Question
If the ratio of 0.5 : x is equivalent to 1.5 : 2.25, what is the value of x ?
- 0.75
- 1,6875
- 3
- 3.25
The correct answer is: 0.75
0.5: x = 1.5 : 2.25
0.5: x = 3[0.5:0.75]
X = 0.75
Related Questions to study
Number of Flight Arrivals at Centerville Airport in a Month
|
On time |
Delayed |
Total |
|
Airline A Airline B |
861 700 |
2,890 1,850 |
|
Total |
1,561 |
4,740 |
Number of Flight Arrivals at Centerville Airport in a Month
|
On time |
Delayed |
Total |
|
Airline A Airline B |
861 700 |
2,890 1,850 |
|
Total |
1,561 |
4,740 |
y=x2 -6x - 16
The graph of the equation above in the xy-plane is a parabola. Which of the following equivalent forms of the equation includes the x- and y-coordinates of the
vertex as constants?
y=x2 -6x - 16
The graph of the equation above in the xy-plane is a parabola. Which of the following equivalent forms of the equation includes the x- and y-coordinates of the
vertex as constants?
s = 9.8t
The equation above can be used to approximate the speed s, in meters per second (m/s), of an object t seconds after being dropped into a free fall. Which of the following is the best interpretation of the number 9.8 in this context?
s = 9.8t
The equation above can be used to approximate the speed s, in meters per second (m/s), of an object t seconds after being dropped into a free fall. Which of the following is the best interpretation of the number 9.8 in this context?
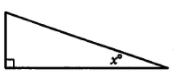
Note: Figure not drawn to scale.
In the figure above, sin(90° - x0) =  . What is the value of sin x0 ?
. What is the value of sin x0 ?

Note: Figure not drawn to scale.
In the figure above, sin(90° - x0) =  . What is the value of sin x0 ?
. What is the value of sin x0 ?
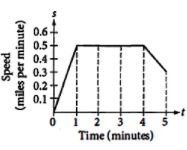
The graph above models the speed, s, of an automobile during the first 5 minutes of travel time, t. What was the total distance traveled from t=1 to t=4?

The graph above models the speed, s, of an automobile during the first 5 minutes of travel time, t. What was the total distance traveled from t=1 to t=4?
The energy pyramid below shows four trophic levels in an ecosystem and the direction of energy transfer between those levels.
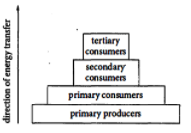
On average, 10% of the net energy of one trophic level is transferred to the next trophic level in an ecosystem. Based on the energy pyramid, if primary producers have 5,000 joules (J) of energy, approximately how much of this energy, in calories, is transferred to the secondary consumers in this ecosystem? (1 calorie= 4.18 J)
Energy flow direction within an ecosystem
1. An ecosystem's energy flow is always unidirectional.
2. It is said to be unidirectional because energy is lost in heat when moving from one trophic level to the next to maintain an organism's homeostasis.
3. As a result, each successive trophic level receives less energy than the previous trophic level.
4. Some energy is lost as heat when an organism moves from one trophic level to the next to maintain homeostasis.
5. As a result, each successive trophic level receives less energy than the previous trophic level.
6. Because the sun is the only energy source for all ecosystems on Earth, the energy flow in the food chain is unidirectional.
7. The energy captured by autotrophs does not return to the sun.
8. As a result, energy flows through various trophic levels in a food chain.
9. Energy comes from the sun and is consumed by producers in most natural ecosystems.
10. It is then passed down through the trophic levels as food.
11. As a result, energy flows from the prey to the predator rather than the other way around.
The energy pyramid below shows four trophic levels in an ecosystem and the direction of energy transfer between those levels.

On average, 10% of the net energy of one trophic level is transferred to the next trophic level in an ecosystem. Based on the energy pyramid, if primary producers have 5,000 joules (J) of energy, approximately how much of this energy, in calories, is transferred to the secondary consumers in this ecosystem? (1 calorie= 4.18 J)
Energy flow direction within an ecosystem
1. An ecosystem's energy flow is always unidirectional.
2. It is said to be unidirectional because energy is lost in heat when moving from one trophic level to the next to maintain an organism's homeostasis.
3. As a result, each successive trophic level receives less energy than the previous trophic level.
4. Some energy is lost as heat when an organism moves from one trophic level to the next to maintain homeostasis.
5. As a result, each successive trophic level receives less energy than the previous trophic level.
6. Because the sun is the only energy source for all ecosystems on Earth, the energy flow in the food chain is unidirectional.
7. The energy captured by autotrophs does not return to the sun.
8. As a result, energy flows through various trophic levels in a food chain.
9. Energy comes from the sun and is consumed by producers in most natural ecosystems.
10. It is then passed down through the trophic levels as food.
11. As a result, energy flows from the prey to the predator rather than the other way around.



