General
General
Easy
Question
____________ pairs of parallel lines are there in regular hexagon?
- 2
- 3
- 6
- 1

General Synopsis of Regular Hexagon.
The correct answer is: 3
*In mathematics, a polygon is a closed two-dimensional figure made up of line segments.
* Poly means many gon means angle. Hence, polygon is a closed figure that is made of many angles.
*In General there are 4 types of polygons. They are:
Regular Polygon
Irregular Polygon
Convex Polygon
Concave polygon
>>>Hexagon is a Regular Polygon that has six sides and six angles as shown in below.
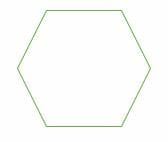
>>>From figure, we can say that there are 3 parallel pairs exist and are in opposite direction.
>>>Hence, we can say that the every opposite sides of a Hexagon are parallel to each other.
>>>Therefore, wen say that there are exactly Three pairs of parallel sides present in Hexagon.
Hexagon is a closed figure which has six sides and six corners. Given is a regular hexagon, which means it has equal interior angles and equal side lengths. So, there will be 3 pairs of parallel lines in a regular hexagon.
>>>Hence, we can say that the Hexagon has 3 parallel pairs.
Related Questions to study
Physics-
Statement–I : In gravity free space, the liquid in a capillary tube will rise to infinite height
Statement–II : In the absence of gravity , there will be no force to prevent the rise of liquid due to surface tension
Statement–I : In gravity free space, the liquid in a capillary tube will rise to infinite height
Statement–II : In the absence of gravity , there will be no force to prevent the rise of liquid due to surface tension
Physics-General
Physics-
Statement–I : The velocity of horizontal flow of a ideal liquid is smaller where pressure is large and vice versa. Statement–II : According to Barnoullis theorem for the stream line flow of an ideal liquid, the total energy per unit mass remains constant
Statement–I : The velocity of horizontal flow of a ideal liquid is smaller where pressure is large and vice versa. Statement–II : According to Barnoullis theorem for the stream line flow of an ideal liquid, the total energy per unit mass remains constant
Physics-General
Physics-
A concave mirror of focal length 2 cm is placed on a glass slab as shown in the figure. Then the image of object O formed due to reflection at mirror and then refraction by the slab :

A concave mirror of focal length 2 cm is placed on a glass slab as shown in the figure. Then the image of object O formed due to reflection at mirror and then refraction by the slab :

Physics-General
Physics-
In the figure shown a point object O is placed in air. A spherical boundary separates various media of radius of curvature 1.0 m. AB is principal axis. The refractive index above AB is 1.6 and below AB is 2.0. The separation between the images formed due to refraction at spherical surface is:

In the figure shown a point object O is placed in air. A spherical boundary separates various media of radius of curvature 1.0 m. AB is principal axis. The refractive index above AB is 1.6 and below AB is 2.0. The separation between the images formed due to refraction at spherical surface is:

Physics-General
Physics-
A wooden block with mass 2.0 kg is moving up an inclined surface  At point S it has a speed of 8 m/sec; the block comes to a halt at point P (see the figure which is a vertical cross-section). The friction coefficient m between the block and the inclined surface is 0.25 (assume that g = 10
At point S it has a speed of 8 m/sec; the block comes to a halt at point P (see the figure which is a vertical cross-section). The friction coefficient m between the block and the inclined surface is 0.25 (assume that g = 10  and that the kinetic and the static friction coefficients are the same).
and that the kinetic and the static friction coefficients are the same).

A wooden block with mass 2.0 kg is moving up an inclined surface  At point S it has a speed of 8 m/sec; the block comes to a halt at point P (see the figure which is a vertical cross-section). The friction coefficient m between the block and the inclined surface is 0.25 (assume that g = 10
At point S it has a speed of 8 m/sec; the block comes to a halt at point P (see the figure which is a vertical cross-section). The friction coefficient m between the block and the inclined surface is 0.25 (assume that g = 10  and that the kinetic and the static friction coefficients are the same).
and that the kinetic and the static friction coefficients are the same).

Physics-General
Physics-
A fish, F in the pond, is at a depth of 0.8 m from water surface and is moving vertically upwards with velocity  At the same instant, a bird B is a height of 6m from water surface and is moving downwards with velocity
At the same instant, a bird B is a height of 6m from water surface and is moving downwards with velocity  At this instant both are on the same vertical lines as shown in the Figure. Which of the following statement(s) is(are) correct?
At this instant both are on the same vertical lines as shown in the Figure. Which of the following statement(s) is(are) correct?
i) Height of B, observed by F (from itself) is equal to 5.30 m.
ii) Depth of F, observed by B (from itself) is equal to 6.60 m.
iii) Velocity of B, observed by F (relative to itself) is equal to 
iv) Velocity of F, observed by B (relative to itself) is equal to 

A fish, F in the pond, is at a depth of 0.8 m from water surface and is moving vertically upwards with velocity  At the same instant, a bird B is a height of 6m from water surface and is moving downwards with velocity
At the same instant, a bird B is a height of 6m from water surface and is moving downwards with velocity  At this instant both are on the same vertical lines as shown in the Figure. Which of the following statement(s) is(are) correct?
At this instant both are on the same vertical lines as shown in the Figure. Which of the following statement(s) is(are) correct?
i) Height of B, observed by F (from itself) is equal to 5.30 m.
ii) Depth of F, observed by B (from itself) is equal to 6.60 m.
iii) Velocity of B, observed by F (relative to itself) is equal to 
iv) Velocity of F, observed by B (relative to itself) is equal to 

Physics-General
Physics-
What is the length of the image of the rod in mirror, according to the observer in air? (The refractive index of liquid is m.)

What is the length of the image of the rod in mirror, according to the observer in air? (The refractive index of liquid is m.)

Physics-General
Physics-
A man looks down on a fish of length 20 cm. His eye is 2 m above the surface of the water (m = 4/3) and the fish is 2 m below the surface as shown in the figure. The ratio of angular width  of the fish as seen by the man in presence of water to the
of the fish as seen by the man in presence of water to the  in the absence of water is
in the absence of water is

A man looks down on a fish of length 20 cm. His eye is 2 m above the surface of the water (m = 4/3) and the fish is 2 m below the surface as shown in the figure. The ratio of angular width  of the fish as seen by the man in presence of water to the
of the fish as seen by the man in presence of water to the  in the absence of water is
in the absence of water is

Physics-General
Physics-
The reflecting surface is represented by the equation  as shown in figure. A ray travelling horizontal becomes vertical after reflection. The co-ordinates of the point of incidence can be
as shown in figure. A ray travelling horizontal becomes vertical after reflection. The co-ordinates of the point of incidence can be

The reflecting surface is represented by the equation  as shown in figure. A ray travelling horizontal becomes vertical after reflection. The co-ordinates of the point of incidence can be
as shown in figure. A ray travelling horizontal becomes vertical after reflection. The co-ordinates of the point of incidence can be

Physics-General
Physics-
The rectangular box is the place of a spherical mirror. The point S is the position of an object and the point I is the position of its image. The height of the point S from the axis is two times that of point I. The horizontal separation between S and I is equal to 15 cm.

The rectangular box is the place of a spherical mirror. The point S is the position of an object and the point I is the position of its image. The height of the point S from the axis is two times that of point I. The horizontal separation between S and I is equal to 15 cm.

Physics-General
Physics-
A given mass of a gas expands from the state A to the state B by three paths 1, 2 and 3 as shown in V-T indicator diagram. If  respectively be the work done by the gas along the three paths, then
respectively be the work done by the gas along the three paths, then

A given mass of a gas expands from the state A to the state B by three paths 1, 2 and 3 as shown in V-T indicator diagram. If  respectively be the work done by the gas along the three paths, then
respectively be the work done by the gas along the three paths, then

Physics-General
Physics-
A point-like object of mass 2.0 kg moves along the x-axis with a velocity of + 4.0 m/s. A net horizontal force acting along the x-axis is applied to the object with the force-time profile shown. What is the total work that was done by the force?

A point-like object of mass 2.0 kg moves along the x-axis with a velocity of + 4.0 m/s. A net horizontal force acting along the x-axis is applied to the object with the force-time profile shown. What is the total work that was done by the force?

Physics-General
Physics-
Consider the cyclic process ABCA shown in figure, performed on a sample of 1 mole of an ideal gas. A total of 1000 J of heat is withdrawn from the sample in the process, the work done on the gas during part BC is 1830 J, the value of 

Consider the cyclic process ABCA shown in figure, performed on a sample of 1 mole of an ideal gas. A total of 1000 J of heat is withdrawn from the sample in the process, the work done on the gas during part BC is 1830 J, the value of 

Physics-General
Physics-
A rubber ball bounces on the ground as shown. After each bounce, the ball reaches one-half the highest of the bounce before it. If the time the ball was in the air between the first and second bounce was 1 second, what would be the time between the second and third bounce?

A rubber ball bounces on the ground as shown. After each bounce, the ball reaches one-half the highest of the bounce before it. If the time the ball was in the air between the first and second bounce was 1 second, what would be the time between the second and third bounce?

Physics-General
Physics-
A particle with mass 2 kg moves in one dimension, in the presence of a force that is described by the following potential energy graph. In parts (a)-(c), specify your numerical answers to 2 significant figure accuracy.

A particle with mass 2 kg moves in one dimension, in the presence of a force that is described by the following potential energy graph. In parts (a)-(c), specify your numerical answers to 2 significant figure accuracy.

Physics-General





