Physics-
General
Easy
Question
The log-log graph between the energy E of an electron and its de-Broglie wavelength  will be
will be


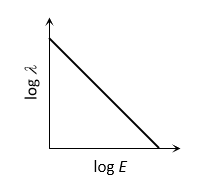

The correct answer is: 
 . Taking log of both sides
. Taking log of both sides  Þ
Þ

This is the equation of straight line having slope (–1/2) and positive intercept on log l axis
Related Questions to study
Physics-
In the graph given below. If the slope is  V-sec, then value of ‘h’ should be
V-sec, then value of ‘h’ should be

In the graph given below. If the slope is  V-sec, then value of ‘h’ should be
V-sec, then value of ‘h’ should be

Physics-General
Physics-
The variation of wavelength  of the
of the  line with atomic number Z of the target is shown by the following curve of
line with atomic number Z of the target is shown by the following curve of

The variation of wavelength  of the
of the  line with atomic number Z of the target is shown by the following curve of
line with atomic number Z of the target is shown by the following curve of

Physics-General
Physics-
The dependence of the short wavelength limit  on the accelerating potential V is represented by the curve of figure
on the accelerating potential V is represented by the curve of figure

The dependence of the short wavelength limit  on the accelerating potential V is represented by the curve of figure
on the accelerating potential V is represented by the curve of figure

Physics-General
Physics-
The continuous x-ray spectrum obtained from a Coolidge tube is of the form
The continuous x-ray spectrum obtained from a Coolidge tube is of the form
Physics-General
Physics-
The correct graph between the maximum energy of a photoelectron and the inverse of wavelength of the incident radiation is given by the curve

The correct graph between the maximum energy of a photoelectron and the inverse of wavelength of the incident radiation is given by the curve

Physics-General
Physics-
The intensity distribution of X-rays from two coolidge tubes operated on different voltages V1 and V2 and using different target materials of atomic numbers Z1 and Z2 is shown in the figure. Which one of the following inequalities is true?

The intensity distribution of X-rays from two coolidge tubes operated on different voltages V1 and V2 and using different target materials of atomic numbers Z1 and Z2 is shown in the figure. Which one of the following inequalities is true?

Physics-General
Physics-
Figure represents the graph of photo current I versus applied voltage (V). The maximum energy of the emitted photoelectrons is

Figure represents the graph of photo current I versus applied voltage (V). The maximum energy of the emitted photoelectrons is

Physics-General
Physics-
Figure represents a graph of kinetic energy (K) of photoelectrons (in eV) and frequency (v) for a metal used as cathode in photoelectric experiment. The work function of metal is

Figure represents a graph of kinetic energy (K) of photoelectrons (in eV) and frequency (v) for a metal used as cathode in photoelectric experiment. The work function of metal is

Physics-General
Physics-
The stopping potential  versus frequency (n) plot of a substance is shown in figure the threshold wave length is
versus frequency (n) plot of a substance is shown in figure the threshold wave length is

The stopping potential  versus frequency (n) plot of a substance is shown in figure the threshold wave length is
versus frequency (n) plot of a substance is shown in figure the threshold wave length is

Physics-General
Physics-
A point source of light is used in an experiment on photoelectric effect. Which of the following curves best represents the variation of photo current (i) with distance (d) of the source from the emitter

A point source of light is used in an experiment on photoelectric effect. Which of the following curves best represents the variation of photo current (i) with distance (d) of the source from the emitter

Physics-General
Physics-
In the following diagram if V2 > V1 then

In the following diagram if V2 > V1 then

Physics-General
Physics-
on relative change of momentum with respect to surface. Let any instant the velocity of surface is u, then above equation becomes – null Based on above concept, in the below given figure, if the cart is frictionless and free to move in horizontal direction, then answer the following :

Given cross-section area of jet null velocity of jet null, density of liquid null of cart null. In the above problem, what is the acceleration of cart at this instant –
on relative change of momentum with respect to surface. Let any instant the velocity of surface is u, then above equation becomes – null Based on above concept, in the below given figure, if the cart is frictionless and free to move in horizontal direction, then answer the following :

Given cross-section area of jet null velocity of jet null, density of liquid null of cart null. In the above problem, what is the acceleration of cart at this instant –
Physics-General
Physics-
on relative change of momentum with respect to surface. Let any instant the velocity of surface is u, then above equation becomes – null Based on above concept, in the below given figure, if the cart is frictionless and free to move in horizontal direction, then answer the following :

Given cross-section area of jet null velocity of jet null, density of liquid null of cart null. Velocity of cart at t = 10 sec. is equal to :
on relative change of momentum with respect to surface. Let any instant the velocity of surface is u, then above equation becomes – null Based on above concept, in the below given figure, if the cart is frictionless and free to move in horizontal direction, then answer the following :

Given cross-section area of jet null velocity of jet null, density of liquid null of cart null. Velocity of cart at t = 10 sec. is equal to :
Physics-General
Physics-
on relative change of momentum with respect to surface. Let any instant the velocity of surface is u, then above equation becomes – null Based on above concept, in the below given figure, if the cart is frictionless and free to move in horizontal direction, then answer the following :

Given cross-section area of jet null velocity of jet null, density of liquid null of cart null. Initially null the force on the cart is equal to :
on relative change of momentum with respect to surface. Let any instant the velocity of surface is u, then above equation becomes – null Based on above concept, in the below given figure, if the cart is frictionless and free to move in horizontal direction, then answer the following :

Given cross-section area of jet null velocity of jet null, density of liquid null of cart null. Initially null the force on the cart is equal to :
Physics-General
Physics-
One mole of an ideal monoatomic gas undergoes a cyclic process as shown in figure. Temperature at point 1 = 300 K and process 2-3 is isothermal. Net work done by gas in complete cycle is

One mole of an ideal monoatomic gas undergoes a cyclic process as shown in figure. Temperature at point 1 = 300 K and process 2-3 is isothermal. Net work done by gas in complete cycle is

Physics-General



