Chemistry-
General
Easy
Question
.The gas molecules randomly move in all directions and collide with each other and with the wall of the container. It is difficult to determine the speed of an individual molecule but it has become possible to work out the distribution of molecules among different molecular speeds. This is known as Maxwell Boltzmann distribution. Consider the following graph about Maxwell's distribution of speeds at two different temperatures  and
and  :
:

In the above graph the point 'P' refers to:
- root mean square speed at

- average speed at

- most probable speed at

- highest possible speed at

The correct answer is: root mean square speed at 
Related Questions to study
Chemistry-

A gas jar of 10 liter volume filled with  at 300 K is connected to glycerine manometer. The manometer shows 5 m difference in the level as shown in figure. What will be the . number of moles of
at 300 K is connected to glycerine manometer. The manometer shows 5 m difference in the level as shown in figure. What will be the . number of moles of  in the gas jar ? (Give dglycerine = 2.72 g/mL; d mercury 13.6 g/mL}
in the gas jar ? (Give dglycerine = 2.72 g/mL; d mercury 13.6 g/mL}

A gas jar of 10 liter volume filled with  at 300 K is connected to glycerine manometer. The manometer shows 5 m difference in the level as shown in figure. What will be the . number of moles of
at 300 K is connected to glycerine manometer. The manometer shows 5 m difference in the level as shown in figure. What will be the . number of moles of  in the gas jar ? (Give dglycerine = 2.72 g/mL; d mercury 13.6 g/mL}
in the gas jar ? (Give dglycerine = 2.72 g/mL; d mercury 13.6 g/mL}
Chemistry-General
Chemistry-
Two balloons A and B are taken at 300K. Maximum capacity of balloon A and balloon Bare 800 mL and 1800 mL respectively. When the balloon system is heated; which one will burst first?

Two balloons A and B are taken at 300K. Maximum capacity of balloon A and balloon Bare 800 mL and 1800 mL respectively. When the balloon system is heated; which one will burst first?

Chemistry-General
Chemistry-
Two gas bulbs are connected by a thin tube. Calculate the partial pressure of helium after the connective valve is opened at a constant temperature of  :
:

Two gas bulbs are connected by a thin tube. Calculate the partial pressure of helium after the connective valve is opened at a constant temperature of  :
:

Chemistry-General
Physics-
Two rods P and Q of different metals having the same area A and the same length L are placed between two rigid walls as shown in fig. The coefficients of linear expansion of P and Q are  and
and  respectively and their Young's moduli are
respectively and their Young's moduli are  and
and  . The temperature of both rods is now raised by T degrees.
. The temperature of both rods is now raised by T degrees.

The force exerted by one rod on the other is
Two rods P and Q of different metals having the same area A and the same length L are placed between two rigid walls as shown in fig. The coefficients of linear expansion of P and Q are  and
and  respectively and their Young's moduli are
respectively and their Young's moduli are  and
and  . The temperature of both rods is now raised by T degrees.
. The temperature of both rods is now raised by T degrees.

The force exerted by one rod on the other is
Physics-General
Physics-
Two wires A and B of same length are made of same material. The figure represents the load F versus extension  graph for the two wires. Then
graph for the two wires. Then

Two wires A and B of same length are made of same material. The figure represents the load F versus extension  graph for the two wires. Then
graph for the two wires. Then

Physics-General
Physics-
A wire suspended vertically from one of the ends is stretched by attaching a weight of 200 N to the lower end. If the weight stretches the wire by 1 mm. The elastic energy stored in the wire is :
A wire suspended vertically from one of the ends is stretched by attaching a weight of 200 N to the lower end. If the weight stretches the wire by 1 mm. The elastic energy stored in the wire is :
Physics-General
Physics-
The young’s modulus of the material of a rod is  pascal. When the longitudinal strain is 0.04%, The energy stored per unit volume is
pascal. When the longitudinal strain is 0.04%, The energy stored per unit volume is
The young’s modulus of the material of a rod is  pascal. When the longitudinal strain is 0.04%, The energy stored per unit volume is
pascal. When the longitudinal strain is 0.04%, The energy stored per unit volume is
Physics-General
Physics-
One mole of a monoatomic ideal gas occupies two chambers of a cylinder partitioned by means of a movable piston. The walls of the cylinder as well as the piston are thermal insulators. Initially equal amounts of gas fill both the chambers at  . A coil is burnt in the left chamber which absorbs heat and expands, pushing the piston to the right. The gas on the right chamber is compressed until to pressure becomes
. A coil is burnt in the left chamber which absorbs heat and expands, pushing the piston to the right. The gas on the right chamber is compressed until to pressure becomes  . The final volume of left chamber is
. The final volume of left chamber is

One mole of a monoatomic ideal gas occupies two chambers of a cylinder partitioned by means of a movable piston. The walls of the cylinder as well as the piston are thermal insulators. Initially equal amounts of gas fill both the chambers at  . A coil is burnt in the left chamber which absorbs heat and expands, pushing the piston to the right. The gas on the right chamber is compressed until to pressure becomes
. A coil is burnt in the left chamber which absorbs heat and expands, pushing the piston to the right. The gas on the right chamber is compressed until to pressure becomes  . The final volume of left chamber is
. The final volume of left chamber is

Physics-General
Physics-
A material has normal density  and bulk modulus K. The increase in the density of the material when it is subjected to an external pressure 'p' from all sides is
and bulk modulus K. The increase in the density of the material when it is subjected to an external pressure 'p' from all sides is
A material has normal density  and bulk modulus K. The increase in the density of the material when it is subjected to an external pressure 'p' from all sides is
and bulk modulus K. The increase in the density of the material when it is subjected to an external pressure 'p' from all sides is
Physics-General
Physics-
A tungsten wire, 0.5 mm in diameter, is just stretched between two fixed points at a temperature of 40°C. Determine the tension in the wire when the temperature falls to 20°C. (coefficient of linear expansion of tungsten  ; Young's modulus of tungsten
; Young's modulus of tungsten  )
)
A tungsten wire, 0.5 mm in diameter, is just stretched between two fixed points at a temperature of 40°C. Determine the tension in the wire when the temperature falls to 20°C. (coefficient of linear expansion of tungsten  ; Young's modulus of tungsten
; Young's modulus of tungsten  )
)
Physics-General
Physics-
When the tension on a wire is 4 N its length is  When the tension on the wire is 5 N its length is
When the tension on the wire is 5 N its length is  . Find its natural length.
. Find its natural length.
When the tension on a wire is 4 N its length is  When the tension on the wire is 5 N its length is
When the tension on the wire is 5 N its length is  . Find its natural length.
. Find its natural length.
Physics-General
Physics-
A conductor having conductivity ' k ' and whose radius varies linearly with length L is as shown is figure
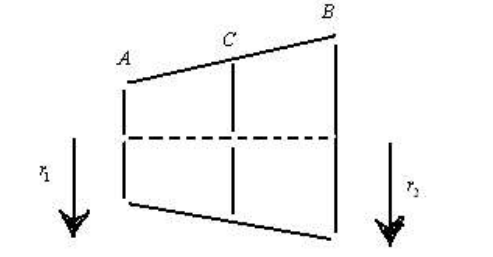 The radius of a conductor having uniform cross sectional area which gives same thermal resistance as the given conductor for same length with same conductivity is
The radius of a conductor having uniform cross sectional area which gives same thermal resistance as the given conductor for same length with same conductivity is
A conductor having conductivity ' k ' and whose radius varies linearly with length L is as shown is figure
 The radius of a conductor having uniform cross sectional area which gives same thermal resistance as the given conductor for same length with same conductivity is
The radius of a conductor having uniform cross sectional area which gives same thermal resistance as the given conductor for same length with same conductivity is
Physics-General
Physics-
A linear rod of length L and uniform cross section area A is having thermal conductivity, which varies along its length as,  where
where  is measured from one of its ends as shown in figure. The two ends of the rod are maintained at temperatures of
is measured from one of its ends as shown in figure. The two ends of the rod are maintained at temperatures of  and
and  , the rate at which heat flows at steady state is
, the rate at which heat flows at steady state is

A linear rod of length L and uniform cross section area A is having thermal conductivity, which varies along its length as,  where
where  is measured from one of its ends as shown in figure. The two ends of the rod are maintained at temperatures of
is measured from one of its ends as shown in figure. The two ends of the rod are maintained at temperatures of  and
and  , the rate at which heat flows at steady state is
, the rate at which heat flows at steady state is

Physics-General
Physics-
Two solid spheres of same material but diameters in the ratio of 5:4 are at temperatures 227°C and 127°C respectively. The temperature of the surrounding is 27°C and Stefan's law holds. Calculate the ratio of rates of loss of heat of the two spheres?
Two solid spheres of same material but diameters in the ratio of 5:4 are at temperatures 227°C and 127°C respectively. The temperature of the surrounding is 27°C and Stefan's law holds. Calculate the ratio of rates of loss of heat of the two spheres?
Physics-General
Physics-
A cylinder of radius R and length l is made up of a substance, whose thermal conductivity K varies with the distance  from the axis as
from the axis as  Deter mine the effective thermal conductivity between the flat faces of the cylinder.
Deter mine the effective thermal conductivity between the flat faces of the cylinder.

A cylinder of radius R and length l is made up of a substance, whose thermal conductivity K varies with the distance  from the axis as
from the axis as  Deter mine the effective thermal conductivity between the flat faces of the cylinder.
Deter mine the effective thermal conductivity between the flat faces of the cylinder.

Physics-General



