Maths-
General
Easy
Question
If  then
then 
- 1
- -1
- 0


When we find sin cos and tan values for a triangle, we usually consider these angles: 0°, 30°, 45°, 60° and 90°. It is easy to memorise the values for these certain angles. The trigonometric values are about the knowledge of standard angles for a given triangle as per the trigonometric ratios (sine, cosine, tangent, cotangent, secant and cosecant).
The correct answer is: 1
If  then
then 

Related Questions to study
chemistry-
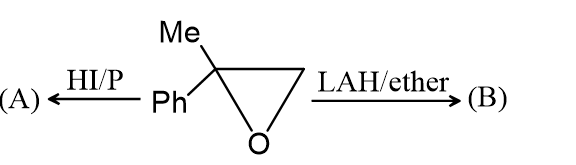 The Products (A) and (B) , respectively, are:
The Products (A) and (B) , respectively, are:
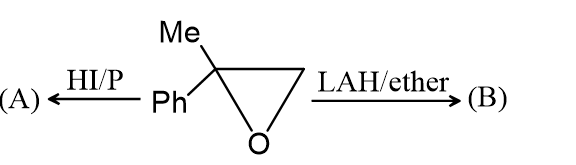 The Products (A) and (B) , respectively, are:
The Products (A) and (B) , respectively, are:
chemistry-General
maths-
The cartesian equation of the plane passing through the line of intersection of the planes  and
and  and perpendicular to the plane
and perpendicular to the plane  is
is
The cartesian equation of the plane passing through the line of intersection of the planes  and
and  and perpendicular to the plane
and perpendicular to the plane  is
is
maths-General
chemistry-
Identify(A) and (B) in the reaction:

Identify(A) and (B) in the reaction:

chemistry-General
maths-
If  then at
then at  is
is
If  then at
then at  is
is
maths-General
chemistry-
In the reaction 
In the reaction 
chemistry-General
chemistry-
 The product (A) formed can:
The product (A) formed can:
 The product (A) formed can:
The product (A) formed can:
chemistry-General
chemistry-
Which of the following is the strongest oxidising agent?
Which of the following is the strongest oxidising agent?
chemistry-General
Maths-
Two circles with radii  , touch each other externally. If
, touch each other externally. If  be the angle between the direct common tangents, then
be the angle between the direct common tangents, then
Two circles with radii  , touch each other externally. If
, touch each other externally. If  be the angle between the direct common tangents, then
be the angle between the direct common tangents, then
Maths-General
Maths-
In triangle ABC, medians AD and BE are drawn. If AD=4, and
, then the area of the △ABC is
In triangle ABC, medians AD and BE are drawn. If AD=4, and
, then the area of the △ABC is
Maths-General
physics-
Two coherent sources S1 and S2 are separated by a distance four times the wavelength  of the source. The sources lie along y axis whereas a detector moves along + x-axis. Leaving the origin and far off points the number of points where maxima are observed is
of the source. The sources lie along y axis whereas a detector moves along + x-axis. Leaving the origin and far off points the number of points where maxima are observed is
Two coherent sources S1 and S2 are separated by a distance four times the wavelength  of the source. The sources lie along y axis whereas a detector moves along + x-axis. Leaving the origin and far off points the number of points where maxima are observed is
of the source. The sources lie along y axis whereas a detector moves along + x-axis. Leaving the origin and far off points the number of points where maxima are observed is
physics-General
physics-
Two coherent sources separated by distance d are radiating in phase having wavelength  . A detector moves in a big circle around the two sources in the plane of the two sources. The angular position of n = 4 interference maxima is given as
. A detector moves in a big circle around the two sources in the plane of the two sources. The angular position of n = 4 interference maxima is given as

Two coherent sources separated by distance d are radiating in phase having wavelength  . A detector moves in a big circle around the two sources in the plane of the two sources. The angular position of n = 4 interference maxima is given as
. A detector moves in a big circle around the two sources in the plane of the two sources. The angular position of n = 4 interference maxima is given as

physics-General
physics-
A beam with wavelength l falls on a stack of partially reflecting planes with separation d. The angle  that the beam should make with the planes so that the beams reflected from successive planes may interfere constructively is (where n =1, 2, ……)
that the beam should make with the planes so that the beams reflected from successive planes may interfere constructively is (where n =1, 2, ……)

A beam with wavelength l falls on a stack of partially reflecting planes with separation d. The angle  that the beam should make with the planes so that the beams reflected from successive planes may interfere constructively is (where n =1, 2, ……)
that the beam should make with the planes so that the beams reflected from successive planes may interfere constructively is (where n =1, 2, ……)

physics-General
physics-
Two ideal slits  and
and  are at a distance d apart and illuminated by light of wavelength
are at a distance d apart and illuminated by light of wavelength  passing through an ideal source slit S placed on the line through
passing through an ideal source slit S placed on the line through  as shown. The distance between the planes of slits and the source slit is D. A screen is held at a distance D from the plane of the slits. The minimum value of d for which there is darkness at O is
as shown. The distance between the planes of slits and the source slit is D. A screen is held at a distance D from the plane of the slits. The minimum value of d for which there is darkness at O is

Two ideal slits  and
and  are at a distance d apart and illuminated by light of wavelength
are at a distance d apart and illuminated by light of wavelength  passing through an ideal source slit S placed on the line through
passing through an ideal source slit S placed on the line through  as shown. The distance between the planes of slits and the source slit is D. A screen is held at a distance D from the plane of the slits. The minimum value of d for which there is darkness at O is
as shown. The distance between the planes of slits and the source slit is D. A screen is held at a distance D from the plane of the slits. The minimum value of d for which there is darkness at O is

physics-General
physics-
A monochromatic beam of light falls on YDSE apparatus at some angle (say  ) as shown in figure. A thin sheet of glass is inserted in front of the lower slit
) as shown in figure. A thin sheet of glass is inserted in front of the lower slit  . The central bright fringe (path difference = 0) will be obtained
. The central bright fringe (path difference = 0) will be obtained

A monochromatic beam of light falls on YDSE apparatus at some angle (say  ) as shown in figure. A thin sheet of glass is inserted in front of the lower slit
) as shown in figure. A thin sheet of glass is inserted in front of the lower slit  . The central bright fringe (path difference = 0) will be obtained
. The central bright fringe (path difference = 0) will be obtained

physics-General
maths-
Find the sum of the infinite series 
Find the sum of the infinite series 
maths-General



