Maths-
General
Easy
Question
 is an Isosceles Triangle, if
is an Isosceles Triangle, if  then find ABD .
then find ABD .

- 44°
- 88°
- 92°
- 136°
The correct answer is: 88°
Related Questions to study
maths-
Lines PS, QT and RU intersect at a common point ‘O’. P is joined to Q, R to S and T to U to form tr iangles. Then f ind the value of 

Lines PS, QT and RU intersect at a common point ‘O’. P is joined to Q, R to S and T to U to form tr iangles. Then f ind the value of 

maths-General
maths-
find the value of x in given figure. and
and 

find the value of x in given figure. and
and 

maths-General
maths-
find the value of x in given figure.

find the value of x in given figure.

maths-General
maths-
if  find the value of x in given figure.
find the value of x in given figure.

if  find the value of x in given figure.
find the value of x in given figure.

maths-General
Maths-
if  find the value of ‘x’ in the given figure.
find the value of ‘x’ in the given figure.

if  find the value of ‘x’ in the given figure.
find the value of ‘x’ in the given figure.

Maths-General
Maths-
In  then find
then find  in the figure.
in the figure.

In  then find
then find  in the figure.
in the figure.

Maths-General
Maths-
if y=2x,z=3x,r=4x then find y in the given figure.

if y=2x,z=3x,r=4x then find y in the given figure.

Maths-General
Maths-
In the given figure, if  find x y z
find x y z

In the given figure, if  find x y z
find x y z

Maths-General
Maths-
Find the value of a+b in the given figure

Find the value of a+b in the given figure

Maths-General
physics-
The figure shows a ray incident at an angle . If the plot drawn shown the variation of
versus
, (r=angle of refraction
The figure shows a ray incident at an angle . If the plot drawn shown the variation of
versus
, (r=angle of refraction
physics-General
physics-
The refracting media are separated by a spherical interface as shown in the figure. PP' is the principal axis,  and
and  are the refractive indices of medium of incidence and medium of refraction respectively. Then :
are the refractive indices of medium of incidence and medium of refraction respectively. Then :

The refracting media are separated by a spherical interface as shown in the figure. PP' is the principal axis,  and
and  are the refractive indices of medium of incidence and medium of refraction respectively. Then :
are the refractive indices of medium of incidence and medium of refraction respectively. Then :

physics-General
physics-
In the figure shown a point object 0 is placed in air on the principal axis. The radius of curvature of the spherical surface is 60 cm. If is the final image formed after all the refractions and reflections.

In the figure shown a point object 0 is placed in air on the principal axis. The radius of curvature of the spherical surface is 60 cm. If is the final image formed after all the refractions and reflections.

physics-General
physics-
In the diagram shown, a ray of light is incident on the interface between 1 and 2 at angle slightly greater than critical angle. The light suffers total internal reflection at this interface. After that the light ray falls at the interface of 1 and 3, and again it suffers total internal reflection. Which of the following relations should hold true?

In the diagram shown, a ray of light is incident on the interface between 1 and 2 at angle slightly greater than critical angle. The light suffers total internal reflection at this interface. After that the light ray falls at the interface of 1 and 3, and again it suffers total internal reflection. Which of the following relations should hold true?

physics-General
physics-
A curved surface of radius  separates two medium of refractive indices
separates two medium of refractive indices  and
and  as shown in figures A and B
as shown in figures A and B
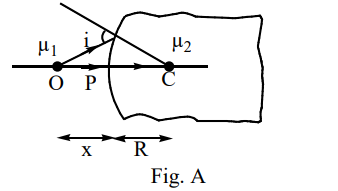
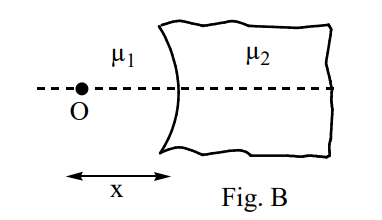
Identify the correct statement (s) related to the formation of images of a real object placed at x from the pole of the concave surface, as shown in figure B
A curved surface of radius  separates two medium of refractive indices
separates two medium of refractive indices  and
and  as shown in figures A and B
as shown in figures A and B


Identify the correct statement (s) related to the formation of images of a real object placed at x from the pole of the concave surface, as shown in figure B
physics-General
physics-
Three right angled prisms of refractive indices  and
and  are fixed together using an optical glue as shown in figure. If a ray passes through the prisms without suffering any deviation, then
are fixed together using an optical glue as shown in figure. If a ray passes through the prisms without suffering any deviation, then

Three right angled prisms of refractive indices  and
and  are fixed together using an optical glue as shown in figure. If a ray passes through the prisms without suffering any deviation, then
are fixed together using an optical glue as shown in figure. If a ray passes through the prisms without suffering any deviation, then

physics-General



