Chemistry-
General
Easy
Question
On reacting with neutral ferric chloride, phenol gives
- Red colour
- Blue colour
- Violet colour
- Green colour
The correct answer is: Violet colour
Phenol reacts with neutral  solution to give violet colour complex which is soluble in water.
solution to give violet colour complex which is soluble in water.
Related Questions to study
physics-
An air bubble in glass (m =1.5) is situated at a distance 3 cm from a convex surface of diameter 10 cm as shown The distance from surface at which the image of bubble appears is

An air bubble in glass (m =1.5) is situated at a distance 3 cm from a convex surface of diameter 10 cm as shown The distance from surface at which the image of bubble appears is

physics-General
physics-
The fig shows a mixture of blue, green, red colours incident on a right angled prism The critical angles of the material of prism for red, green and blue colours are 460 , 440 , 430 respectively, The arrangement will separate

The fig shows a mixture of blue, green, red colours incident on a right angled prism The critical angles of the material of prism for red, green and blue colours are 460 , 440 , 430 respectively, The arrangement will separate

physics-General
chemistry-
Ethanol reacts with thionyl chloride to give ethyl chloride and:
Ethanol reacts with thionyl chloride to give ethyl chloride and:
chemistry-General
physics-
The minimum speed for a particle at the lowest point of a vertical circle of radius  , to describe the circle is
, to describe the circle is  . If the radius of the circle is reduced to one-fourth its value, the corresponding minimum speed will be
. If the radius of the circle is reduced to one-fourth its value, the corresponding minimum speed will be
The minimum speed for a particle at the lowest point of a vertical circle of radius  , to describe the circle is
, to describe the circle is  . If the radius of the circle is reduced to one-fourth its value, the corresponding minimum speed will be
. If the radius of the circle is reduced to one-fourth its value, the corresponding minimum speed will be
physics-General
chemistry-
Scientific aspect of fermentation was first studied by:
Scientific aspect of fermentation was first studied by:
chemistry-General
physics-
The convex surface of a thin concav–convex lens of glass of refractive index 1.5 has a radius of curvature of 20 cm The concave surface has a radius of curvature of 60 cm The convex side is silvered and placed on a horizontal surface as shown in the figure A small object is placed on the principal axis of the combination, at a distance of 30 cm in front of the mirror The magnification of the image is

The convex surface of a thin concav–convex lens of glass of refractive index 1.5 has a radius of curvature of 20 cm The concave surface has a radius of curvature of 60 cm The convex side is silvered and placed on a horizontal surface as shown in the figure A small object is placed on the principal axis of the combination, at a distance of 30 cm in front of the mirror The magnification of the image is

physics-General
physics-
The convex surface of a thin concav–convex lens of glass of refractive index 1.5 has a radius of curvature of 20 cm The concave surface has a radius of curvature of 60 cm The convex side is silvered and placed on a horizontal surface as shown in the figure The combination behaves like

The convex surface of a thin concav–convex lens of glass of refractive index 1.5 has a radius of curvature of 20 cm The concave surface has a radius of curvature of 60 cm The convex side is silvered and placed on a horizontal surface as shown in the figure The combination behaves like

physics-General
physics-
The convex surface of a thin concav–convex lens of glass of refractive index 1.5 has a radius of curvature of 20 cm The concave surface has a radius of curvature of 60 cm The convex side is silvered and placed on a horizontal surface as shown in the figure The focal length of the combination has the magnitude

The convex surface of a thin concav–convex lens of glass of refractive index 1.5 has a radius of curvature of 20 cm The concave surface has a radius of curvature of 60 cm The convex side is silvered and placed on a horizontal surface as shown in the figure The focal length of the combination has the magnitude

physics-General
physics-
A point object O is placed at a distance of 0.3 m from a convex lens of focal length 0.2m It is then cut into two halves each of which is displaced by 0.0005 m as shown in figure
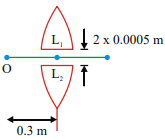
Separation between the images is
A point object O is placed at a distance of 0.3 m from a convex lens of focal length 0.2m It is then cut into two halves each of which is displaced by 0.0005 m as shown in figure

Separation between the images is
physics-General
physics-
A point object O is placed at a distance of 0.3 m from a convex lens of focal length 0.2m It is then cut into two halves each of which is displaced by 0.0005 m as shown in figure
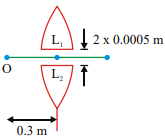
Number of images found is
A point object O is placed at a distance of 0.3 m from a convex lens of focal length 0.2m It is then cut into two halves each of which is displaced by 0.0005 m as shown in figure

Number of images found is
physics-General
physics-
A point object O is placed at a distance of 0.3 m from a convex lens of focal length 0.2m It is then cut into two halves each of which is displaced by 0.0005 m as shown in figure
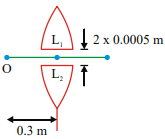
Image will be formed from the lens at a distance of
A point object O is placed at a distance of 0.3 m from a convex lens of focal length 0.2m It is then cut into two halves each of which is displaced by 0.0005 m as shown in figure

Image will be formed from the lens at a distance of
physics-General
chemistry-
The major product obtained on interaction of phenol with sodium hydroxide and carbon dioxide is
The major product obtained on interaction of phenol with sodium hydroxide and carbon dioxide is
chemistry-General
chemistry-
Which will not form a yellow precipitate on heating with an alkaline solution of iodine?
Which will not form a yellow precipitate on heating with an alkaline solution of iodine?
chemistry-General
physics-
A bi-convex lens is formed with two thin planoconvex lenses as shown in the figure Refractive index n of the first lens is 1.5 and that of the second lens s 1.2 Both the curved surfaces are of the same radius of curvature R = 14 cm For this bi-convex lens, for an object distance of 40 cm, the image distance will be

A bi-convex lens is formed with two thin planoconvex lenses as shown in the figure Refractive index n of the first lens is 1.5 and that of the second lens s 1.2 Both the curved surfaces are of the same radius of curvature R = 14 cm For this bi-convex lens, for an object distance of 40 cm, the image distance will be

physics-General
physics-
The graph between the lateral magnification (m) produced by a lens and the distance of the image (v) is given by
The graph between the lateral magnification (m) produced by a lens and the distance of the image (v) is given by
physics-General





