Chemistry-
General
Easy
Question
 The major product is:
The major product is:


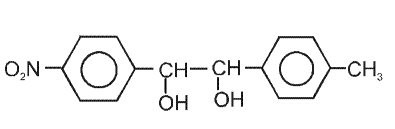

The correct answer is: 
Related Questions to study
chemistry-
 Major product is:
Major product is:
 Major product is:
Major product is:
chemistry-General
chemistry-
n-Propyl bromide on treatment with ethanolic potassium hydroxide produces
n-Propyl bromide on treatment with ethanolic potassium hydroxide produces
chemistry-General
chemistry-
Out of the following compounds, which one will have zero dipole moment
Out of the following compounds, which one will have zero dipole moment
chemistry-General
physics-
A cubical block of glass (μ=1.5) has a concentric spherical cavity of radius r=3 cm. Edge of the cube is l=12 cm long. A luminous point object ' O ' is at a distance a =12 cm from on the left face of the cube as shown in figure. Calculate the apparent position of the object when seen from right side of the cube.

A cubical block of glass (μ=1.5) has a concentric spherical cavity of radius r=3 cm. Edge of the cube is l=12 cm long. A luminous point object ' O ' is at a distance a =12 cm from on the left face of the cube as shown in figure. Calculate the apparent position of the object when seen from right side of the cube.

physics-General
physics-
A ray of light strikes a plane mirror at an angle of incidence 45° as shown in the figure. After reflection, the ray passes through a prism of refractive index 1.50, whose apex angle is 4°. The angle through which the mirror should be rotated if the total deviation of the ray is to be 90° is:

A ray of light strikes a plane mirror at an angle of incidence 45° as shown in the figure. After reflection, the ray passes through a prism of refractive index 1.50, whose apex angle is 4°. The angle through which the mirror should be rotated if the total deviation of the ray is to be 90° is:

physics-General
physics-
For a small angled prism, angle of minimum deviation  varies with the refractive index of the prism as shown in the graph
varies with the refractive index of the prism as shown in the graph

For a small angled prism, angle of minimum deviation  varies with the refractive index of the prism as shown in the graph
varies with the refractive index of the prism as shown in the graph

physics-General
physics-
A light rays is incident upon a prism minimum deviation position and suffers a deviation of 34°. If the shaded half of the prism is knocked off, the ray will

A light rays is incident upon a prism minimum deviation position and suffers a deviation of 34°. If the shaded half of the prism is knocked off, the ray will

physics-General
physics-
A light ray is incident at an angle of incidence (π/4). The graph of  versus sin e is shown in fig. The minimum angle of deviation corresponds to a prism with angle. (e = angle of emergence)
versus sin e is shown in fig. The minimum angle of deviation corresponds to a prism with angle. (e = angle of emergence)

A light ray is incident at an angle of incidence (π/4). The graph of  versus sin e is shown in fig. The minimum angle of deviation corresponds to a prism with angle. (e = angle of emergence)
versus sin e is shown in fig. The minimum angle of deviation corresponds to a prism with angle. (e = angle of emergence)

physics-General
physics-
One face AC of an equilateral prism ABC is silvered as shown in fig. What should be angle of incidence of a light ray in order that it eventually leaves the prism in the opposite direction from base of prism ? 

One face AC of an equilateral prism ABC is silvered as shown in fig. What should be angle of incidence of a light ray in order that it eventually leaves the prism in the opposite direction from base of prism ? 

physics-General
physics-
A concave mirror of radius 40 cm lies an a horizontal table and water is filled in it up to a height of 5.0 a. A small dust particle P floats on the surface of the water. Particle P lies vertically above the point of contact of the minor with the table. Locate the image of the dust particle as seen from a point directly above it. The refractive index of water is 4/3.

A concave mirror of radius 40 cm lies an a horizontal table and water is filled in it up to a height of 5.0 a. A small dust particle P floats on the surface of the water. Particle P lies vertically above the point of contact of the minor with the table. Locate the image of the dust particle as seen from a point directly above it. The refractive index of water is 4/3.

physics-General
physics-
A rod made of glass (μ=1.5) and of square cross-section is bent into shape shown in fig. A parallel beam of light falls perpendicular on the plane flat surface A. Referring to diagram, d is the width of a side and R is the radius of inner semicircle. Find the maximum value of ratio  so that all light entering the glass through surface A emerge from the glass through surface B.
so that all light entering the glass through surface A emerge from the glass through surface B.

A rod made of glass (μ=1.5) and of square cross-section is bent into shape shown in fig. A parallel beam of light falls perpendicular on the plane flat surface A. Referring to diagram, d is the width of a side and R is the radius of inner semicircle. Find the maximum value of ratio  so that all light entering the glass through surface A emerge from the glass through surface B.
so that all light entering the glass through surface A emerge from the glass through surface B.

physics-General
physics-
Consider the situation shown in figure. Water  is filled in a beaker upto a height of 10 cm. A plane mirror is fixed at a height of 5 cm from the surface of water. Distance of image from the mirror after reflection from it of an object O at the bottom of the beaker is:
is filled in a beaker upto a height of 10 cm. A plane mirror is fixed at a height of 5 cm from the surface of water. Distance of image from the mirror after reflection from it of an object O at the bottom of the beaker is:

Consider the situation shown in figure. Water  is filled in a beaker upto a height of 10 cm. A plane mirror is fixed at a height of 5 cm from the surface of water. Distance of image from the mirror after reflection from it of an object O at the bottom of the beaker is:
is filled in a beaker upto a height of 10 cm. A plane mirror is fixed at a height of 5 cm from the surface of water. Distance of image from the mirror after reflection from it of an object O at the bottom of the beaker is:

physics-General
physics-
The graph between sine of angle of refraction (  in medium 2 and sine of angle of incidence
in medium 2 and sine of angle of incidence  in medium 1 indicates that
in medium 1 indicates that 

The graph between sine of angle of refraction (  in medium 2 and sine of angle of incidence
in medium 2 and sine of angle of incidence  in medium 1 indicates that
in medium 1 indicates that 

physics-General
physics-
A rod of glass (μ=1.5) and of square cross section is bent into the shape shown in figure. A parallel beam of light falls on the plane flat surface A as shown in figure. If a is the width of a side and R is the radius of circular arc then for what maximum value of  light entering the glass slab through surface A emerges from the glass through B
light entering the glass slab through surface A emerges from the glass through B

A rod of glass (μ=1.5) and of square cross section is bent into the shape shown in figure. A parallel beam of light falls on the plane flat surface A as shown in figure. If a is the width of a side and R is the radius of circular arc then for what maximum value of  light entering the glass slab through surface A emerges from the glass through B
light entering the glass slab through surface A emerges from the glass through B

physics-General
physics-
A ray of light travelling in glass having refractive index  , is incident at a critical angle C on the glass- air interface. If a thin layer of water is poured on glass air interface, then what will be the angle of emergence of this ray in air when it emerges from water-air interface?
, is incident at a critical angle C on the glass- air interface. If a thin layer of water is poured on glass air interface, then what will be the angle of emergence of this ray in air when it emerges from water-air interface?
A ray of light travelling in glass having refractive index  , is incident at a critical angle C on the glass- air interface. If a thin layer of water is poured on glass air interface, then what will be the angle of emergence of this ray in air when it emerges from water-air interface?
, is incident at a critical angle C on the glass- air interface. If a thin layer of water is poured on glass air interface, then what will be the angle of emergence of this ray in air when it emerges from water-air interface?
physics-General




