Chemistry-
General
Easy
Question
Assertion: Atconstanttemp0ºCand1atm,the changeH2O(s)→H2O(I)DH and DE both are zero.
Reason: During is other mal process Hand E both remains constant.
- If both Assertion and Reason are true and the Reason is correct explanation of the Asser- tion.
- If both Assertion and Reason are true but Rea- son is not correct explanation of the Asser- tion.
- If Assertion is true but the Reason is false.
- If Assertion & Reason both are false
The correct answer is: If Assertion & Reason both are false
Related Questions to study
chemistry-
Assertion: For a particular reaction, heat of combusitionate contant pressure (qp) is always greater than that at constant volume (qv).
Reason: Combustion reactions are invariably accomplished by increase in no. of moles.
Assertion: For a particular reaction, heat of combusitionate contant pressure (qp) is always greater than that at constant volume (qv).
Reason: Combustion reactions are invariably accomplished by increase in no. of moles.
chemistry-General
Maths-
Mean deviation from mean of the data is

Mean deviation from mean of the data is

Maths-General
physics-
A frictionless track 12345 ends in a circular loop of radius R.  body slids down the track from point 1 Which is 6 cm. Maximum value of R for the body to successfully complete the loop is
body slids down the track from point 1 Which is 6 cm. Maximum value of R for the body to successfully complete the loop is

A frictionless track 12345 ends in a circular loop of radius R.  body slids down the track from point 1 Which is 6 cm. Maximum value of R for the body to successfully complete the loop is
body slids down the track from point 1 Which is 6 cm. Maximum value of R for the body to successfully complete the loop is

physics-General
physics-
A body of mass 1.5 kg slide down a curved track which is quadrant of a circle of radias 0.75 meter. All the surfaces are frictionless. If the body starts from rest, its speed at the bottom of the track. is ..... 

A body of mass 1.5 kg slide down a curved track which is quadrant of a circle of radias 0.75 meter. All the surfaces are frictionless. If the body starts from rest, its speed at the bottom of the track. is ..... 

physics-General
physics-
The potential energy of a particle varies with distance  as shown in the graph. The force acting on the particle is zero at.
as shown in the graph. The force acting on the particle is zero at.

The potential energy of a particle varies with distance  as shown in the graph. The force acting on the particle is zero at.
as shown in the graph. The force acting on the particle is zero at.

physics-General
physics-
A spherical ball of mass 15 kg stationary at the top of a hill of height 82 m. It slides down a smooth surface to the ground, then climbs up another hill of height 32 m and finally slides down to horizontal base at a height of 10 m above the ground. The velocity attained by the ball is

A spherical ball of mass 15 kg stationary at the top of a hill of height 82 m. It slides down a smooth surface to the ground, then climbs up another hill of height 32 m and finally slides down to horizontal base at a height of 10 m above the ground. The velocity attained by the ball is

physics-General
Maths-
Mode of the following distribution is

Mode of the following distribution is

Maths-General
physics-
A bomb of 12 kg divedes in two parts whose ratio of masses is 1:4. If kinetic energy of smaller part is  , then momentum of bigger part in
, then momentum of bigger part in  will be
will be
A bomb of 12 kg divedes in two parts whose ratio of masses is 1:4. If kinetic energy of smaller part is  , then momentum of bigger part in
, then momentum of bigger part in  will be
will be
physics-General
physics-
A particle is acted upon by a force  which varies with position
which varies with position  as shown in figure. If the particle at x-0 has kinetic cnergy of 20 J. Then the calculate the kinetic energy of the pal tickle at x=16 cm.
as shown in figure. If the particle at x-0 has kinetic cnergy of 20 J. Then the calculate the kinetic energy of the pal tickle at x=16 cm.

A particle is acted upon by a force  which varies with position
which varies with position  as shown in figure. If the particle at x-0 has kinetic cnergy of 20 J. Then the calculate the kinetic energy of the pal tickle at x=16 cm.
as shown in figure. If the particle at x-0 has kinetic cnergy of 20 J. Then the calculate the kinetic energy of the pal tickle at x=16 cm.

physics-General
physics-
A simple pendulum is released from A as shown in figure. If 10 g and 100 cm represent the mass of the bob and length of the pendulum. what is the gain in K.E. at B? 

A simple pendulum is released from A as shown in figure. If 10 g and 100 cm represent the mass of the bob and length of the pendulum. what is the gain in K.E. at B? 

physics-General
physics-
A particle of mass 0.1 kg is subjected to a force which varies with distance as shown in figure. If it starts its journey from rest at x=0. What is the particle's velocity square at x=6 cm?

A particle of mass 0.1 kg is subjected to a force which varies with distance as shown in figure. If it starts its journey from rest at x=0. What is the particle's velocity square at x=6 cm?

physics-General
physics-
A force  time graph for a linear motion is shown in figure where the segments are circular. what is linear segments are circular. what is linear momentum gained between zero and 8 second?
time graph for a linear motion is shown in figure where the segments are circular. what is linear segments are circular. what is linear momentum gained between zero and 8 second?

A force  time graph for a linear motion is shown in figure where the segments are circular. what is linear segments are circular. what is linear momentum gained between zero and 8 second?
time graph for a linear motion is shown in figure where the segments are circular. what is linear segments are circular. what is linear momentum gained between zero and 8 second?

physics-General
physics-
What is the velocity of the bob of a simple pendulum at its mean position, if it is able to rise to vertical height of 18 cm. (Take g 

What is the velocity of the bob of a simple pendulum at its mean position, if it is able to rise to vertical height of 18 cm. (Take g 

physics-General
physics-
A body having a mass of 0.5 kg slips along the wall of a semispherical smooth surface of radius 20 cm shown in figure. What is the velocity of body at the bottom of the surface? 

A body having a mass of 0.5 kg slips along the wall of a semispherical smooth surface of radius 20 cm shown in figure. What is the velocity of body at the bottom of the surface? 

physics-General
Maths-
Consider the frequency distribution of the given number
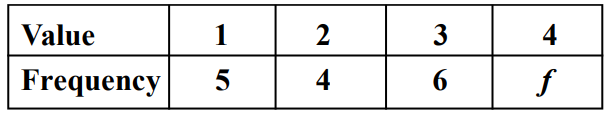
If the mean is known to be ' 3 , then the value of f is
Consider the frequency distribution of the given number

If the mean is known to be ' 3 , then the value of f is
Maths-General





