Physics-
General
Easy
Question
A small disc A slides down with initial velocity equal to zero from the top of a smooth hill of height H having a horizontal portion as shown in figure. What must be the height of horizontal portion 'h' to ensure the maximum horizontal distance 's' covered by the disc? What is it equal to?

- H,2H
- H/2
- H,4H
- H/4, H
The correct answer is: H/2
Related Questions to study
physics-
A smooth narrow tube in form of an arc AB of a circle of centre ' O ' and radius ' R ' is fixed so that A is vertically above ' O ' and OB is horizontal. Particles P of mass ' m ' and Q of mass ' 2 m ' with a light inextensible string of length  connecting them are placed in side the tube with P at A and Q at B and released from rest. Assuming the string remains taut during motion, find the speed of particles when P reaches B ?
connecting them are placed in side the tube with P at A and Q at B and released from rest. Assuming the string remains taut during motion, find the speed of particles when P reaches B ?

A smooth narrow tube in form of an arc AB of a circle of centre ' O ' and radius ' R ' is fixed so that A is vertically above ' O ' and OB is horizontal. Particles P of mass ' m ' and Q of mass ' 2 m ' with a light inextensible string of length  connecting them are placed in side the tube with P at A and Q at B and released from rest. Assuming the string remains taut during motion, find the speed of particles when P reaches B ?
connecting them are placed in side the tube with P at A and Q at B and released from rest. Assuming the string remains taut during motion, find the speed of particles when P reaches B ?

physics-General
physics-
A small block of mass 'M' slides down from top edge 'A' of a smooth curved surface as shown in the figure. The surface becomes horizontal at edge 'B'. The maximum possible horizontal range for the body is

A small block of mass 'M' slides down from top edge 'A' of a smooth curved surface as shown in the figure. The surface becomes horizontal at edge 'B'. The maximum possible horizontal range for the body is

physics-General
physics-
A block of mass 2 kg slides along a frictionless table with a speed of 10 m/sec. Directly in front of it and moving in the same direction is a block of mass 5 kg moving at 3 m/sec. A massless spring of spring constant k=1120 N/m is attached to the back side of 5 kg mass as shown in figure. When the blocks collides, the maximum compression in the spring (if the spring does not ben(D) will be :

A block of mass 2 kg slides along a frictionless table with a speed of 10 m/sec. Directly in front of it and moving in the same direction is a block of mass 5 kg moving at 3 m/sec. A massless spring of spring constant k=1120 N/m is attached to the back side of 5 kg mass as shown in figure. When the blocks collides, the maximum compression in the spring (if the spring does not ben(D) will be :

physics-General
physics-
A particle is projected up from a point at an angle  with the horizontal direction. At any time 't', if
with the horizontal direction. At any time 't', if  is the linear momentum, y is the vertical displacement, ' x ' is horizontal displacement, the graph among the following which does not represent the variation of kinetic energy 'k' of the particle is
is the linear momentum, y is the vertical displacement, ' x ' is horizontal displacement, the graph among the following which does not represent the variation of kinetic energy 'k' of the particle is
A) 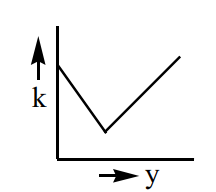
B) 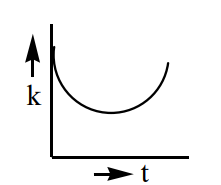
C) 
D) 
A particle is projected up from a point at an angle  with the horizontal direction. At any time 't', if
with the horizontal direction. At any time 't', if  is the linear momentum, y is the vertical displacement, ' x ' is horizontal displacement, the graph among the following which does not represent the variation of kinetic energy 'k' of the particle is
is the linear momentum, y is the vertical displacement, ' x ' is horizontal displacement, the graph among the following which does not represent the variation of kinetic energy 'k' of the particle is
A) 
B) 
C) 
D) 
physics-General
physics-
In the diagram shown in figure, both pulleys and strings are massless. The acceleration of 2 kg block is

In the diagram shown in figure, both pulleys and strings are massless. The acceleration of 2 kg block is

physics-General
physics-
Two particles of masses  and
and  connected by a light inextensible string, are released from rest as shown in the figure. If the contacting surfaces are smooth, at the given position
connected by a light inextensible string, are released from rest as shown in the figure. If the contacting surfaces are smooth, at the given position

Two particles of masses  and
and  connected by a light inextensible string, are released from rest as shown in the figure. If the contacting surfaces are smooth, at the given position
connected by a light inextensible string, are released from rest as shown in the figure. If the contacting surfaces are smooth, at the given position

physics-General
physics-
In the system shown in the adjoining figure, the acceleration of the 1 kg mass is:

In the system shown in the adjoining figure, the acceleration of the 1 kg mass is:

physics-General
physics-
Assuming all the surface to be frictionless, acceleration of the block C shown in the figure is :

Assuming all the surface to be frictionless, acceleration of the block C shown in the figure is :

physics-General
physics-
Two forces  and
and  act on the particles
act on the particles  and
and  respectively. If the ideal pulley-particle system remains in smooth horizontal plane, the tension in the string is :
respectively. If the ideal pulley-particle system remains in smooth horizontal plane, the tension in the string is :

Two forces  and
and  act on the particles
act on the particles  and
and  respectively. If the ideal pulley-particle system remains in smooth horizontal plane, the tension in the string is :
respectively. If the ideal pulley-particle system remains in smooth horizontal plane, the tension in the string is :

physics-General
physics-
Object A and B each of mass  are connected by light inextensible cord. They are constrained to move on a frictionless ring in a vertical plane as shown in figure. The objects are released from rest at the positions shown. The tension in the cord just after release will be
are connected by light inextensible cord. They are constrained to move on a frictionless ring in a vertical plane as shown in figure. The objects are released from rest at the positions shown. The tension in the cord just after release will be

Object A and B each of mass  are connected by light inextensible cord. They are constrained to move on a frictionless ring in a vertical plane as shown in figure. The objects are released from rest at the positions shown. The tension in the cord just after release will be
are connected by light inextensible cord. They are constrained to move on a frictionless ring in a vertical plane as shown in figure. The objects are released from rest at the positions shown. The tension in the cord just after release will be

physics-General
physics-
A force F is applied to the initially stationary cart. The variation of force with time is shown in the figure. The speed of cart at t=5sec is

A force F is applied to the initially stationary cart. The variation of force with time is shown in the figure. The speed of cart at t=5sec is

physics-General
physics-
At t=0, force F=ct is applied to a small body of mass m resting on a smooth horizontal plane (c is a constant). The force is at an angle  with the horizontal .The velocity of the body at the moment of its breaking off the plane and the distance travelled by the body up to this moment are
with the horizontal .The velocity of the body at the moment of its breaking off the plane and the distance travelled by the body up to this moment are

At t=0, force F=ct is applied to a small body of mass m resting on a smooth horizontal plane (c is a constant). The force is at an angle  with the horizontal .The velocity of the body at the moment of its breaking off the plane and the distance travelled by the body up to this moment are
with the horizontal .The velocity of the body at the moment of its breaking off the plane and the distance travelled by the body up to this moment are

physics-General
physics-
A body of mass 8 kg hanging from another body of mass 12 kg is being pulled by a string with an acceleration of  vertically upward. The tension
vertically upward. The tension  in the string pulling 12 kg upward will be
in the string pulling 12 kg upward will be

A body of mass 8 kg hanging from another body of mass 12 kg is being pulled by a string with an acceleration of  vertically upward. The tension
vertically upward. The tension  in the string pulling 12 kg upward will be
in the string pulling 12 kg upward will be

physics-General
physics-
A painter of mass M stands on a platform of mass m and pulls himself up by two ropes which hang over pully as shown Fig. He pulls each rope with force F and moves upward with a uniform acceleration a. Find a neglecting the fact that no one could do this for long time.

A painter of mass M stands on a platform of mass m and pulls himself up by two ropes which hang over pully as shown Fig. He pulls each rope with force F and moves upward with a uniform acceleration a. Find a neglecting the fact that no one could do this for long time.

physics-General
physics-
In the given figure the wedge is fixed, pulley is frictionless and string is light. Surface AB is frictionless whereas AC is rough. if the block of mass 3 m slides down with constant velocity, then the coefficient of friction between surface AC and the block is :

In the given figure the wedge is fixed, pulley is frictionless and string is light. Surface AB is frictionless whereas AC is rough. if the block of mass 3 m slides down with constant velocity, then the coefficient of friction between surface AC and the block is :

physics-General



