Physics-
General
Easy
Question
A thin rod of mass M and length L is struck at one end by a ball of clay of mass m, moving with speed v as shown in figure. The ball sticks to the rod. After the collision, the angular momentum of the clay-rod system about A, the midpoint of the rod, is




- mvL
The correct answer is: mvL
Related Questions to study
Physics-
A uniform rod of mass M is hinged at its upper end. A particle of mass m moving horizontally strikes the rod at its mid point elastically. If the particle comes to rest after collision find the value of M/m =?

A uniform rod of mass M is hinged at its upper end. A particle of mass m moving horizontally strikes the rod at its mid point elastically. If the particle comes to rest after collision find the value of M/m =?

Physics-General
Physics-
A uniform rod AB of length L and mass M is lying on a smooth table. A small particle of mass m strike the rod with a velocity v0 at point C a distance x from the centre O. The particle comes to rest after collision. The value of x, so that point A of the rod remains stationary just after collision, is :

A uniform rod AB of length L and mass M is lying on a smooth table. A small particle of mass m strike the rod with a velocity v0 at point C a distance x from the centre O. The particle comes to rest after collision. The value of x, so that point A of the rod remains stationary just after collision, is :

Physics-General
Physics-
A uniform rod AB of length L and mass M is lying on a smooth table. A small particle of mass m strike the rod with a velocity v0 at point C at a distance x from the centre O. The particle comes to rest after collision. The value of x, so that point A of the rod remains ststionary just after collision is:

A uniform rod AB of length L and mass M is lying on a smooth table. A small particle of mass m strike the rod with a velocity v0 at point C at a distance x from the centre O. The particle comes to rest after collision. The value of x, so that point A of the rod remains ststionary just after collision is:

Physics-General
Physics-
A ball of mass m moving with velocity v, collide with the wall elastically as shown in the figure. After impact the change in angular momentum about P is:

A ball of mass m moving with velocity v, collide with the wall elastically as shown in the figure. After impact the change in angular momentum about P is:

Physics-General
Physics-
A thin uniform straight rod of mass 2 kg and length 1 m is free to rotate about its upper end when at rest. It receives an impulsive blow of 10 Ns at its lowest point, normal to its length as shown in figure. The kinetic energy of rod just after impact is

A thin uniform straight rod of mass 2 kg and length 1 m is free to rotate about its upper end when at rest. It receives an impulsive blow of 10 Ns at its lowest point, normal to its length as shown in figure. The kinetic energy of rod just after impact is

Physics-General
Physics-
Two equal masses each of mass M are joined by a massless rod of length L. Now an impulse MV is given to the mass M making an angle of 30° with the length of the rod. The angular veloctiy of the rod just after imparting the impulse is

Two equal masses each of mass M are joined by a massless rod of length L. Now an impulse MV is given to the mass M making an angle of 30° with the length of the rod. The angular veloctiy of the rod just after imparting the impulse is

Physics-General
Physics-
In the figure shown a ring A is initially rolling without sliding with a velocity v on the horizontal surface of the body B (of same mass as A). All surfaces are smooth. B has no initial velocity. What will be the maximum height reached by A on B.

In the figure shown a ring A is initially rolling without sliding with a velocity v on the horizontal surface of the body B (of same mass as A). All surfaces are smooth. B has no initial velocity. What will be the maximum height reached by A on B.

Physics-General
Physics-
One ice skater of mass m moves with speed 2v to the right, while another of the same mass m moves with speed v toward the left, as shown in figure I. Their paths are separated by a distance b. At t = 0, when they are both at x = 0, they grasp a pole of length b and negligible mass. For t > 0, consider the system as a rigid body of two masses m separated by distance b, as shown in figure II. Which of the following is the correct formula for the motion after t = 0 of the skater initially at y = b/2?
 i
i
One ice skater of mass m moves with speed 2v to the right, while another of the same mass m moves with speed v toward the left, as shown in figure I. Their paths are separated by a distance b. At t = 0, when they are both at x = 0, they grasp a pole of length b and negligible mass. For t > 0, consider the system as a rigid body of two masses m separated by distance b, as shown in figure II. Which of the following is the correct formula for the motion after t = 0 of the skater initially at y = b/2?
 i
i
Physics-General
Physics-
In the following problems, indicate the correct direction of friction force acting on the cylinder, which is pulled on a rough surface by a constant force F.
A spool is pulled vertically by a constant force F (< Mg) as shown in figure The friction force can be given by which of the following diagrams

In the following problems, indicate the correct direction of friction force acting on the cylinder, which is pulled on a rough surface by a constant force F.
A spool is pulled vertically by a constant force F (< Mg) as shown in figure The friction force can be given by which of the following diagrams

Physics-General
Physics-
In the following problems, indicate the correct direction of friction force acting on the cylinder, which is pulled on a rough surface by a constant force F.
A spool is pulled horizontally by a constant force F below the centre of mass. The friction force can be given by which of the following diagrams

In the following problems, indicate the correct direction of friction force acting on the cylinder, which is pulled on a rough surface by a constant force F.
A spool is pulled horizontally by a constant force F below the centre of mass. The friction force can be given by which of the following diagrams

Physics-General
Physics-
In the following problems, indicate the correct direction of friction force acting on the cylinder, which is pulled on a rough surface by a constant force F.
A cylinder is placed on a rough plank which in turn is placed on a smooth surface. The plank is pulled with a constant force F. The friction force can be given by which of the following diagrams

In the following problems, indicate the correct direction of friction force acting on the cylinder, which is pulled on a rough surface by a constant force F.
A cylinder is placed on a rough plank which in turn is placed on a smooth surface. The plank is pulled with a constant force F. The friction force can be given by which of the following diagrams

Physics-General
Maths-
 then root of the equation
then root of the equation 
 then root of the equation
then root of the equation 
Maths-General
Maths-
If an angle is divided into two parts A&B such that A-B=x and  then the value of
then the value of  is
is
If an angle is divided into two parts A&B such that A-B=x and  then the value of
then the value of  is
is
Maths-General
Physics-
Two capacitors C1 and C2 are charged to same potential V, but with opposite polarity as shown in the figure. The switch S1 and S2 are then closed
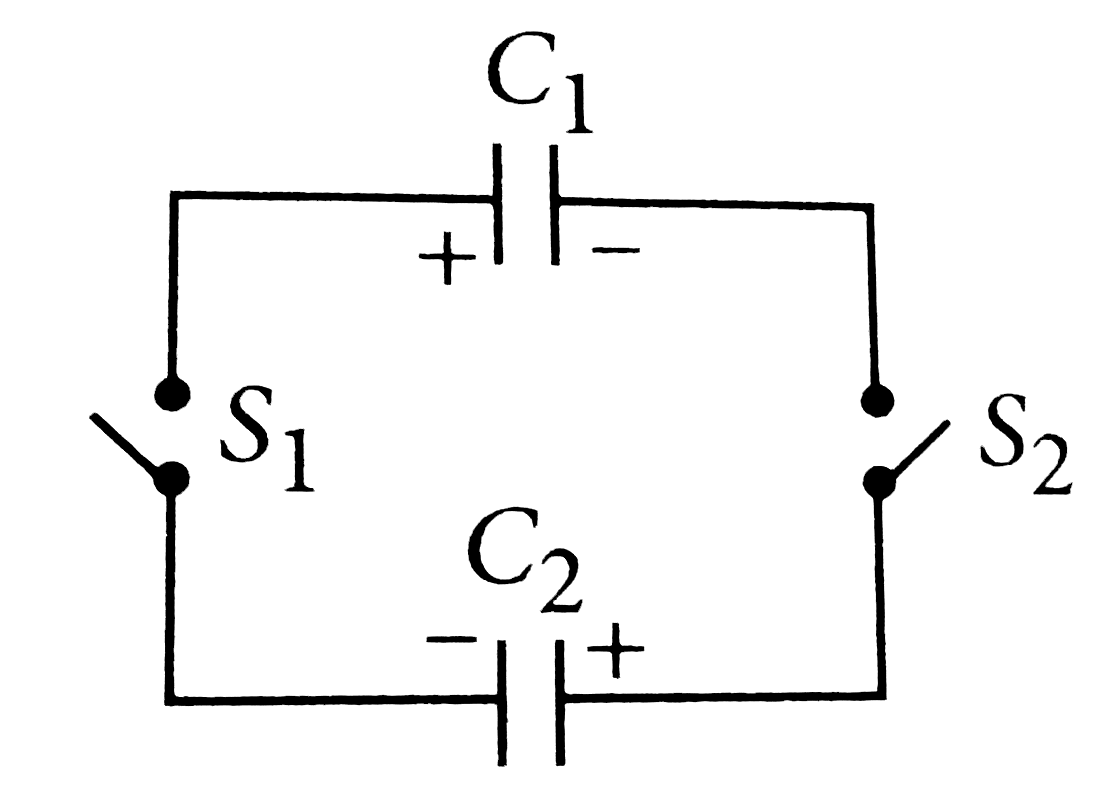
Two capacitors C1 and C2 are charged to same potential V, but with opposite polarity as shown in the figure. The switch S1 and S2 are then closed

Physics-General
Maths-
Maths-General



