Physics-
General
Easy
Question
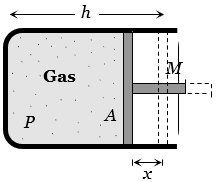
A cylindrical piston of mass M slides smoothly inside a long cylinder closed at one end, enclosing a certain mass of gas. The cylinder is kept with its axis horizontal. If the piston is disturbed from its equilibrium position, it oscillates simple harmonically. The period of oscillation will be

The correct answer is: 
Let the piston be displaced through distance x towards left, then volume decreases, pressure increases. If  is increase in pressure and
is increase in pressure and  is decrease in volume, then considering the process to take place gradually (i.e. isothermal)
is decrease in volume, then considering the process to take place gradually (i.e. isothermal)



 (neglecting
(neglecting 

This excess pressure is responsible for providing the restoring force (F) to the piston of mass M.
Hence 
Comparing it with 

Short trick : by checking the options dimensionally. Option (a) is correct.
Related Questions to study
Physics-
Two blocks A and B each of mass m are connected by a massless spring of natural length L and spring constant K. The blocks are initially resting on a smooth horizontal floor with the spring at its natural length as shown in figure. A third identical block C also of mass m moves on the floor with a speed v along the line joining A and B and collides with A. Then

Two blocks A and B each of mass m are connected by a massless spring of natural length L and spring constant K. The blocks are initially resting on a smooth horizontal floor with the spring at its natural length as shown in figure. A third identical block C also of mass m moves on the floor with a speed v along the line joining A and B and collides with A. Then

Physics-General
Physics-
Two masses m1 and m2 are suspended together by a massless spring of constant K. When the masses are in equilibrium, m1 is removed without disturbing the system. The amplitude of oscillations is

Two masses m1 and m2 are suspended together by a massless spring of constant K. When the masses are in equilibrium, m1 is removed without disturbing the system. The amplitude of oscillations is

Physics-General
Physics-
The springs shown are identical. When  , the elongation of spring is 1 cm. If
, the elongation of spring is 1 cm. If  , the elongation produced by it is
, the elongation produced by it is

The springs shown are identical. When  , the elongation of spring is 1 cm. If
, the elongation of spring is 1 cm. If  , the elongation produced by it is
, the elongation produced by it is

Physics-General
Physics-
Two springs of force constants K and 2K are connected to a mass as shown below. The frequency of oscillation of the mass is 
Two springs of force constants K and 2K are connected to a mass as shown below. The frequency of oscillation of the mass is 
Physics-General
Physics-
A mass m is suspended separately by two different springs of spring constant K1 and K2 gives the time-period  and
and  respectively. If same mass m is connected by both springs as shown in figure then time-period t is given by the relation
respectively. If same mass m is connected by both springs as shown in figure then time-period t is given by the relation

A mass m is suspended separately by two different springs of spring constant K1 and K2 gives the time-period  and
and  respectively. If same mass m is connected by both springs as shown in figure then time-period t is given by the relation
respectively. If same mass m is connected by both springs as shown in figure then time-period t is given by the relation

Physics-General
Physics-
The frequency of oscillation of the springs shown in the figure will be

The frequency of oscillation of the springs shown in the figure will be

Physics-General
Physics-
A mass M is suspended by two springs of force constants K1 and K2 respectively as shown in the diagram. The total elongation (stretch) of the two springs is

A mass M is suspended by two springs of force constants K1 and K2 respectively as shown in the diagram. The total elongation (stretch) of the two springs is

Physics-General
Physics-
The effective spring constant of two spring system as shown in figure will be

The effective spring constant of two spring system as shown in figure will be

Physics-General
Physics-
What will be the force constant of the spring system shown in the figure

What will be the force constant of the spring system shown in the figure

Physics-General
Physics-
Five identical springs are used in the following three configurations. The time periods of vertical oscillations in configurations (i), (ii) and (iii) are in the ratio

Five identical springs are used in the following three configurations. The time periods of vertical oscillations in configurations (i), (ii) and (iii) are in the ratio

Physics-General
Physics-
In the figure,  and
and  are identical springs. The oscillation frequency of the mass m is
are identical springs. The oscillation frequency of the mass m is  . If one spring is removed, the frequency will become
. If one spring is removed, the frequency will become

In the figure,  and
and  are identical springs. The oscillation frequency of the mass m is
are identical springs. The oscillation frequency of the mass m is  . If one spring is removed, the frequency will become
. If one spring is removed, the frequency will become

Physics-General
Physics-
Two identical spring of constant K are connected in series and parallel as shown in figure. A mass m is suspended from them. The ratio of their frequencies of vertical oscillations will be

Two identical spring of constant K are connected in series and parallel as shown in figure. A mass m is suspended from them. The ratio of their frequencies of vertical oscillations will be

Physics-General
Physics-
In arrangement given in figure, if the block of mass m is displaced, the frequency is given by

In arrangement given in figure, if the block of mass m is displaced, the frequency is given by

Physics-General
Physics-
A mass m is suspended by means of two coiled spring which have the same length in unstretched condition as in figure. Their force constant are k1 and k2 respectively. When set into vertical vibrations, the period will be

A mass m is suspended by means of two coiled spring which have the same length in unstretched condition as in figure. Their force constant are k1 and k2 respectively. When set into vertical vibrations, the period will be

Physics-General
Physics-
What is the velocity of the bob of a simple pendulum at its mean position, if it is able to rise to vertical height of 10cm (g = 9.8 m/s2)

What is the velocity of the bob of a simple pendulum at its mean position, if it is able to rise to vertical height of 10cm (g = 9.8 m/s2)

Physics-General





