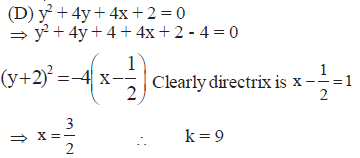Maths-
General
Easy
Question
The equation of the directrix of the parabola 

- x=-1
- x=1


The correct answer is: 
Related Questions to study
Maths-
The equation of the common tangent touching the circle  and the parabola
and the parabola  above the
above the  ‐axis is:
‐axis is:
The equation of the common tangent touching the circle  and the parabola
and the parabola  above the
above the  ‐axis is:
‐axis is:
Maths-General
Maths-
If the line x‐1 =0 is the directrix of the parabola  , then one of the values of
, then one of the values of  is :
is :
If the line x‐1 =0 is the directrix of the parabola  , then one of the values of
, then one of the values of  is :
is :
Maths-General
maths-
Assertion (A): Three normals are drawn from the point  ’ with slopes
’ with slopes  to the parabola
to the parabola  If locus of ‘
If locus of ‘  ’ with
’ with  is a part of the parabola itself then
is a part of the parabola itself then 
Reason (R): If normals at  and
and  are concurrent then
are concurrent then 
Assertion (A): Three normals are drawn from the point  ’ with slopes
’ with slopes  to the parabola
to the parabola  If locus of ‘
If locus of ‘  ’ with
’ with  is a part of the parabola itself then
is a part of the parabola itself then 
Reason (R): If normals at  and
and  are concurrent then
are concurrent then 
maths-General
maths-
ABCD and EFGC are squares and the curve  passes through the origin
passes through the origin  and the points
and the points  and F The ratio
and F The ratio  is:
is:

ABCD and EFGC are squares and the curve  passes through the origin
passes through the origin  and the points
and the points  and F The ratio
and F The ratio  is:
is:

maths-General
maths-
Statement‐I :: With respect to a hyperbola  pependicular are drawn from a point (5, 0) on the lines
pependicular are drawn from a point (5, 0) on the lines  , then their feet lie on circle
, then their feet lie on circle 
Statement‐II :: If from any foci of a hyperbola perpendicular are drawn on the asymptotes of the hyperbola then their feet lie on auxiliary circle.
Statement‐I :: With respect to a hyperbola  pependicular are drawn from a point (5, 0) on the lines
pependicular are drawn from a point (5, 0) on the lines  , then their feet lie on circle
, then their feet lie on circle 
Statement‐II :: If from any foci of a hyperbola perpendicular are drawn on the asymptotes of the hyperbola then their feet lie on auxiliary circle.
maths-General
maths-
A hyperbola, having the transverse axis of length  , is confocal with the ellipse
, is confocal with the ellipse  Then its equation is ‐
Then its equation is ‐
A hyperbola, having the transverse axis of length  , is confocal with the ellipse
, is confocal with the ellipse  Then its equation is ‐
Then its equation is ‐
maths-General
Maths-
The latus rectum of the hyperbola  is‐
is‐
The latus rectum of the hyperbola  is‐
is‐
Maths-General
maths-
Statement‐I :: If a point  lies in the shaded region
lies in the shaded region  , show in the figure, then
, show in the figure, then 
Statement‐II ::  lies outside the hyperbola
lies outside the hyperbola  , then
, then 

Statement‐I :: If a point  lies in the shaded region
lies in the shaded region  , show in the figure, then
, show in the figure, then 
Statement‐II ::  lies outside the hyperbola
lies outside the hyperbola  , then
, then 

maths-General
Maths-
Statement‐I The ellipse  and
and  are congruent.
are congruent.
Statement‐II The ellipse  and
and  have the same eccentricity.
have the same eccentricity.
For such questions, we should know properties of ellipse. We should know all the formulas related to ellipse. The axis which is larger is always the major axis.
Statement‐I The ellipse  and
and  are congruent.
are congruent.
Statement‐II The ellipse  and
and  have the same eccentricity.
have the same eccentricity.
Maths-General
For such questions, we should know properties of ellipse. We should know all the formulas related to ellipse. The axis which is larger is always the major axis.
Maths-
The minimum area of triangle formed by tangent to the ellipse  and coordinate axes‐
and coordinate axes‐
The minimum area of triangle formed by tangent to the ellipse  and coordinate axes‐
and coordinate axes‐
Maths-General
Maths-
An ellipse has OB as semi minor axis,  and
and  its focii and the angle FBF’ is a right angle Then the eccentricity of the ellipse is‐
its focii and the angle FBF’ is a right angle Then the eccentricity of the ellipse is‐
Therefore, the eccentricity of the ellipse is
An ellipse has OB as semi minor axis,  and
and  its focii and the angle FBF’ is a right angle Then the eccentricity of the ellipse is‐
its focii and the angle FBF’ is a right angle Then the eccentricity of the ellipse is‐
Maths-General
Therefore, the eccentricity of the ellipse is
Maths-
The number of values of  such that the straight line y=4x+c touches the curve
such that the straight line y=4x+c touches the curve  is‐
is‐
Therefore, there are two values of c.
The number of values of  such that the straight line y=4x+c touches the curve
such that the straight line y=4x+c touches the curve  is‐
is‐
Maths-General
Therefore, there are two values of c.
Maths-
Let P be any point on any directrix of an ellipse Then the chords of contact of point P with respect to the ellipse and its auxiliary circle intersect at
Let P be any point on any directrix of an ellipse Then the chords of contact of point P with respect to the ellipse and its auxiliary circle intersect at
Maths-General
maths-
An ellipse having foci at (3, 3) and (-4,4) and passing through the origin has eccentricity equal to‐
An ellipse having foci at (3, 3) and (-4,4) and passing through the origin has eccentricity equal to‐
maths-General
maths-
Normals  are drawn to parabola
are drawn to parabola  from the pointA (h, 0) If triangle
from the pointA (h, 0) If triangle  (
(  being the origin) is equilateral, then possible value of h’ is
being the origin) is equilateral, then possible value of h’ is
Normals  are drawn to parabola
are drawn to parabola  from the pointA (h, 0) If triangle
from the pointA (h, 0) If triangle  (
(  being the origin) is equilateral, then possible value of h’ is
being the origin) is equilateral, then possible value of h’ is
maths-General