Physics-
General
Easy
Question
For maximum power dissipated in the external load of resistance R, R =




- r
The correct answer is: r
Related Questions to study
Physics-
Two cells of emf 4 V and 6 V are connected to an external load R = ¾ ohm. If = ¼ ohm the power dissipated in the load is

Two cells of emf 4 V and 6 V are connected to an external load R = ¾ ohm. If = ¼ ohm the power dissipated in the load is

Physics-General
General
The property of attracting or repelling objects on rubbing is called_____________.
The property of attracting or repelling objects on rubbing is called_____________.
GeneralGeneral
Physics-
In the given circuit, the voltmeter records 5 V. The resistance of the voltmeter (in ohms) is

In the given circuit, the voltmeter records 5 V. The resistance of the voltmeter (in ohms) is

Physics-General
Physics-
A, B and C are voltmeters of resistance R, 1.5 R and 3R respectively. When same potential difference is applied between x and y, the voltmeter readings are VA, VB and VC. Then 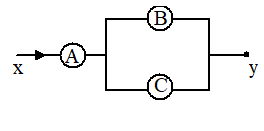
A, B and C are voltmeters of resistance R, 1.5 R and 3R respectively. When same potential difference is applied between x and y, the voltmeter readings are VA, VB and VC. Then 
Physics-General
Physics-
In the figure, if the ammeter reads 5 A and voltmeter reads 50 V, then the resistance R is

In the figure, if the ammeter reads 5 A and voltmeter reads 50 V, then the resistance R is

Physics-General
Physics-
In the circuit shown, the reading of the voltmeter V is

In the circuit shown, the reading of the voltmeter V is

Physics-General
Physics-
In the circuit shown here the readings of the ammeter and voltmeter are

In the circuit shown here the readings of the ammeter and voltmeter are

Physics-General
Physics-
If an ammeter is to be used in place of a voltmeter, then we must connect ammeter with a:
If an ammeter is to be used in place of a voltmeter, then we must connect ammeter with a:
Physics-General
Physics-
In the given circuit, the voltmeter records 5 V. The resistance of the voltmeter (in ohms) is :

In the given circuit, the voltmeter records 5 V. The resistance of the voltmeter (in ohms) is :

Physics-General
Chemistry-
The properties such as boiling point, freezing point and vapour pressure of a pure solvent change when solute molecules are added to get homogeneous solution. These are called colligative properties. Applications of colligative properties are very useful in day-to-day life. One of its examples is the use of ethylene gal/Col and water mixture as anti-freezing liquid in the radiator of automobiles.
A solution M is prepared by mixing ethanol and water. The mole fraction of ethanol in the mixture is 0:9:
Given: Freezing point depression constant of' water (  for water)
for water) 
Freezing point depression constant of ethanol  for ethanol)
for ethanol) 
Boiling point elevation constant of ethanol (  for ethanol)
for ethanol) 
Standard freezing point of water = 273 K
Standard freezing point of ethanol: 155.7 K
Standard boiling point of water = 373 K
Standard boiling point of ethanol 351.5 K
Vapour pressure of pure water 32.8- mm Hg
Vapour pressure of pure ethanol = 40 mm Hg
Molecular weight of water = 18 g 
Molecular weight of ethanol = 46 g 
In answering the following questions, consider the solutions to be ideal dilute solutions and solutes, to be non-volatile and non-dissociative.
Water is Added the solution M such that the mole fraction of water in the solution becomes 0.9 the boiling point of this solution is :
The properties such as boiling point, freezing point and vapour pressure of a pure solvent change when solute molecules are added to get homogeneous solution. These are called colligative properties. Applications of colligative properties are very useful in day-to-day life. One of its examples is the use of ethylene gal/Col and water mixture as anti-freezing liquid in the radiator of automobiles.
A solution M is prepared by mixing ethanol and water. The mole fraction of ethanol in the mixture is 0:9:
Given: Freezing point depression constant of' water (  for water)
for water) 
Freezing point depression constant of ethanol  for ethanol)
for ethanol) 
Boiling point elevation constant of ethanol (  for ethanol)
for ethanol) 
Standard freezing point of water = 273 K
Standard freezing point of ethanol: 155.7 K
Standard boiling point of water = 373 K
Standard boiling point of ethanol 351.5 K
Vapour pressure of pure water 32.8- mm Hg
Vapour pressure of pure ethanol = 40 mm Hg
Molecular weight of water = 18 g 
Molecular weight of ethanol = 46 g 
In answering the following questions, consider the solutions to be ideal dilute solutions and solutes, to be non-volatile and non-dissociative.
Water is Added the solution M such that the mole fraction of water in the solution becomes 0.9 the boiling point of this solution is :
Chemistry-General
Chemistry-
The solutions which boil at constant temperature like a pure liquid and possess same composition in liquid as well as vapour state are called azeotropes. The components of azeotropes cannot be separated by fractional distillation. Only non-ideal solutions form azeotropes. Solutions with negative deviation form maximum boiling azeotrope and the solutions with positive deviation form minimum boiling azeotrope. Boiling poin't of an azeotrope is never equal to the boiling points of any of the components of the azeotrope
The azeotropic mixture of water and HCI boils at  . This solution is:
. This solution is:
The solutions which boil at constant temperature like a pure liquid and possess same composition in liquid as well as vapour state are called azeotropes. The components of azeotropes cannot be separated by fractional distillation. Only non-ideal solutions form azeotropes. Solutions with negative deviation form maximum boiling azeotrope and the solutions with positive deviation form minimum boiling azeotrope. Boiling poin't of an azeotrope is never equal to the boiling points of any of the components of the azeotrope
The azeotropic mixture of water and HCI boils at  . This solution is:
. This solution is:
Chemistry-General
Chemistry-

Compartments 'A' and 'B' have the following combinations of solutions
The solution in which there will be no change in the level of the solution in the compartments' A' and 'B' is:

Compartments 'A' and 'B' have the following combinations of solutions
The solution in which there will be no change in the level of the solution in the compartments' A' and 'B' is:
Chemistry-General
Chemistry-

Compartments 'A' and 'B' have the following combinations of solutions
Indicate the solution(s)in which the compartment' B' will show the increase in volume:

Compartments 'A' and 'B' have the following combinations of solutions
Indicate the solution(s)in which the compartment' B' will show the increase in volume:
Chemistry-General
Chemistry-

Compartments 'A' and 'B' have the following combinations of solutions
Indicate the solution(s) in which the compartment' A' will show the increase in volume:

Compartments 'A' and 'B' have the following combinations of solutions
Indicate the solution(s) in which the compartment' A' will show the increase in volume:
Chemistry-General
Chemistry-

Compartments 'A' and 'B' have the following combinations of solutions

The solutions in which the compartment 'B' is hypertonic:

Compartments 'A' and 'B' have the following combinations of solutions

The solutions in which the compartment 'B' is hypertonic:
Chemistry-General



