Physics-
General
Easy
Question
Radius of a conductor increases uniformly from left end to right end as shown in fig.

Material of the conductor is isotropic and its curved surface is thermally isolated from surrounding. Its ends are maintained at temperatures T1 and T2 (T1 > T2): If, in steady state, heat flow rate is equal to H, then which of the following graphs is correct


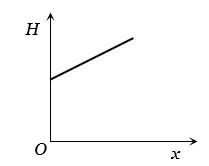

The correct answer is: 
Since the curved surface of the conductor is thermally insulated, therefore, in steady state, the rate of flow of heat at every section will be the same. Hence the curve between H and x will be straight line parallel to x-axis.
Related Questions to study
Chemistry-
The IUPAC name of 
The IUPAC name of 
Chemistry-General
Chemistry-
The order of stability of the following cabocations 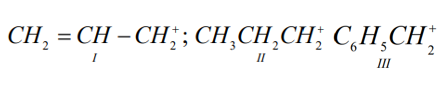 is
is
The order of stability of the following cabocations 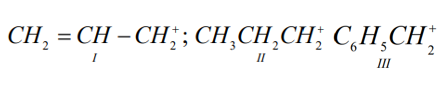 is
is
Chemistry-General
Chemistry-
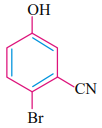 IUPAC name of the compound is
IUPAC name of the compound is
 IUPAC name of the compound is
IUPAC name of the compound is
Chemistry-General
Chemistry-
The IUPAC name of 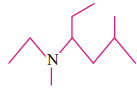 is
is
The IUPAC name of  is
is
Chemistry-General
Chemistry-
IUPAC name of the compound 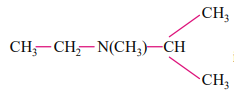 is
is
IUPAC name of the compound 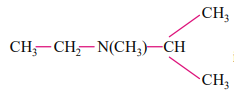 is
is
Chemistry-General
Chemistry-
The IUPAC name of the given structure 
The IUPAC name of the given structure 
Chemistry-General
Chemistry-
The IUPAC name of  is
is
The IUPAC name of  is
is
Chemistry-General
Chemistry-
The IUPAC name of the compound  is
is
The IUPAC name of the compound  is
is
Chemistry-General
Chemistry-
The IUPAC name of the given structure  (or)
(or) 
The IUPAC name of the given structure  (or)
(or) 
Chemistry-General
Chemistry-
Which of the following is non aromatic compound
Which of the following is non aromatic compound
Chemistry-General
Chemistry-
.What is the IUPAC name of the following 
.What is the IUPAC name of the following 
Chemistry-General
Chemistry-
What is the IUPAC name of the following 
What is the IUPAC name of the following 
Chemistry-General
Chemistry-
IUPAC name of 
IUPAC name of 
Chemistry-General
Chemistry-
The number of  electrons in anthracene is
electrons in anthracene is
The number of  electrons in anthracene is
electrons in anthracene is
Chemistry-General
Chemistry-
 which of the following explains this structure
which of the following explains this structure
 which of the following explains this structure
which of the following explains this structure
Chemistry-General



