Maths-
General
Easy
Question
In Figure. PS is the bisector of  and
and  . Then
. Then  is equal to
is equal to


The correct answer is: 
Value of angle TPS should be calculated
Hence Choice 2 is correct
Related Questions to study
physics-
Two identical blocks A and B are placed on two inclined planes as shown in diagram. Neglect air resistance and other friction. Choose the correct statement:
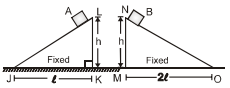
Statement I: Kinetic energy of 'A' on sliding to J will be greater than the kinetic energy of B on falling to M.
Statement II: Acceleration of 'A' will be greater than acceleration of 'B' when both are released to slide on inclined plane. Statement III: Work done by external agent to move block slowly from position B to O is negative
Two identical blocks A and B are placed on two inclined planes as shown in diagram. Neglect air resistance and other friction. Choose the correct statement:

Statement I: Kinetic energy of 'A' on sliding to J will be greater than the kinetic energy of B on falling to M.
Statement II: Acceleration of 'A' will be greater than acceleration of 'B' when both are released to slide on inclined plane. Statement III: Work done by external agent to move block slowly from position B to O is negative
physics-General
physics-
Figure shows the roller coaster track. Each car will start from rest at point A and will roll with negligible friction. It is important that there should be at least some small positive normal force exerted by the track on the car at all points, otherwise the car would leave the track. With the above fact, the minimum safe value for the radius of curvature at point B is (g = 10  ):
):

Figure shows the roller coaster track. Each car will start from rest at point A and will roll with negligible friction. It is important that there should be at least some small positive normal force exerted by the track on the car at all points, otherwise the car would leave the track. With the above fact, the minimum safe value for the radius of curvature at point B is (g = 10  ):
):

physics-General
physics-
A collar 'B' of mass 2 kg is constrained to move along a horizontal smooth and fixed circular track of radius 5m. The spring lying in the plane of the circular track and having spring constant 200  is undeformed when the collar is at 'A'. If the collar starts from rest at B' the normal reaction exerted by the track on the collar when it passes through 'A' is:
is undeformed when the collar is at 'A'. If the collar starts from rest at B' the normal reaction exerted by the track on the collar when it passes through 'A' is:

A collar 'B' of mass 2 kg is constrained to move along a horizontal smooth and fixed circular track of radius 5m. The spring lying in the plane of the circular track and having spring constant 200  is undeformed when the collar is at 'A'. If the collar starts from rest at B' the normal reaction exerted by the track on the collar when it passes through 'A' is:
is undeformed when the collar is at 'A'. If the collar starts from rest at B' the normal reaction exerted by the track on the collar when it passes through 'A' is:

physics-General
physics-
The blocks A and B shown in the figure have masses  . The system is released from rest. The speed of B after A has travelled a distance 1 m along the incline is:
. The system is released from rest. The speed of B after A has travelled a distance 1 m along the incline is:

The blocks A and B shown in the figure have masses  . The system is released from rest. The speed of B after A has travelled a distance 1 m along the incline is:
. The system is released from rest. The speed of B after A has travelled a distance 1 m along the incline is:

physics-General
physics-
Two bodies of mass  are connected by a light inextensible string which passes through a smooth fixed pulley. The instantaneous power delivered by an external agent to pull
are connected by a light inextensible string which passes through a smooth fixed pulley. The instantaneous power delivered by an external agent to pull  with constant velocity v is:
with constant velocity v is:

Two bodies of mass  are connected by a light inextensible string which passes through a smooth fixed pulley. The instantaneous power delivered by an external agent to pull
are connected by a light inextensible string which passes through a smooth fixed pulley. The instantaneous power delivered by an external agent to pull  with constant velocity v is:
with constant velocity v is:

physics-General
physics-
A small block slides with velocity  on the horizontal frictionless surface as shown in the figure. The block leaves the surface at point C. The angle q in the figure is:
on the horizontal frictionless surface as shown in the figure. The block leaves the surface at point C. The angle q in the figure is:

A small block slides with velocity  on the horizontal frictionless surface as shown in the figure. The block leaves the surface at point C. The angle q in the figure is:
on the horizontal frictionless surface as shown in the figure. The block leaves the surface at point C. The angle q in the figure is:

physics-General
physics-
A bob hangs from a rigid support by an inextensible string of length  If it is displaced through a distance
If it is displaced through a distance  (from the lowest position) keeping the string straight & released, the speed of the bob at the lowest position is:
(from the lowest position) keeping the string straight & released, the speed of the bob at the lowest position is:

A bob hangs from a rigid support by an inextensible string of length  If it is displaced through a distance
If it is displaced through a distance  (from the lowest position) keeping the string straight & released, the speed of the bob at the lowest position is:
(from the lowest position) keeping the string straight & released, the speed of the bob at the lowest position is:

physics-General
Maths-
The angle of rotation of the axes so that the equation  may be reduced to the form
may be reduced to the form 
The angle of rotation of the axes so that the equation  may be reduced to the form
may be reduced to the form 
Maths-General
maths-
By translation of axes the equation  C=
C=
By translation of axes the equation  C=
C=
maths-General
maths-
In the adjoining figure  AB = 14 units, BC = 12 units and BD = 13 units. Find the value of sec
AB = 14 units, BC = 12 units and BD = 13 units. Find the value of sec

In the adjoining figure  AB = 14 units, BC = 12 units and BD = 13 units. Find the value of sec
AB = 14 units, BC = 12 units and BD = 13 units. Find the value of sec

maths-General
chemistry-
Glycerol has:
Glycerol has:
chemistry-General
physics-
In the figure shown, the system is released from rest. Find the velocity of block m m A B P A when block B has fallen a distance  '. Assume all pulleys to be massless and frictionless.
'. Assume all pulleys to be massless and frictionless.

In the figure shown, the system is released from rest. Find the velocity of block m m A B P A when block B has fallen a distance  '. Assume all pulleys to be massless and frictionless.
'. Assume all pulleys to be massless and frictionless.

physics-General
physics-
A block of mass m is attached to two spring of spring constant  as shown in figure. The block is displaced by x towards right and released. The velocity of the block when it is at
as shown in figure. The block is displaced by x towards right and released. The velocity of the block when it is at  will be :
will be :

A block of mass m is attached to two spring of spring constant  as shown in figure. The block is displaced by x towards right and released. The velocity of the block when it is at
as shown in figure. The block is displaced by x towards right and released. The velocity of the block when it is at  will be :
will be :

physics-General
Maths-
Hence answer is isinx
Maths-General
Hence answer is isinx
physics-
A block attached to a spring, pulled by a constant horizontal force, is kept on a smooth surface as shown in the figure. Initially, the spring is in the natural state. Then the maximum positive work that the applied force F can do is : [Given that spring does not break]

A block attached to a spring, pulled by a constant horizontal force, is kept on a smooth surface as shown in the figure. Initially, the spring is in the natural state. Then the maximum positive work that the applied force F can do is : [Given that spring does not break]

physics-General





