Maths-
General
Easy
Question
The derivative of even function is
- Even function
- Odd function
- Cannot be definitely known
- Even function or odd function

We are asked the derivative of an even function. We will see the definition of even function first. Then we will find it's derivative.
The correct answer is: Odd function
Let f(x) be any function.
f(x) is said to be an even function if it statisfy the given condition.
f(x) = f(-x) ...(1)
It means if the input is negative or positive we will get the same output.
f(x) is said to be an odd function if it satisfy the given condition.
f(-x) = -f(x) ...(2)
Now, we will take the derivative of equation (1)
f'(x) = -f'(-x)
We can see that the derivative of even function satisfy the condition of an odd function.
So, the derivative of an even function is an odd function.
For such questions, we should know the definition of even and odd function.
Related Questions to study
Maths-
If 
 [x] is the greatest integer not exceeding (x) then the set of discontinuity of f is...
[x] is the greatest integer not exceeding (x) then the set of discontinuity of f is...
If 
 [x] is the greatest integer not exceeding (x) then the set of discontinuity of f is...
[x] is the greatest integer not exceeding (x) then the set of discontinuity of f is...
Maths-General
Maths-
 then {x/f(x)
then {x/f(x) }=
}=
 then {x/f(x)
then {x/f(x) }=
}=
Maths-General
Chemistry-
The order of reactivity of following alcohols, towards conc. HCl is:
i) 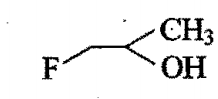
ii) 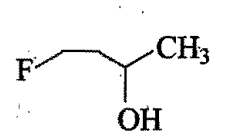
iii) 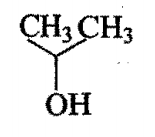
iv) 
The order of reactivity of following alcohols, towards conc. HCl is:
i) 
ii) 
iii) 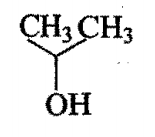
iv) 
Chemistry-General
Chemistry-
In the following compounds piperidine
I) pyridine
II) morpho line
III) and pyrrole
IV) the order of basicity is:
In the following compounds piperidine
I) pyridine
II) morpho line
III) and pyrrole
IV) the order of basicity is:
Chemistry-General
Maths-
If denotes the greatestinterger not exceeding x and if the function f defined by
denotes the greatestinterger not exceeding x and if the function f defined by the order pair (a,b)=
the order pair (a,b)=
If denotes the greatestinterger not exceeding x and if the function f defined by
denotes the greatestinterger not exceeding x and if the function f defined by the order pair (a,b)=
the order pair (a,b)=
Maths-General
Maths-
 is continuous in the interval [0,
is continuous in the interval [0,  ) then an ordered pair (a, b) is
) then an ordered pair (a, b) is
 is continuous in the interval [0,
is continuous in the interval [0,  ) then an ordered pair (a, b) is
) then an ordered pair (a, b) is
Maths-General
Physics-
Mosley measured the frequency (f) of the characteristic X-rays from many metals of different atomic number (Z) and represented his results by a relation known as Mosley's law. This law is (a, b are constants)
Mosley measured the frequency (f) of the characteristic X-rays from many metals of different atomic number (Z) and represented his results by a relation known as Mosley's law. This law is (a, b are constants)
Physics-General
Physics-
X-rays which can penetrate through longer distances in substance are called
X-rays which can penetrate through longer distances in substance are called
Physics-General
Physics-
X-rays are known to be electromagnetic radiations. Therefore the X-ray photon has
X-rays are known to be electromagnetic radiations. Therefore the X-ray photon has
Physics-General
Physics-
When the accelerating voltage applied on the electrons increased beyond a critical value
When the accelerating voltage applied on the electrons increased beyond a critical value
Physics-General
Physics-
X-rays are not used for radar purpose because
X-rays are not used for radar purpose because
Physics-General
Physics-
X-rays were discovered by
X-rays were discovered by
Physics-General
Physics-
In radio theraphy, X-rays are used to
In radio theraphy, X-rays are used to
Physics-General
Physics-
The light rays having photons of energy 1.8 eV are falling on a metal surface having a work function 1.2 eV. What is the stopping potential to be applied to stop the emitting electrons
The light rays having photons of energy 1.8 eV are falling on a metal surface having a work function 1.2 eV. What is the stopping potential to be applied to stop the emitting electrons
Physics-General
Physics-
The velocity of photon is proportional to (where n is frequency)
The velocity of photon is proportional to (where n is frequency)
Physics-General



