Physics-
General
Easy
Question
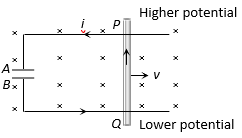
A conducting rod PQ of length L = 1.0 m is moving with a uniform speed v = 2 m/s in a uniform magnetic field  directed into the paper. A capacitor of capacity C = 10 mF is connected as shown in figure. Then
directed into the paper. A capacitor of capacity C = 10 mF is connected as shown in figure. Then

- qA = + 80 mC and qB = – 80 mC
- qA = – 80 mC and qB = + 80 mC
- qA = 0 = qB
- Charge stored in the capacitor increases exponentially with time
The correct answer is: qA = + 80 mC and qB = – 80 mC
Q = CV = C (Bvl) = 10 ´ 10– 6 ´ 4 ´ 2 ´ 1 = 80 mC
According to Fleming's right hand rule induced current flows from Q to P. Hence P is at higher potential and Q is at lower potential. Therefore A is positively charged and B is negatively charged.
Related Questions to study
Maths-
Let f(x) = 
Assertion (A): Fundamental period of f(x) is 2
Reason (R) : period of sin x and cos x is 2
Let f(x) = 
Assertion (A): Fundamental period of f(x) is 2
Reason (R) : period of sin x and cos x is 2
Maths-General
maths-
If (x1 ,y1) and (x2, y2) and ends of a focal chord of the parabola  = 4ax, then square of G.M. of x1 and x2 is-
= 4ax, then square of G.M. of x1 and x2 is-
If (x1 ,y1) and (x2, y2) and ends of a focal chord of the parabola  = 4ax, then square of G.M. of x1 and x2 is-
= 4ax, then square of G.M. of x1 and x2 is-
maths-General
physics-
A conductor ABOCD moves along its bisector with a velocity of 1 m/s through a perpendicular magnetic field of 1 wb/m2, as shown in fig. If all the four sides are of 1m length each, then the induced emf between points A and D is

A conductor ABOCD moves along its bisector with a velocity of 1 m/s through a perpendicular magnetic field of 1 wb/m2, as shown in fig. If all the four sides are of 1m length each, then the induced emf between points A and D is

physics-General
physics-
A square metallic wire loop of side 0.1 m and resistance of 1W is moved with a constant velocity in a magnetic field of 2 wb/m2 as shown in figure. The magnetic field is perpendicular to the plane of the loop, loop is connected to a network of resistances. What should be the velocity of loop so as to have a steady current of 1mA in loop

A square metallic wire loop of side 0.1 m and resistance of 1W is moved with a constant velocity in a magnetic field of 2 wb/m2 as shown in figure. The magnetic field is perpendicular to the plane of the loop, loop is connected to a network of resistances. What should be the velocity of loop so as to have a steady current of 1mA in loop

physics-General
physics-
A conducting wire frame is placed in a magnetic field which is directed into the paper. The magnetic field is increasing at a constant rate. The directions of induced current in wires AB and CD are

A conducting wire frame is placed in a magnetic field which is directed into the paper. The magnetic field is increasing at a constant rate. The directions of induced current in wires AB and CD are

physics-General
physics-
As shown in the figure a metal rod makes contact and complete the circuit. The circuit is perpendicular to the magnetic field with  If the resistance is
If the resistance is  , force needed to move the rod as indicated with a constant speed of
, force needed to move the rod as indicated with a constant speed of  is
is

As shown in the figure a metal rod makes contact and complete the circuit. The circuit is perpendicular to the magnetic field with  If the resistance is
If the resistance is  , force needed to move the rod as indicated with a constant speed of
, force needed to move the rod as indicated with a constant speed of  is
is

physics-General
physics-
As shown in the figure, P and Q are two coaxial conducting loops separated by some distance. When the switch S is closed, a clockwise current  flows in P (as seen by E) and an induced current
flows in P (as seen by E) and an induced current  flows in Q. The switch remains closed for a long time. When S is opened, a current
flows in Q. The switch remains closed for a long time. When S is opened, a current  flows in Q. Then the directions of
flows in Q. Then the directions of  and
and  (as seen by E) are
(as seen by E) are

As shown in the figure, P and Q are two coaxial conducting loops separated by some distance. When the switch S is closed, a clockwise current  flows in P (as seen by E) and an induced current
flows in P (as seen by E) and an induced current  flows in Q. The switch remains closed for a long time. When S is opened, a current
flows in Q. The switch remains closed for a long time. When S is opened, a current  flows in Q. Then the directions of
flows in Q. Then the directions of  and
and  (as seen by E) are
(as seen by E) are

physics-General
Maths-
A particle moves along a line by  then S is decreasing when t
then S is decreasing when t 
A particle moves along a line by  then S is decreasing when t
then S is decreasing when t 
Maths-General
maths-
Assertion: f(x) = ln  is an odd function.
is an odd function.
Reason: Let f be a function with domain D such that
i) x  D
D  – x
– x  D
D
ii) f(–x) = – f(x) and
iii) f (0) = 0 or f (0) is not defined
Then the function f(x) is an odd function
Assertion: f(x) = ln  is an odd function.
is an odd function.
Reason: Let f be a function with domain D such that
i) x  D
D  – x
– x  D
D
ii) f(–x) = – f(x) and
iii) f (0) = 0 or f (0) is not defined
Then the function f(x) is an odd function
maths-General
physics-
A conducting rod of length 2l is rotating with constant angular speed w about its perpendicular bisector. A uniform magnetic field  exists parallel to the axis of rotation. The e.m.f. induced between two ends of the rod is
exists parallel to the axis of rotation. The e.m.f. induced between two ends of the rod is

A conducting rod of length 2l is rotating with constant angular speed w about its perpendicular bisector. A uniform magnetic field  exists parallel to the axis of rotation. The e.m.f. induced between two ends of the rod is
exists parallel to the axis of rotation. The e.m.f. induced between two ends of the rod is

physics-General
physics-
A metallic square loop ABCD is moving in its own plane with velocity v in a uniform magnetic field perpendicular to its plane as shown in the figure. An electric field is induced

A metallic square loop ABCD is moving in its own plane with velocity v in a uniform magnetic field perpendicular to its plane as shown in the figure. An electric field is induced

physics-General
physics-
Two circular coils can be arranged in any of the three situations shown in the figure. Their mutual inductance will be

Two circular coils can be arranged in any of the three situations shown in the figure. Their mutual inductance will be

physics-General
physics-
A uniform but time-varying magnetic field B(t) exists in a circular region of radius a and is directed into the plane of the paper, as shown. The magnitude of the induced electric field at point P at a distance r from the centre of the circular region

A uniform but time-varying magnetic field B(t) exists in a circular region of radius a and is directed into the plane of the paper, as shown. The magnitude of the induced electric field at point P at a distance r from the centre of the circular region

physics-General
maths-
With the usual meaning for a, b, c and s if  be the area of a triangle then the error in
be the area of a triangle then the error in  resulting from a small error in the measurement of c, is
resulting from a small error in the measurement of c, is
With the usual meaning for a, b, c and s if  be the area of a triangle then the error in
be the area of a triangle then the error in  resulting from a small error in the measurement of c, is
resulting from a small error in the measurement of c, is
maths-General
physics-
Consider the situation shown in the figure. The wire AB is sliding on the fixed rails with a constant velocity. If the wire AB is replaced by semicircular wire, the magnitude of the induced current will

Consider the situation shown in the figure. The wire AB is sliding on the fixed rails with a constant velocity. If the wire AB is replaced by semicircular wire, the magnitude of the induced current will

physics-General





