Physics-
General
Easy
Question
A small mass  is attached to a massless string whose other end is fixed at
is attached to a massless string whose other end is fixed at  as shown in the figure. The mass is undergoing circular motion in the
as shown in the figure. The mass is undergoing circular motion in the  plane with center at
plane with center at  and constant angular speed
and constant angular speed  . If the angular momentum of the system, calculated about
. If the angular momentum of the system, calculated about  and
and  are denoted by
are denoted by  and
and  respectively, then
respectively, then

 and
and  do not vary with time
do not vary with time
 varies with time while
varies with time while  remains constant
remains constant
 remains constant while
remains constant while  varies with time
varies with time
 and
and  both vary with time
both vary with time
The correct answer is:  remains constant while
remains constant while  varies with time
varies with time
Related Questions to study
chemistry-
The monomer used to produce neoprene is
The monomer used to produce neoprene is
chemistry-General
chemistry-
What is ‘A’ in the following reaction?

What is ‘A’ in the following reaction?

chemistry-General
chemistry-
What is ‘A’ in the following reaction?

What is ‘A’ in the following reaction?

chemistry-General
Physics-
Three identical particles are joined together by a thread as shown in figure. All the three particles are moving in a horizontal plane. If the velocity of the outermost particle is  , then the ratio of tensions in the three sections of the string is
, then the ratio of tensions in the three sections of the string is
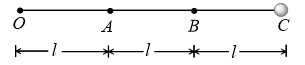
Three identical particles are joined together by a thread as shown in figure. All the three particles are moving in a horizontal plane. If the velocity of the outermost particle is  , then the ratio of tensions in the three sections of the string is
, then the ratio of tensions in the three sections of the string is

Physics-General
physics-
A weightless thread can bear tension up to wt. A stone of mass
wt. A stone of mass  is tied to it and revolved in a circular path of radius
is tied to it and revolved in a circular path of radius  in a vertical plane. If
in a vertical plane. If  , then the maximum angular velocity of the stone will be
, then the maximum angular velocity of the stone will be
A weightless thread can bear tension up to wt. A stone of mass
wt. A stone of mass  is tied to it and revolved in a circular path of radius
is tied to it and revolved in a circular path of radius  in a vertical plane. If
in a vertical plane. If  , then the maximum angular velocity of the stone will be
, then the maximum angular velocity of the stone will be
physics-General
physics-
A man 80 kg is supported by two cables as shown in the figure. Then the ratio of tensions  and
and  is
is

A man 80 kg is supported by two cables as shown in the figure. Then the ratio of tensions  and
and  is
is

physics-General
Maths-
A square matrix  for
for  and
and  (constant) for
(constant) for  is called a
is called a
A square matrix  for
for  and
and  (constant) for
(constant) for  is called a
is called a
Maths-General
chemistry-
DS for the reaction: MgCO3(s) → MgO(s) + CO2(g) will be -
DS for the reaction: MgCO3(s) → MgO(s) + CO2(g) will be -
chemistry-General
physics-
A point P moves in counter-clockwise direction on a circular path as shown in the figure. The movement of P is such that it sweeps out length  where
where  is in metre and t is in second. The radius of the path is 20 m. The acceleration of P when t =2s is nearly
is in metre and t is in second. The radius of the path is 20 m. The acceleration of P when t =2s is nearly
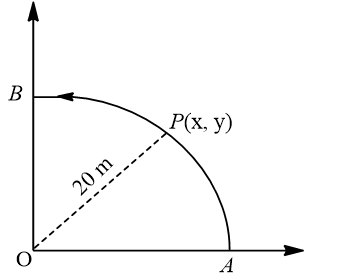
A point P moves in counter-clockwise direction on a circular path as shown in the figure. The movement of P is such that it sweeps out length  where
where  is in metre and t is in second. The radius of the path is 20 m. The acceleration of P when t =2s is nearly
is in metre and t is in second. The radius of the path is 20 m. The acceleration of P when t =2s is nearly

physics-General
chemistry-
For the reaction N2(g)+3H2(g)→2NH3(g),DH is-
For the reaction N2(g)+3H2(g)→2NH3(g),DH is-
chemistry-General
physics-
Three identical spheres of mass  each are placed at the corners of an equilateral triangle of side 2
each are placed at the corners of an equilateral triangle of side 2 . Taking one of the corner as the origin, the position vector of the centre of mass is
. Taking one of the corner as the origin, the position vector of the centre of mass is
Three identical spheres of mass  each are placed at the corners of an equilateral triangle of side 2
each are placed at the corners of an equilateral triangle of side 2 . Taking one of the corner as the origin, the position vector of the centre of mass is
. Taking one of the corner as the origin, the position vector of the centre of mass is
physics-General
physics-
Four bodies of equal mass start moving with same speed are shown in the figure. In which of the following combination the centre of mass will remain at origin?

Four bodies of equal mass start moving with same speed are shown in the figure. In which of the following combination the centre of mass will remain at origin?

physics-General
chemistry-
From the reactions: C(s)+2H2(g)→CH4(g)DH=–XK cal C(g)+4H(g)→CH4(g),DH=–X1Kcal CH4(g)→CH3(g)+H(g)DH=+Y(Kcal) Bond energy of C–H bond is-
From the reactions: C(s)+2H2(g)→CH4(g)DH=–XK cal C(g)+4H(g)→CH4(g),DH=–X1Kcal CH4(g)→CH3(g)+H(g)DH=+Y(Kcal) Bond energy of C–H bond is-
chemistry-General
physics-
From a circular disc of radius  and mass 9
and mass 9  , a small disc of radius
, a small disc of radius  /3 is removed from the disc. The moment of inertia of the remaining disc about an axis perpendicular to the plane of the disc and passing through
/3 is removed from the disc. The moment of inertia of the remaining disc about an axis perpendicular to the plane of the disc and passing through  is
is

From a circular disc of radius  and mass 9
and mass 9  , a small disc of radius
, a small disc of radius  /3 is removed from the disc. The moment of inertia of the remaining disc about an axis perpendicular to the plane of the disc and passing through
/3 is removed from the disc. The moment of inertia of the remaining disc about an axis perpendicular to the plane of the disc and passing through  is
is

physics-General
physics-
The instantaneous velocity of a point  of the given rod of length 0.5 m is 3
of the given rod of length 0.5 m is 3  in the represented direction. The angular velocity of the rod for minimum velocity of end A is
in the represented direction. The angular velocity of the rod for minimum velocity of end A is

The instantaneous velocity of a point  of the given rod of length 0.5 m is 3
of the given rod of length 0.5 m is 3  in the represented direction. The angular velocity of the rod for minimum velocity of end A is
in the represented direction. The angular velocity of the rod for minimum velocity of end A is

physics-General



