Chemistry-
General
Easy
Question
Consider the following reaction.

The product (A) is :
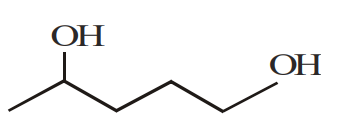
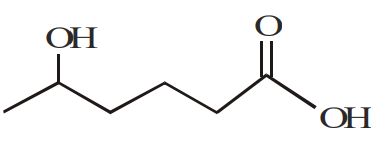
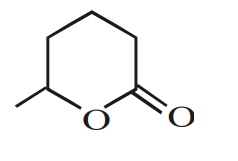
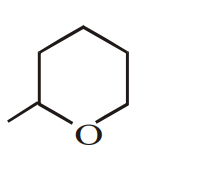
The correct answer is: 
Related Questions to study
chemistry-
In the following sequence of reactions

the product (B) is:
In the following sequence of reactions

the product (B) is:
chemistry-General
chemistry-
The regents A and B in the reaction sequence

are given by the set :-
The regents A and B in the reaction sequence

are given by the set :-
chemistry-General
chemistry-
 X is
X is
 X is
X is
chemistry-General
chemistry-
Given three acids
X) 
Y) 
Z) 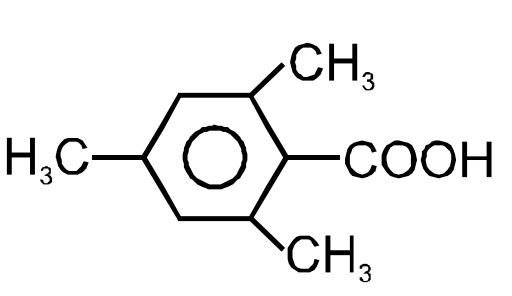
The correct order of ease of acid catalysed esterification is :
Given three acids
X) 
Y) 
Z) 
The correct order of ease of acid catalysed esterification is :
chemistry-General
chemistry-
 Product is/are
Product is/are
 Product is/are
Product is/are
chemistry-General
chemistry-
Arrange following compounds in decreasing order of reactivity for hydrolysis reaction :
I) 
II) 
III) 
IV) 
Arrange following compounds in decreasing order of reactivity for hydrolysis reaction :
I) 
II) 
III) 
IV) 
chemistry-General
chemistry-
 Reagent [X] is :
Reagent [X] is :
 Reagent [X] is :
Reagent [X] is :
chemistry-General
chemistry-
The acid D obtained through the following sequence of reactions is

The acid D obtained through the following sequence of reactions is

chemistry-General
physics-
A wire having cross-sectional area S is attached to wall on one side and a block of mass M on the other side which placed on a horizontal surface having coefficient of friction  as shown. Material of wire has coefficient of thermal expansion
as shown. Material of wire has coefficient of thermal expansion  and Young's modulus Y. At initial temperature there is no stress in the wire. Now the wire is cooled. At what decrease in temperature the block will begin to move.
and Young's modulus Y. At initial temperature there is no stress in the wire. Now the wire is cooled. At what decrease in temperature the block will begin to move.

A wire having cross-sectional area S is attached to wall on one side and a block of mass M on the other side which placed on a horizontal surface having coefficient of friction  as shown. Material of wire has coefficient of thermal expansion
as shown. Material of wire has coefficient of thermal expansion  and Young's modulus Y. At initial temperature there is no stress in the wire. Now the wire is cooled. At what decrease in temperature the block will begin to move.
and Young's modulus Y. At initial temperature there is no stress in the wire. Now the wire is cooled. At what decrease in temperature the block will begin to move.

physics-General
physics-
In the given figure F = 10 N, R = 1 m, mass of the body is 2 kg and moment of inertia of the body about an axis passing through O and perpendicular to plane of body  O is the centre of mass of the body.
O is the centre of mass of the body.

If ground is sufficiently rough to ensure rolling, what is kinetic energy of the body now in the given time interval
In the given figure F = 10 N, R = 1 m, mass of the body is 2 kg and moment of inertia of the body about an axis passing through O and perpendicular to plane of body  O is the centre of mass of the body.
O is the centre of mass of the body.

If ground is sufficiently rough to ensure rolling, what is kinetic energy of the body now in the given time interval
physics-General
physics-
In the given figure F = 10 N, R = 1 m, mass of the body is 2 kg and moment of inertia of the body about an axis passing through O and perpendicular to plane of body  O is the centre of mass of the body.
O is the centre of mass of the body.

If the ground is smooth what is total kinetic energy of the body after 2 seconds
In the given figure F = 10 N, R = 1 m, mass of the body is 2 kg and moment of inertia of the body about an axis passing through O and perpendicular to plane of body  O is the centre of mass of the body.
O is the centre of mass of the body.

If the ground is smooth what is total kinetic energy of the body after 2 seconds
physics-General
physics-
A conical pendulum consists of a mass M suspended from a string of length l. The mass executes a circle of radius R in a horizontal plane with speed v. At time t, the mass is at position  and has velocity
and has velocity  At time t, the angular momentum vector of the mass M about the point from which the string suspended is :
At time t, the angular momentum vector of the mass M about the point from which the string suspended is :

A conical pendulum consists of a mass M suspended from a string of length l. The mass executes a circle of radius R in a horizontal plane with speed v. At time t, the mass is at position  and has velocity
and has velocity  At time t, the angular momentum vector of the mass M about the point from which the string suspended is :
At time t, the angular momentum vector of the mass M about the point from which the string suspended is :

physics-General
physics-
Velocity of the centre of smaller cylinder is v. There is no slipping anywhere. The velocity of the centre of larger cylinder is

Velocity of the centre of smaller cylinder is v. There is no slipping anywhere. The velocity of the centre of larger cylinder is

physics-General
physics-
A system of uniform cylinders and plates is shown. All the cylinders are identical and there is no slipping at any contact. Velocity of lower & upper plate is V and 2V respectively as shown. Then the ratio of angular speed of the upper cylinders to lower cylinders is

A system of uniform cylinders and plates is shown. All the cylinders are identical and there is no slipping at any contact. Velocity of lower & upper plate is V and 2V respectively as shown. Then the ratio of angular speed of the upper cylinders to lower cylinders is

physics-General
physics-
A ladder AP of length 5 m is inclined to a vertical wall is slipping over a horizontal surface with velocity of 2 m/s, when A is at a distance 3m from ground what is the velocity of C.M. at this moment

A ladder AP of length 5 m is inclined to a vertical wall is slipping over a horizontal surface with velocity of 2 m/s, when A is at a distance 3m from ground what is the velocity of C.M. at this moment

physics-General



