Physics-
General
Easy
Question
A magnetic field (B), uniform between two magnets can be determined measuring the induced voltage in the loop as it is pulled through the gap at uniform speed 20 m/sec. Size of magnet and coil is  and
and  as shown in figure. The correct variation of induced emf with time is : (Assume at t = 0, the coil enters in the magnetic field)
as shown in figure. The correct variation of induced emf with time is : (Assume at t = 0, the coil enters in the magnetic field)




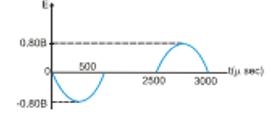
The correct answer is: 
Related Questions to study
physics-
A metallic ring of mass m and radius r with a uniform metallic spoke of same mass m and length r is rotated about its axis with angular velocity  in a perpendicular uniform magnetic field B as shown. If the central end of the spoke is connected to the rim of the wheel through a resistor R as shown. The resistor does not rotate, its one end is always at the center of the ring and other end is always in contact with the ring. A force F as shown is needed to maintain constant angular velocity of the wheel. F is equal to (The ring and the spoke has zero resistance)
in a perpendicular uniform magnetic field B as shown. If the central end of the spoke is connected to the rim of the wheel through a resistor R as shown. The resistor does not rotate, its one end is always at the center of the ring and other end is always in contact with the ring. A force F as shown is needed to maintain constant angular velocity of the wheel. F is equal to (The ring and the spoke has zero resistance)

A metallic ring of mass m and radius r with a uniform metallic spoke of same mass m and length r is rotated about its axis with angular velocity  in a perpendicular uniform magnetic field B as shown. If the central end of the spoke is connected to the rim of the wheel through a resistor R as shown. The resistor does not rotate, its one end is always at the center of the ring and other end is always in contact with the ring. A force F as shown is needed to maintain constant angular velocity of the wheel. F is equal to (The ring and the spoke has zero resistance)
in a perpendicular uniform magnetic field B as shown. If the central end of the spoke is connected to the rim of the wheel through a resistor R as shown. The resistor does not rotate, its one end is always at the center of the ring and other end is always in contact with the ring. A force F as shown is needed to maintain constant angular velocity of the wheel. F is equal to (The ring and the spoke has zero resistance)

physics-General
physics-
A conducting ring of radius r with a conducting spoke is in pure rolling on a horizontal surface in a region having a uniform magnetic field B as shown, v being the velocity of the centre of the ring. Then the potential difference  is –
is –

A conducting ring of radius r with a conducting spoke is in pure rolling on a horizontal surface in a region having a uniform magnetic field B as shown, v being the velocity of the centre of the ring. Then the potential difference  is –
is –

physics-General
physics-
AB and CD are fixed conducting smooth rails placed in a vertical plane and joined by a constant current source at its upper end. PQ is a conducting rod which is free to slide on the rails. A horizontal uniform magnetic field exists in space as shown. If the rod PQ is released from rest then

AB and CD are fixed conducting smooth rails placed in a vertical plane and joined by a constant current source at its upper end. PQ is a conducting rod which is free to slide on the rails. A horizontal uniform magnetic field exists in space as shown. If the rod PQ is released from rest then

physics-General
physics-
AB is a resistance less conducting rod which forms a diameter of a conducting ring of radius r rotating in a uniform magnetic field B as shown. The resistors  and
and  do not rotate. Then current through the resistor R1 is
do not rotate. Then current through the resistor R1 is

AB is a resistance less conducting rod which forms a diameter of a conducting ring of radius r rotating in a uniform magnetic field B as shown. The resistors  and
and  do not rotate. Then current through the resistor R1 is
do not rotate. Then current through the resistor R1 is

physics-General
physics-
A uniform magnetic field of induction B is confined to a cylindrical region of radius R. The magnetic field is increasing at a constant rate of  (tesla/second). An electron of charge q, placed at the point P on the periphery of the field experiences an acceleration:
(tesla/second). An electron of charge q, placed at the point P on the periphery of the field experiences an acceleration:

A uniform magnetic field of induction B is confined to a cylindrical region of radius R. The magnetic field is increasing at a constant rate of  (tesla/second). An electron of charge q, placed at the point P on the periphery of the field experiences an acceleration:
(tesla/second). An electron of charge q, placed at the point P on the periphery of the field experiences an acceleration:

physics-General
physics-
In the circuit shown in figure, the switch S was initially at position 1. After sufficiently long time, the switch S was thrown from position 1 to position 2. The voltage drop across the resistor at that instant is :

In the circuit shown in figure, the switch S was initially at position 1. After sufficiently long time, the switch S was thrown from position 1 to position 2. The voltage drop across the resistor at that instant is :

physics-General
physics-
Two identical conducting rings A & B of radius R are in pure rolling over a horizontal conducting plane with same speed (of center of mass)u but in opposite direction. A constant magnetic field B is present pointing inside the plane of paper. Then the potential difference between the highest points of the two rings, is:

Two identical conducting rings A & B of radius R are in pure rolling over a horizontal conducting plane with same speed (of center of mass)u but in opposite direction. A constant magnetic field B is present pointing inside the plane of paper. Then the potential difference between the highest points of the two rings, is:

physics-General
physics-
A vertical conducting ring of radius R falls vertically with a speed V in a horizontal uniform magnetic field B which is perpendicular to the plane of the ring :

A vertical conducting ring of radius R falls vertically with a speed V in a horizontal uniform magnetic field B which is perpendicular to the plane of the ring :

physics-General
physics-
A and B are two metallic rings placed at opposite sides of an infinitely long straight conducting wire as shown. If current in the wire is slowly decreased, the direction of induced current will be :

A and B are two metallic rings placed at opposite sides of an infinitely long straight conducting wire as shown. If current in the wire is slowly decreased, the direction of induced current will be :

physics-General
physics-
Figure shows a square loop of side 1 m and resistance 1  . The magnetic field on left side of line PQ has a magnitude B = 1.0T. The work done in pulling the loop out of the field uniformly in 1 s is
. The magnetic field on left side of line PQ has a magnitude B = 1.0T. The work done in pulling the loop out of the field uniformly in 1 s is

Figure shows a square loop of side 1 m and resistance 1  . The magnetic field on left side of line PQ has a magnitude B = 1.0T. The work done in pulling the loop out of the field uniformly in 1 s is
. The magnetic field on left side of line PQ has a magnitude B = 1.0T. The work done in pulling the loop out of the field uniformly in 1 s is

physics-General
physics-
A constant force F is being applied on a rod of length 'l' kept at rest on two parallel conducting rails connected at ends by resistance R in uniform magnetic field B as shown

A constant force F is being applied on a rod of length 'l' kept at rest on two parallel conducting rails connected at ends by resistance R in uniform magnetic field B as shown

physics-General
physics-
Switch S is closed for a long time at t = 0. It is opened, then:

Switch S is closed for a long time at t = 0. It is opened, then:

physics-General
physics-
In the figure shown, the magnet is pushed towards the fixed ring along the axis of the ring and it passes through the ring

In the figure shown, the magnet is pushed towards the fixed ring along the axis of the ring and it passes through the ring

physics-General
physics-
In the figure shown the section EDFG is fixed. A rod having resistance 'R' is moved with constant velocity in a uniform magnetic field B as shown in the figure. DE & FG are smooth and resistance less. Initially capacitor is uncharged. The charge on the capacitor:

In the figure shown the section EDFG is fixed. A rod having resistance 'R' is moved with constant velocity in a uniform magnetic field B as shown in the figure. DE & FG are smooth and resistance less. Initially capacitor is uncharged. The charge on the capacitor:

physics-General
physics-
Figure shows three regions of magnetic field, each of area A, and in each region magnitude of magnetic field decreases at a constant rate  . If
. If  is induced electric field then value of line integral
is induced electric field then value of line integral  along the given loop is equal to
along the given loop is equal to

Figure shows three regions of magnetic field, each of area A, and in each region magnitude of magnetic field decreases at a constant rate  . If
. If  is induced electric field then value of line integral
is induced electric field then value of line integral  along the given loop is equal to
along the given loop is equal to

physics-General





