Physics
General
Easy
Question
The ratio of pathlength and the respective time interval is
- Mean velocity
- Mean speed
- instantaneous velocity
- instantaneous speed
The correct answer is: Mean speed
Related Questions to study
physics
A particle is thrown in upward direction with initial velocity of 60 m/s. Find average speed and average velocity after 10 seconds. [g =10 MS2]
A particle is thrown in upward direction with initial velocity of 60 m/s. Find average speed and average velocity after 10 seconds. [g =10 MS2]
physicsGeneral
physics-
The work done in deforming body is given by
The work done in deforming body is given by
physics-General
physics-
A wire of length  and radius
and radius  is stretched between
is stretched between  and
and  without the application of any tension. If
without the application of any tension. If  is the Young’s modulus of the wire and it is stretched like
is the Young’s modulus of the wire and it is stretched like  , then the tension in the wire will be
, then the tension in the wire will be

A wire of length  and radius
and radius  is stretched between
is stretched between  and
and  without the application of any tension. If
without the application of any tension. If  is the Young’s modulus of the wire and it is stretched like
is the Young’s modulus of the wire and it is stretched like  , then the tension in the wire will be
, then the tension in the wire will be

physics-General
physics-
A cube of aluminium of sides 0.1 m is subjected to a sharing force of 100 N. The top face of the cube is displaced through 0.02 cm with respect to the bottom face. The shearing strain would be
A cube of aluminium of sides 0.1 m is subjected to a sharing force of 100 N. The top face of the cube is displaced through 0.02 cm with respect to the bottom face. The shearing strain would be
physics-General
physics-
A uniform slender rod of length L, cross-sectional area A and Young’s modulus Y is acted upon by the forces shown in the figure. The elongation of the rod is

A uniform slender rod of length L, cross-sectional area A and Young’s modulus Y is acted upon by the forces shown in the figure. The elongation of the rod is

physics-General
physics-
The graph shows the behaviour of a length of wire in the region for which the substance obeys Hooke’s law.  and
and  represent
represent
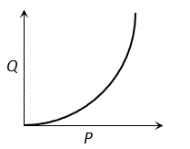
The graph shows the behaviour of a length of wire in the region for which the substance obeys Hooke’s law.  and
and  represent
represent

physics-General
physics-
If the shear modulus of a wire material is 5.9 then the potential energy of a wire of
then the potential energy of a wire of  in diameter and 5 cm long twisted through an angle of 10’ , is
in diameter and 5 cm long twisted through an angle of 10’ , is
If the shear modulus of a wire material is 5.9 then the potential energy of a wire of
then the potential energy of a wire of  in diameter and 5 cm long twisted through an angle of 10’ , is
in diameter and 5 cm long twisted through an angle of 10’ , is
physics-General
physics-
The Young’s modulus of the material of a wire is equal to the
The Young’s modulus of the material of a wire is equal to the
physics-General
Maths-
Maths-General
physics-
Two short bar magnets of equal dipole moment M are fastened perpendicularly at their centers, figure. The magnitude of resultant of two magnetic field at a distance  from the center on the bisector of the right angle is
from the center on the bisector of the right angle is

Two short bar magnets of equal dipole moment M are fastened perpendicularly at their centers, figure. The magnitude of resultant of two magnetic field at a distance  from the center on the bisector of the right angle is
from the center on the bisector of the right angle is

physics-General
physics-
Two magnets of equal mass are joined at 90 each other as shown in figure. Magnet
each other as shown in figure. Magnet  has a magnetic moment
has a magnetic moment  times that of
times that of  . The arrangement is pivoted so that it is free to rotate in horizontal plane. When in equilibrium, what angle should
. The arrangement is pivoted so that it is free to rotate in horizontal plane. When in equilibrium, what angle should  make with magnetic meridian?
make with magnetic meridian?

Two magnets of equal mass are joined at 90 each other as shown in figure. Magnet
each other as shown in figure. Magnet  has a magnetic moment
has a magnetic moment  times that of
times that of  . The arrangement is pivoted so that it is free to rotate in horizontal plane. When in equilibrium, what angle should
. The arrangement is pivoted so that it is free to rotate in horizontal plane. When in equilibrium, what angle should  make with magnetic meridian?
make with magnetic meridian?

physics-General
physics-
The pressure applied from all directions on a cube is  . How much its temperature should be raised to maintain the original volume? The volume elasticity of the cube is
. How much its temperature should be raised to maintain the original volume? The volume elasticity of the cube is  and the coefficient of volume expansion is
and the coefficient of volume expansion is 
The pressure applied from all directions on a cube is  . How much its temperature should be raised to maintain the original volume? The volume elasticity of the cube is
. How much its temperature should be raised to maintain the original volume? The volume elasticity of the cube is  and the coefficient of volume expansion is
and the coefficient of volume expansion is 
physics-General
physics-
A wire  has length 1 m and cross-sectional area 1
has length 1 m and cross-sectional area 1  The work required to increase the length by 2 mm is
The work required to increase the length by 2 mm is
A wire  has length 1 m and cross-sectional area 1
has length 1 m and cross-sectional area 1  The work required to increase the length by 2 mm is
The work required to increase the length by 2 mm is
physics-General
physics-
The diagram shows a force-extension graph for a rubber band. Consider the following statements
I. It will be easier to compress this rubber than expand it
II. Rubber does not return to its original length after it is stretched
III. The rubber band will get heated if it is stretched and released
Which of these can be deduced from the graph
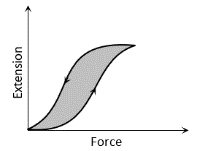
The diagram shows a force-extension graph for a rubber band. Consider the following statements
I. It will be easier to compress this rubber than expand it
II. Rubber does not return to its original length after it is stretched
III. The rubber band will get heated if it is stretched and released
Which of these can be deduced from the graph

physics-General
physics-
A wire of length Land radius  rigidly fixed at one end. On stretching the other end of the wire with a force F, the increase in its length is
rigidly fixed at one end. On stretching the other end of the wire with a force F, the increase in its length is  If another wire of same material but of length 2L and radius
If another wire of same material but of length 2L and radius  is stretched with a force 2F, the increase in its length will be
is stretched with a force 2F, the increase in its length will be
A wire of length Land radius  rigidly fixed at one end. On stretching the other end of the wire with a force F, the increase in its length is
rigidly fixed at one end. On stretching the other end of the wire with a force F, the increase in its length is  If another wire of same material but of length 2L and radius
If another wire of same material but of length 2L and radius  is stretched with a force 2F, the increase in its length will be
is stretched with a force 2F, the increase in its length will be
physics-General



