Maths-
General
Easy
Question
Let f : R → R be a differentiable function satisfying f (x) = f (x – y) f (y) " x, y Î R and f ¢ (0) = a, f ¢ (2) = b then f ¢ (-2) is
The correct answer is: 
Related Questions to study
physics-
A thin equiconvex lens of refractive index 3/2 is placed on a horizontal plane mirror as shown in figure. The space between the lens and the mirror is filled with a liquid of refractive index 4/3. It is found that when a point object is placed 15 cm above the lens on its principal axis, the object coincides with its own image. If another liquid is filled instead of water, the object and the image coincide at a distance 25 cm from the lens. Calculate the refractive index of the liquid

A thin equiconvex lens of refractive index 3/2 is placed on a horizontal plane mirror as shown in figure. The space between the lens and the mirror is filled with a liquid of refractive index 4/3. It is found that when a point object is placed 15 cm above the lens on its principal axis, the object coincides with its own image. If another liquid is filled instead of water, the object and the image coincide at a distance 25 cm from the lens. Calculate the refractive index of the liquid

physics-General
physics-
A thin equiconvex lens of refractive index 3/2 is placed on a horizontal plane mirror as shown in figure. The space between the lens and the mirror is filled with a liquid of refractive index 4/3. It is found that when a point object is placed 15 cm above the lens on its principal axis, the object coincides with its own image. The radius of curvature of the convex surface is

A thin equiconvex lens of refractive index 3/2 is placed on a horizontal plane mirror as shown in figure. The space between the lens and the mirror is filled with a liquid of refractive index 4/3. It is found that when a point object is placed 15 cm above the lens on its principal axis, the object coincides with its own image. The radius of curvature of the convex surface is

physics-General
physics-
A glass shere of radius 2R and refractive index ‘n’ has a spherical. When viewer is on right side of the hollow sphere, what will be the apparent change in position of the object?

A glass shere of radius 2R and refractive index ‘n’ has a spherical. When viewer is on right side of the hollow sphere, what will be the apparent change in position of the object?

physics-General
physics-
A glass shere of radius 2R and refractive index ‘n’ has a spherical. When viewer is on left side of the hollow sphere, what will be the shift in position of the object?

A glass shere of radius 2R and refractive index ‘n’ has a spherical. When viewer is on left side of the hollow sphere, what will be the shift in position of the object?

physics-General
physics-
Consider the situation in the figure. The bottom of the pot is a reflecting plane mirror, S is a small fish, and T is a human eye. Refractive index of water is m. At what distance from itself will the eye see the image of the fish by observing from the mirror?

Consider the situation in the figure. The bottom of the pot is a reflecting plane mirror, S is a small fish, and T is a human eye. Refractive index of water is m. At what distance from itself will the eye see the image of the fish by observing from the mirror?

physics-General
physics-
Consider the situation in the figure. The bottom of the pot is a reflecting plane mirror, S is a small fish, and T is a human eye. Refractive index of water is m. At what distance from it self will the eye see the image of the fish upon direct observation?

Consider the situation in the figure. The bottom of the pot is a reflecting plane mirror, S is a small fish, and T is a human eye. Refractive index of water is m. At what distance from it self will the eye see the image of the fish upon direct observation?

physics-General
physics-
Consider the situation in the figure. The bottom of the pot is a reflecting plane mirror, S is a small fish, and T is a human eye. Refractive index of water is m. At what distance from itself will the fish see or observe the image of eye by observing through mirror is

Consider the situation in the figure. The bottom of the pot is a reflecting plane mirror, S is a small fish, and T is a human eye. Refractive index of water is m. At what distance from itself will the fish see or observe the image of eye by observing through mirror is

physics-General
physics-
Consider the situation in the figure. The bottom of the pot is a reflecting plane mirror, S is a small fish, and T is a human eye. Refractive index of water is m. At what distance from itself will the fish see the image of the eye by direct observation? 
Consider the situation in the figure. The bottom of the pot is a reflecting plane mirror, S is a small fish, and T is a human eye. Refractive index of water is m. At what distance from itself will the fish see the image of the eye by direct observation? 
physics-General
physics-
A point object O is placed in front of a concave mirror of focal length 10 cm. A glass slab of refractive index m = 3/ 2 and thicikness 6 cm is inserted between the object and mirror. Find the position of the final image when the distance x shown in figure is 20cm

A point object O is placed in front of a concave mirror of focal length 10 cm. A glass slab of refractive index m = 3/ 2 and thicikness 6 cm is inserted between the object and mirror. Find the position of the final image when the distance x shown in figure is 20cm

physics-General
physics-
A point object O is placed in front of a concave mirror of focal length 10 cm. A glass slab of refractive index m = 3/ 2 and thicikness 6 cm is inserted between the object and mirror. Find the position and nature of the final image when the distance x shown in figure, is 5 cm

A point object O is placed in front of a concave mirror of focal length 10 cm. A glass slab of refractive index m = 3/ 2 and thicikness 6 cm is inserted between the object and mirror. Find the position and nature of the final image when the distance x shown in figure, is 5 cm

physics-General
physics-
A ray of light incident normally on an isosceles right angled prism travels as shown in the figure. The refractive index of the prism must be greater than

A ray of light incident normally on an isosceles right angled prism travels as shown in the figure. The refractive index of the prism must be greater than

physics-General
physics-
A bi-convex lens is formed with two thin planoconvex lenses as shown in the figure. Refractive index ‘n’ of the first lens is 1.5 and that of the second lens is 1.2. Both the curved surface are of the same radius of curvature R=14 cm. For this bi-convex lens, for an object distance of 40 cm, the image distance will be

A bi-convex lens is formed with two thin planoconvex lenses as shown in the figure. Refractive index ‘n’ of the first lens is 1.5 and that of the second lens is 1.2. Both the curved surface are of the same radius of curvature R=14 cm. For this bi-convex lens, for an object distance of 40 cm, the image distance will be

physics-General
physics-
The effective focal length of the lens combination shown in figure is - 60 cm. The radii of curvature of the curved surfaces of the plano-convex lenses are 12 cm each and refractive index of the material of the lens is 1.5. The refractive index of the liquid is

The effective focal length of the lens combination shown in figure is - 60 cm. The radii of curvature of the curved surfaces of the plano-convex lenses are 12 cm each and refractive index of the material of the lens is 1.5. The refractive index of the liquid is

physics-General
physics-
A transparent thin film of uniform thickness and refractive index  is coated on the convex spherical surface of radius R at one end of a long solid glass cylinder of refractive index
is coated on the convex spherical surface of radius R at one end of a long solid glass cylinder of refractive index  , as shown in figure. Rays of light parallel to the axis of the cylinder traversing through the film from air to glass get focused at distance f1 from the film, while rays of light traversing from glass to air get focused at distacnce f2 from the film. Then
, as shown in figure. Rays of light parallel to the axis of the cylinder traversing through the film from air to glass get focused at distance f1 from the film, while rays of light traversing from glass to air get focused at distacnce f2 from the film. Then

A transparent thin film of uniform thickness and refractive index  is coated on the convex spherical surface of radius R at one end of a long solid glass cylinder of refractive index
is coated on the convex spherical surface of radius R at one end of a long solid glass cylinder of refractive index  , as shown in figure. Rays of light parallel to the axis of the cylinder traversing through the film from air to glass get focused at distance f1 from the film, while rays of light traversing from glass to air get focused at distacnce f2 from the film. Then
, as shown in figure. Rays of light parallel to the axis of the cylinder traversing through the film from air to glass get focused at distance f1 from the film, while rays of light traversing from glass to air get focused at distacnce f2 from the film. Then

physics-General
physics-
A ray of light travelling in air is incident at a grazing angle on a large transparent slab of thickness  . The point of incidence is the origin. The medium has a variable refractive index(y) given by
. The point of incidence is the origin. The medium has a variable refractive index(y) given by  Where y is in m and
Where y is in m and 
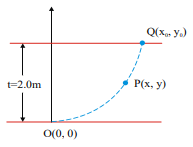
a) Express a relation between the angle of incidence and the slope of the trajectory m, in terms of the refractive index at that point m ( y)</span
A ray of light travelling in air is incident at a grazing angle on a large transparent slab of thickness  . The point of incidence is the origin. The medium has a variable refractive index(y) given by
. The point of incidence is the origin. The medium has a variable refractive index(y) given by  Where y is in m and
Where y is in m and 

a) Express a relation between the angle of incidence and the slope of the trajectory m, in terms of the refractive index at that point m ( y)</span
physics-General





