Physics-
General
Easy
Question
A tungsten wire, 0.5 mm in diameter, is just stretched between two fixed points at a temperature of 40°C. Determine the tension in the wire when the temperature falls to 20°C. (coefficient of linear expansion of tungsten  ; Young's modulus of tungsten
; Young's modulus of tungsten  )
)
- 6.097 N
- 3.097 N
- 5.097 N
- 7.097 N
The correct answer is: 6.097 N
Related Questions to study
Physics-
When the tension on a wire is 4 N its length is  When the tension on the wire is 5 N its length is
When the tension on the wire is 5 N its length is  . Find its natural length.
. Find its natural length.
When the tension on a wire is 4 N its length is  When the tension on the wire is 5 N its length is
When the tension on the wire is 5 N its length is  . Find its natural length.
. Find its natural length.
Physics-General
Physics-
A conductor having conductivity ' k ' and whose radius varies linearly with length L is as shown is figure
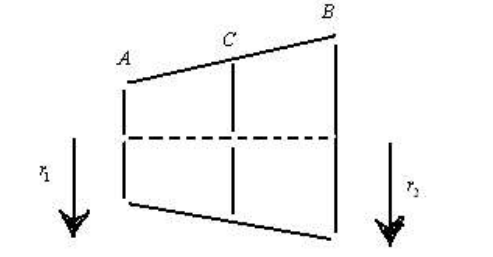 The radius of a conductor having uniform cross sectional area which gives same thermal resistance as the given conductor for same length with same conductivity is
The radius of a conductor having uniform cross sectional area which gives same thermal resistance as the given conductor for same length with same conductivity is
A conductor having conductivity ' k ' and whose radius varies linearly with length L is as shown is figure
 The radius of a conductor having uniform cross sectional area which gives same thermal resistance as the given conductor for same length with same conductivity is
The radius of a conductor having uniform cross sectional area which gives same thermal resistance as the given conductor for same length with same conductivity is
Physics-General
Physics-
A linear rod of length L and uniform cross section area A is having thermal conductivity, which varies along its length as,  where
where  is measured from one of its ends as shown in figure. The two ends of the rod are maintained at temperatures of
is measured from one of its ends as shown in figure. The two ends of the rod are maintained at temperatures of  and
and  , the rate at which heat flows at steady state is
, the rate at which heat flows at steady state is

A linear rod of length L and uniform cross section area A is having thermal conductivity, which varies along its length as,  where
where  is measured from one of its ends as shown in figure. The two ends of the rod are maintained at temperatures of
is measured from one of its ends as shown in figure. The two ends of the rod are maintained at temperatures of  and
and  , the rate at which heat flows at steady state is
, the rate at which heat flows at steady state is

Physics-General
Physics-
Two solid spheres of same material but diameters in the ratio of 5:4 are at temperatures 227°C and 127°C respectively. The temperature of the surrounding is 27°C and Stefan's law holds. Calculate the ratio of rates of loss of heat of the two spheres?
Two solid spheres of same material but diameters in the ratio of 5:4 are at temperatures 227°C and 127°C respectively. The temperature of the surrounding is 27°C and Stefan's law holds. Calculate the ratio of rates of loss of heat of the two spheres?
Physics-General
Physics-
A cylinder of radius R and length l is made up of a substance, whose thermal conductivity K varies with the distance  from the axis as
from the axis as  Deter mine the effective thermal conductivity between the flat faces of the cylinder.
Deter mine the effective thermal conductivity between the flat faces of the cylinder.

A cylinder of radius R and length l is made up of a substance, whose thermal conductivity K varies with the distance  from the axis as
from the axis as  Deter mine the effective thermal conductivity between the flat faces of the cylinder.
Deter mine the effective thermal conductivity between the flat faces of the cylinder.

Physics-General
Physics-
Two rods(One semi - circular and other straight) of same material and of same cross -sectional area are joined as shown in the figure. The points A and B are maintained at different temperatures. Find the ratio of the heat transferred through a cross - section of a semi - circular rod to the heat transferred A through a cross section of the straight rod in a given time.

Two rods(One semi - circular and other straight) of same material and of same cross -sectional area are joined as shown in the figure. The points A and B are maintained at different temperatures. Find the ratio of the heat transferred through a cross - section of a semi - circular rod to the heat transferred A through a cross section of the straight rod in a given time.

Physics-General
Physics-
Four identical rods AB,CD,CF and DE are connected as shown in figure. The length, cross- sectional area and thermal conductivity of each rod are L,A, K respectively. The ends A, E, F are maintained at temperature  and
and  respectively. Assuming no loss of heat to the atmosphere, calculate the temperature at B [CB = BD].
respectively. Assuming no loss of heat to the atmosphere, calculate the temperature at B [CB = BD].

Four identical rods AB,CD,CF and DE are connected as shown in figure. The length, cross- sectional area and thermal conductivity of each rod are L,A, K respectively. The ends A, E, F are maintained at temperature  and
and  respectively. Assuming no loss of heat to the atmosphere, calculate the temperature at B [CB = BD].
respectively. Assuming no loss of heat to the atmosphere, calculate the temperature at B [CB = BD].

Physics-General
Physics-
Figure shows a cylinder of cross sectional area A and total length 4 L, containing  moles of oxygen each at temperature
moles of oxygen each at temperature  and
and  are separated by a fixed piston of length 2 L and thermal conductivity K. Find the rate of heat flow through the piston after time
are separated by a fixed piston of length 2 L and thermal conductivity K. Find the rate of heat flow through the piston after time  . (Given
. (Given  )
)

Figure shows a cylinder of cross sectional area A and total length 4 L, containing  moles of oxygen each at temperature
moles of oxygen each at temperature  and
and  are separated by a fixed piston of length 2 L and thermal conductivity K. Find the rate of heat flow through the piston after time
are separated by a fixed piston of length 2 L and thermal conductivity K. Find the rate of heat flow through the piston after time  . (Given
. (Given  )
)

Physics-General
Physics-
Solid copper cube of edge 1 cm is suspended an evacuated enclosure. Its temperature is found to fall from 100°C to 99°C in 100 seconds. Another solid copper cube of edge 2 cm with similar surface nature is suspended in similar manner. Find the time required for this cube to cool from 100°C to 99°C.
Solid copper cube of edge 1 cm is suspended an evacuated enclosure. Its temperature is found to fall from 100°C to 99°C in 100 seconds. Another solid copper cube of edge 2 cm with similar surface nature is suspended in similar manner. Find the time required for this cube to cool from 100°C to 99°C.
Physics-General
Physics-
The graph shown give the temperature along x-axis that extends directly through a wall consisting of three layers A, B and C. The air temperature on one side of the wall differ from that on the other side. Thermal conduction through the wall is steady. Out of the three layers A, B and C thermal conductivity is greatest for layer

The graph shown give the temperature along x-axis that extends directly through a wall consisting of three layers A, B and C. The air temperature on one side of the wall differ from that on the other side. Thermal conduction through the wall is steady. Out of the three layers A, B and C thermal conductivity is greatest for layer

Physics-General
Physics-
No heat flows through the central rod of conductivity  in the arrangement of five identical rods of different conductivity
in the arrangement of five identical rods of different conductivity  and
and  Temperature are constant at
Temperature are constant at  and at
and at  then
then

No heat flows through the central rod of conductivity  in the arrangement of five identical rods of different conductivity
in the arrangement of five identical rods of different conductivity  and
and  Temperature are constant at
Temperature are constant at  and at
and at  then
then

Physics-General
Physics-
Three - rods AB, BC and BD made of the same cross-section have been joined as shown in figure. The ends A, C and D are held at temperatures of 20°C, 80°C, and 80°C respectively . If each rod is of same length, then the temperature at the junction B of the three rods is :

Three - rods AB, BC and BD made of the same cross-section have been joined as shown in figure. The ends A, C and D are held at temperatures of 20°C, 80°C, and 80°C respectively . If each rod is of same length, then the temperature at the junction B of the three rods is :

Physics-General
Physics-
Two slabs A & B having lengths  and
and  , respectively, and same cross - section have thermal conductivities
, respectively, and same cross - section have thermal conductivities  and
and  respecitvely. They are placed in contact and a constant temperature difference is maintained across the combination. The ratio of the quantities of heat flowing through A and B in a given time is
respecitvely. They are placed in contact and a constant temperature difference is maintained across the combination. The ratio of the quantities of heat flowing through A and B in a given time is
Two slabs A & B having lengths  and
and  , respectively, and same cross - section have thermal conductivities
, respectively, and same cross - section have thermal conductivities  and
and  respecitvely. They are placed in contact and a constant temperature difference is maintained across the combination. The ratio of the quantities of heat flowing through A and B in a given time is
respecitvely. They are placed in contact and a constant temperature difference is maintained across the combination. The ratio of the quantities of heat flowing through A and B in a given time is
Physics-General
Physics-
The rate of emission of radiation of a black body at temperature 27°C is  If its temperature is increased to 327°C the rate of emission of radiation is
If its temperature is increased to 327°C the rate of emission of radiation is  The relation between
The relation between  and
and  is
is
The rate of emission of radiation of a black body at temperature 27°C is  If its temperature is increased to 327°C the rate of emission of radiation is
If its temperature is increased to 327°C the rate of emission of radiation is  The relation between
The relation between  and
and  is
is
Physics-General
Physics-
A gas is expanded from volume  to 2
to 2  under three different processes. Process 1 is isobaric process, process 2 is isothermal and process 3 is adiabatic. Let
under three different processes. Process 1 is isobaric process, process 2 is isothermal and process 3 is adiabatic. Let  and
and  , be the change in internal energy of the gas is these processes. Then :–
, be the change in internal energy of the gas is these processes. Then :–

A gas is expanded from volume  to 2
to 2  under three different processes. Process 1 is isobaric process, process 2 is isothermal and process 3 is adiabatic. Let
under three different processes. Process 1 is isobaric process, process 2 is isothermal and process 3 is adiabatic. Let  and
and  , be the change in internal energy of the gas is these processes. Then :–
, be the change in internal energy of the gas is these processes. Then :–

Physics-General



