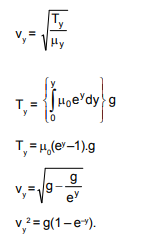Physics-
General
Easy
Question
A non–uniform rope of length l hangs from a ceiling. Mass per unit length of rope (m) changes as m = m0 e y , where y is the distance along the string from its lowest point. Then graph between square of velocity of wave and y will be best represented as :




- None of these



The correct answer is: 
Related Questions to study
Physics-
A thin horizontal movable plate P is separated from two fixed horizontal plates P1 and P2 by two highly viscous liquids of coefficient of viscosity h1 and h2 as shown, where h2 = 4h1 . Area of contact of movable plate with each fluid is same. If the distance between two fixed plates is h, then the distance h1 of movable plate from upper fixed plate such that the movable plate can be moved with a constant velocity by applying a minimum constant horizontal force F on movable plate is (assume velocity gradient to be uniform in each liquid).

A thin horizontal movable plate P is separated from two fixed horizontal plates P1 and P2 by two highly viscous liquids of coefficient of viscosity h1 and h2 as shown, where h2 = 4h1 . Area of contact of movable plate with each fluid is same. If the distance between two fixed plates is h, then the distance h1 of movable plate from upper fixed plate such that the movable plate can be moved with a constant velocity by applying a minimum constant horizontal force F on movable plate is (assume velocity gradient to be uniform in each liquid).

Physics-General
Physics-
In a cylinder-piston arrangement, air is under a pressure P1. A soap bubble of radius r lies inside the cylinder, soap bubble has surface tension T. The radius of soap bubble is to be reduced to half, The new pressure P2 to which air should be compressed isothermally. (Assume r is very small as compared to height of cylinder)

In a cylinder-piston arrangement, air is under a pressure P1. A soap bubble of radius r lies inside the cylinder, soap bubble has surface tension T. The radius of soap bubble is to be reduced to half, The new pressure P2 to which air should be compressed isothermally. (Assume r is very small as compared to height of cylinder)

Physics-General
Maths-
Which of the following is an equivalence relation ?
Which of the following is an equivalence relation ?
Maths-General
Maths-
If R = {(x,y): x, yÎN, y is the remainder when x is divided by 7}.Then sum of all numbers in range of R
If R = {(x,y): x, yÎN, y is the remainder when x is divided by 7}.Then sum of all numbers in range of R
Maths-General
Maths-
Let  and
and  then R is
then R is
Let  and
and  then R is
then R is
Maths-General
Maths-
Let  and
and  then the relation R on A is
then the relation R on A is
Let  and
and  then the relation R on A is
then the relation R on A is
Maths-General
Maths-
Let Y = { 1,2,3,4,5}, A = {1,2}, B ={3,4,5} and  denote the null set. If A ´ B denotes the cartesian product of sets A and B, then
denote the null set. If A ´ B denotes the cartesian product of sets A and B, then 
Let Y = { 1,2,3,4,5}, A = {1,2}, B ={3,4,5} and  denote the null set. If A ´ B denotes the cartesian product of sets A and B, then
denote the null set. If A ´ B denotes the cartesian product of sets A and B, then 
Maths-General
Physics-
A container filled with viscous liquid is moving vertically downwards with constant speed 3v0 . At the instant shown, a sphere of radius r is moving vertically downwards (in liquid) has speed v0 . The coefficient of viscosity is h. There is no relative motion between the liquid and the container. Then at the shown instant, the magnitude of viscous force acting on sphere is

A container filled with viscous liquid is moving vertically downwards with constant speed 3v0 . At the instant shown, a sphere of radius r is moving vertically downwards (in liquid) has speed v0 . The coefficient of viscosity is h. There is no relative motion between the liquid and the container. Then at the shown instant, the magnitude of viscous force acting on sphere is

Physics-General
Physics-
A cubical block of side 'a' and density 'r' slides over a fixed inclined plane with constant velocity ' v ' . There is a thin film of viscous fluid of thickness ' t ' between the plane and the block . Then the coefficient of viscosity of the thin film will be : (Acceleration due to gravity is g)

A cubical block of side 'a' and density 'r' slides over a fixed inclined plane with constant velocity ' v ' . There is a thin film of viscous fluid of thickness ' t ' between the plane and the block . Then the coefficient of viscosity of the thin film will be : (Acceleration due to gravity is g)

Physics-General
Physics-
In the figure shown, a light container is kept on a horizontal rough surface of coefficient of friction . A very small hole of area S is made at depth 'h'. Water of volume 'V' is filled in the container. The friction is not sufficient to keep the container at rest. The acceleration of the container initially is
. A very small hole of area S is made at depth 'h'. Water of volume 'V' is filled in the container. The friction is not sufficient to keep the container at rest. The acceleration of the container initially is

In the figure shown, a light container is kept on a horizontal rough surface of coefficient of friction . A very small hole of area S is made at depth 'h'. Water of volume 'V' is filled in the container. The friction is not sufficient to keep the container at rest. The acceleration of the container initially is
. A very small hole of area S is made at depth 'h'. Water of volume 'V' is filled in the container. The friction is not sufficient to keep the container at rest. The acceleration of the container initially is

Physics-General
Physics-
A spherical ball of mass 4m, density sand radius r is attached to a pulley-mass system as shown in figure. The ball is released in a liquid of coefficient of viscosity hand density r(< 2 s ). If the length of the liquid column is sufficiently long, the terminal velocity attained by the ball is given by (assume all pulleys to be massless and string as massless and inextensible) :

A spherical ball of mass 4m, density sand radius r is attached to a pulley-mass system as shown in figure. The ball is released in a liquid of coefficient of viscosity hand density r(< 2 s ). If the length of the liquid column is sufficiently long, the terminal velocity attained by the ball is given by (assume all pulleys to be massless and string as massless and inextensible) :

Physics-General
Physics-
A piece of Ice floats in a vessel with water above which a layer of lighter oil is poured. When ice melts :

1. The level of oil water interface falls
2. The level of oil water interface rises
3. The thickness of oil layer decreases
4. The thickness of oil layer remain same
5. The thickness of oil layer increases
6. The level of oil-air interface falls
7. The level of oil-air interface remains same
8. The level of oil-air interface rises Select the correct alternatives :
A piece of Ice floats in a vessel with water above which a layer of lighter oil is poured. When ice melts :

1. The level of oil water interface falls
2. The level of oil water interface rises
3. The thickness of oil layer decreases
4. The thickness of oil layer remain same
5. The thickness of oil layer increases
6. The level of oil-air interface falls
7. The level of oil-air interface remains same
8. The level of oil-air interface rises Select the correct alternatives :
Physics-General
Physics-
A container open from top, filled with water (density rw ) upto the top, is placed on a weighing machine and the reading is W. A wooden ball of volume V and mass m is put in the water by the given two arrangements. In arrangement–1, the ball is connected by a rigid rod (of negligible volume) and pushed in the water. In arrangement–2, the ball is attached with bottom by a massless string. The reading of weighing machine, (density of wood is less than water) (choose incorrect option) :

A container open from top, filled with water (density rw ) upto the top, is placed on a weighing machine and the reading is W. A wooden ball of volume V and mass m is put in the water by the given two arrangements. In arrangement–1, the ball is connected by a rigid rod (of negligible volume) and pushed in the water. In arrangement–2, the ball is attached with bottom by a massless string. The reading of weighing machine, (density of wood is less than water) (choose incorrect option) :

Physics-General
Physics-
Two forces F1 and F2act on a thin uniform elastic rod placed in space. Force F1 acts at right end of rod and F2acts exactly at centre of rod as shown (both forces act parallel to length of the rod).

i) F1 causes extension of rod while F2 causes compression of rod.
ii) F1 causes extension of rod and F2 also causes extension of rod.
iii) F1 causes extension of rod while F2 does not change total length of rod.
The correct order of True / False in above statements is
Two forces F1 and F2act on a thin uniform elastic rod placed in space. Force F1 acts at right end of rod and F2acts exactly at centre of rod as shown (both forces act parallel to length of the rod).

i) F1 causes extension of rod while F2 causes compression of rod.
ii) F1 causes extension of rod and F2 also causes extension of rod.
iii) F1 causes extension of rod while F2 does not change total length of rod.
The correct order of True / False in above statements is
Physics-General
Physics-
In the given figure, two elastic rods A & B are rigidly joined to end supports. A small block of mass ‘ m ‘ is moving with velocity v between the rods. All collisions are assumed to be elastic & the surface is given to be smooth. The time period of oscillations of small mass ‘ m ‘ will be: (A = area of cross section, Y = young’s modulus, L = length of each rod)

In the given figure, two elastic rods A & B are rigidly joined to end supports. A small block of mass ‘ m ‘ is moving with velocity v between the rods. All collisions are assumed to be elastic & the surface is given to be smooth. The time period of oscillations of small mass ‘ m ‘ will be: (A = area of cross section, Y = young’s modulus, L = length of each rod)

Physics-General