Physics-
General
Easy
Question
What will be the force constant of the spring system shown in the figure

The correct answer is: 
In series combination

Þ 

Related Questions to study
Physics-
Five identical springs are used in the following three configurations. The time periods of vertical oscillations in configurations (i), (ii) and (iii) are in the ratio

Five identical springs are used in the following three configurations. The time periods of vertical oscillations in configurations (i), (ii) and (iii) are in the ratio

Physics-General
Physics-
In the figure,  and
and  are identical springs. The oscillation frequency of the mass m is
are identical springs. The oscillation frequency of the mass m is  . If one spring is removed, the frequency will become
. If one spring is removed, the frequency will become

In the figure,  and
and  are identical springs. The oscillation frequency of the mass m is
are identical springs. The oscillation frequency of the mass m is  . If one spring is removed, the frequency will become
. If one spring is removed, the frequency will become

Physics-General
Physics-
Two identical spring of constant K are connected in series and parallel as shown in figure. A mass m is suspended from them. The ratio of their frequencies of vertical oscillations will be

Two identical spring of constant K are connected in series and parallel as shown in figure. A mass m is suspended from them. The ratio of their frequencies of vertical oscillations will be

Physics-General
Physics-
In arrangement given in figure, if the block of mass m is displaced, the frequency is given by

In arrangement given in figure, if the block of mass m is displaced, the frequency is given by

Physics-General
Physics-
A mass m is suspended by means of two coiled spring which have the same length in unstretched condition as in figure. Their force constant are k1 and k2 respectively. When set into vertical vibrations, the period will be

A mass m is suspended by means of two coiled spring which have the same length in unstretched condition as in figure. Their force constant are k1 and k2 respectively. When set into vertical vibrations, the period will be

Physics-General
Physics-
What is the velocity of the bob of a simple pendulum at its mean position, if it is able to rise to vertical height of 10cm (g = 9.8 m/s2)

What is the velocity of the bob of a simple pendulum at its mean position, if it is able to rise to vertical height of 10cm (g = 9.8 m/s2)

Physics-General
Physics-
A pendulum of length 2m lift at P. When it reaches Q, it losses 10% of its total energy due to air resistance. The velocity at Q is

A pendulum of length 2m lift at P. When it reaches Q, it losses 10% of its total energy due to air resistance. The velocity at Q is

Physics-General
Physics-
A simple pendulum with a bob of mass ‘m’ oscillates from A to C and back to A such that PB is H. If the acceleration due to gravity is ‘g’, then the velocity of the bob as it passes through B is

A simple pendulum with a bob of mass ‘m’ oscillates from A to C and back to A such that PB is H. If the acceleration due to gravity is ‘g’, then the velocity of the bob as it passes through B is

Physics-General
Physics-
A man measures the period of a simple pendulum inside a stationary lift and finds it to be T sec. If the lift accelerates upwards with an acceleration  , then the period of the pendulum will be
, then the period of the pendulum will be

A man measures the period of a simple pendulum inside a stationary lift and finds it to be T sec. If the lift accelerates upwards with an acceleration  , then the period of the pendulum will be
, then the period of the pendulum will be

Physics-General
Physics-
The period of oscillation of a simple pendulum of constant length at earth surface is T. Its period inside a mine is

The period of oscillation of a simple pendulum of constant length at earth surface is T. Its period inside a mine is

Physics-General
Physics-
Which of the following is the nm = T graph for a perfectly black body (nm =maximum frequency of radiation)

Which of the following is the nm = T graph for a perfectly black body (nm =maximum frequency of radiation)

Physics-General
Physics-
In the figure, the distribution of energy density of the radiation emitted by a black body at a given temperature is shown. The possible temperature of the black body is

In the figure, the distribution of energy density of the radiation emitted by a black body at a given temperature is shown. The possible temperature of the black body is

Physics-General
Physics-
Radius of a conductor increases uniformly from left end to right end as shown in fig.

Material of the conductor is isotropic and its curved surface is thermally isolated from surrounding. Its ends are maintained at temperatures T1 and T2 (T1 > T2): If, in steady state, heat flow rate is equal to H, then which of the following graphs is correct
Radius of a conductor increases uniformly from left end to right end as shown in fig.

Material of the conductor is isotropic and its curved surface is thermally isolated from surrounding. Its ends are maintained at temperatures T1 and T2 (T1 > T2): If, in steady state, heat flow rate is equal to H, then which of the following graphs is correct
Physics-General
Chemistry-
The IUPAC name of 
The IUPAC name of 
Chemistry-General
Chemistry-
The order of stability of the following cabocations 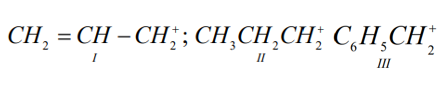 is
is
The order of stability of the following cabocations 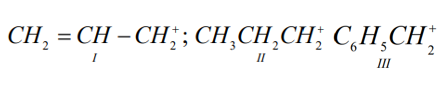 is
is
Chemistry-General



