cabling through which power is distributed to various devices associated with electricity in a structured manner to ensure a continuous power supply. These devices include fuses, switches, sockets, lights, fans, etc.
Electrical wiring refers to the process of distributing electrical power through wires in a manner that is optimized to meet the electrical as well as the economic requirements of a certain location. It is connected to the electrical supply methodically to ensure no interruption in the power supply.
If the electrical wiring in a structure, such as a building, is installed correctly, then load control and distribution will be improved. These wiring conductors in that location, building, home, etc., are available for affordable use and can be put to various uses.
Various kinds of wires can be purchased, and each kind serves a distinct purpose. These wires are all accessible on the market. Before beginning an electrical project that requires electrical connections, an individual needs to educate themselves on the various types of wiring and the various types of electrical wiring connections. This is necessary to determine which type of electrical wiring will be most suitable for the wired structure.
Types of Electrical Wiring
The various types of electrical wire and types of wiring connectors have been provided below:
1. Tee System or Joint Box System
Using this wiring, the various appliances can be connected. Since it does not require excessive cable size, it is perfect for doing temporary installations because it is economical.
2. Loop in System
This system is utilized, so lamps and other appliances are connected in parallel to enable individual control of each device. They are readily available and easy to obtain for locating errors.
3. Cleat Wiring
Insulated wires with VIR or PVC are used in this wiring, and the wires are braided and mounted on the walls and ceilings using porcelain cleats, wood, or plastic. Since it is more of a temporary solution, it is not something that can be used in a home setting. Take, for instance, a structure that is now undergoing development.
4. Batten Wiring
TRS cables with one core, two, and three cores are utilized in this wiring configuration. These cables may be resistant to steam and chemicals and water resistant. It has a low cost compared to every other electrical wiring system that might be used in an electric circuit.
5. Casing and Capping Wiring
Wooden enclosures protect the VIR cables within this wiring configuration. It is a practice that is no longer used nowadays. Repairs are much simpler when the phase and the neutral wires are individually put in their slot.
6. Lead Sheathed Wiring
These are electrical conductors encased in an aluminum alloy that is 95% lead and have a sheath that protects them from the atmosphere. The cables are shielded from atmospheric corrosion and damage caused by moisture and mechanical stress by this coating.
7. Conduit Wiring
A further subdivision of this form of wiring is as follows:
Surface conduit wiring: It is a type of wiring typically put on the surface of a wall or ceiling. In this step, holes are drilled at regular intervals, and plugs are used to connect the conduit to the holes.
- Concealed Conduit Wiring: This type of wiring is concealed within the walls by plastering over it using either plastic or metallic pipe. These are again divided into the following categories according to the type of piping:
- Metallic Conduit: These are manufactured from steel, an expensive material but extremely durable. Once more, the metallic conduit can be divided into the following categories:
- Class A Conduit: It is defined as a thin layer of a sheet of steel, also referred to as a low gauge conduit.
- Class B Conduit: Often referred to as high gauge conduits, class B conduits are characterized by their thick layers of steel sheets.
- Non-Metallic Conduit: This conduit employs pliable and simple wires to curve like a solid PVC conduit.
8. Electrical Wires
The wire is the term used to refer to a single electrical conductor or a single channel that is capable of carrying electricity. The component of the wire that carries electrical current is called the conductor. It can be constructed of copper or aluminum or copper-sheathed aluminum that is then encased in a covering of plastic that is not conducive. On the other hand, the term “cable” refers to assembling one or more of these wires differently (side-by-side, bundled, etc.) to transport an electric current.
When working with various applications and installations, having a solid understanding of the National Electrical Code’s (NEC) regulations on the types of wiring and the properties of those wires is necessary. The following aspects of electrical cables need to be taken into consideration to make an informed choice regarding the composition:
- Size of the Wires: The wire gauge is responsible for determining the size ranges of the wires. The numbers 10, 12, 14, 18, etc., are typical wire diameters. Let’s say that for around ten amps, you will need a wire with an 18-gauge gauge. In addition, a wire with a gauge of 2 is essential for 100 Amps.
- Letterings of the Wire: According to the Instructions of the NEC, the insulation in types of wiring is represented by certain letters. Electrical insulations come in various configurations; some more common ones include THHN, THWN, THW, and THHN. What do these letters stand for?
- H stands for “heat resistance.”
- HH stands for “High Heat resistance,” meaning that the material can withstand temperatures up to 194 degrees Fahrenheit.
- N-Nylon is to provide resistance.
- T-Thermoplastic Insulation
- W- Wet Locations Suitability
- X- Coating is a synthetic polymer that is resistant to flame.
Electric Wire Color Codes
When working with electrical circuits, there are numerous types of wires, each of which has its unique color code. These color codes are often established by central authorities to facilitate the development of standard operating procedures.
- The red wires are the ones that carry current and are called “live.”
- Wires with a white tint are always considered neutral (neutral wires are also black).
- Wires of a green tint are typically utilized whenever earthing or grounding is performed.
- Black wires are the Hotwires. These wires are used for the outlets and the switches.
- Wires that are blue and yellow indicate that they are hot wires used for various equipment.
Conclusion
There is a good chance that every person on the planet who uses electricity is aware of the contributions that wire and cable have made. Since the existence of wires and cables is so widely acknowledged, we can state with confidence that their length is what holds the entire globe together. Additionally, scientists have developed a one thousand times thinner wire than a single strand of human hair. This wire was invented by scientists (the wire is only one atom length tall and four atoms wide).
Therefore, with the advent of technology, one must know about the different types of wiring and types of wiring connectors as these are what keep not only the gadgets connected, but through them, human life is possible.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What kinds of dangers are involved while working with electrical wiring?
A. All modern homes and structures contain electrical wire. Therefore installing it is a crucial part of the construction. Even the simplest wiring mistake can cause catastrophic flames, as we’ve seen many times. Wires need proper insulation and no cutting. Any cuts could cause a short circuit, causing structural damage.
2. Why is it important to color code the wires in an electrical circuit?
A. Color coded cables are used in equipment like the TV and refrigerator. The government regulator sets these color codes to achieve universality in the application of electrical wires and to ensure that technicians may work according to a consistent way regardless of the wires’ color. Due to the possibility of a fire or short circuit if a live and neutral wire touches, appropriate color coding must be followed.
3. Why do we use copper or aluminum to transfer electricity from one place to another?
A. Electrical wires have two parts. The outside part is an insulating layer that doesn’t conduct electricity, and the inside part is a wire that does. This conductive wire is made of metal, a good conductor of electricity. Silver, which is the best conductor of electricity and can be used in wires, is the best conductor of electricity. Still, it is very expensive and not a good choice for the high demand for electrical cables. Copper and aluminum are also used in wires because they are good conductors.

Relevant Articles
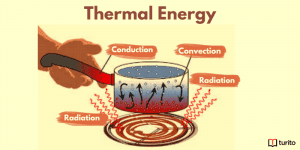
Understanding Thermal Energy: What It Is and How It Works
Thermal energy is essential to our daily lives, from warming …
Understanding Thermal Energy: What It Is and How It Works Read More »
Read More >>Avogadro’s Number: Meaning, Importance, and More
Introduction The concept of measuring the microscopic particles that make …
Avogadro’s Number: Meaning, Importance, and More Read More »
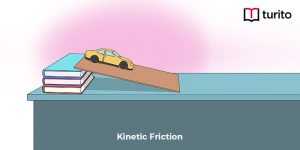
Read More >>Kinetic Friction – Definition, Laws, Types
Kinetic Friction Kinetic force is a force acting between two …
Kinetic Friction – Definition, Laws, Types Read More »
Read More >>

















Comments: