Physics-
General
Easy
Question
Find the external work done by the system in kcal, when 20 kcal of heat is supplied to the system the increase in the internal energy is 8400J JJ 4200J/kcal )
- 16kcal
- 18kcal
- 20kcal
- 19kcal
The correct answer is: 18kcal
Related Questions to study
Physics-
The specific heat of a substance is 0.09cal/ gm°C. If the temperature is measured on Fahrenheit scale the value of its specific heat in cal/gm/ is
is
The specific heat of a substance is 0.09cal/ gm°C. If the temperature is measured on Fahrenheit scale the value of its specific heat in cal/gm/ is
is
Physics-General
Physics-
If the rms velocity of oxygen molecule at certain temperature is 0.5 km/s, the rms velocity for hydrogen molecule at the same temperature will be
If the rms velocity of oxygen molecule at certain temperature is 0.5 km/s, the rms velocity for hydrogen molecule at the same temperature will be
Physics-General
Physics-
What is the velocity of monoatomic gas having pressure 1 kilopascal and density 
What is the velocity of monoatomic gas having pressure 1 kilopascal and density 
Physics-General
Physics-
The pressure P for a gas is plotted against its absolute temperature T for two different volumes  and
and  where
where  . If P is plotted on y - axis and T on x-axis, then :
. If P is plotted on y - axis and T on x-axis, then :
The pressure P for a gas is plotted against its absolute temperature T for two different volumes  and
and  where
where  . If P is plotted on y - axis and T on x-axis, then :
. If P is plotted on y - axis and T on x-axis, then :
Physics-General
Physics-
An ideal gas is initially at temperature T and volume V. Its volume is increased by  due to an increase in temperature
due to an increase in temperature  ⋅Pressure remaining constant . The physical quantity
⋅Pressure remaining constant . The physical quantity  varies with temperature as :
varies with temperature as :
An ideal gas is initially at temperature T and volume V. Its volume is increased by  due to an increase in temperature
due to an increase in temperature  ⋅Pressure remaining constant . The physical quantity
⋅Pressure remaining constant . The physical quantity  varies with temperature as :
varies with temperature as :
Physics-General
Physics-
One litre of oxygen at a pressure of 1 atm and two litres of nitrogen at a pressure of 0.5 atm are introduced into a vessel of volume 1litre. If there is no change in temperature, the final pressure of the gas in atm is
One litre of oxygen at a pressure of 1 atm and two litres of nitrogen at a pressure of 0.5 atm are introduced into a vessel of volume 1litre. If there is no change in temperature, the final pressure of the gas in atm is
Physics-General
Physics-
A spool of mass M and radius 2R lies on an inclined plane as shown in fig. A light thread is wound around the connecting tube of the spool and its free end carries a weight of mass m. The value of m so that system is in equilibrium is

A spool of mass M and radius 2R lies on an inclined plane as shown in fig. A light thread is wound around the connecting tube of the spool and its free end carries a weight of mass m. The value of m so that system is in equilibrium is

Physics-General
Physics-
Two different curves at constant temperature. The relationship between volume V and the pressure P at a given temp. of same ideal gas are shown for masses  and
and  of the gas respectively. Then
of the gas respectively. Then

Two different curves at constant temperature. The relationship between volume V and the pressure P at a given temp. of same ideal gas are shown for masses  and
and  of the gas respectively. Then
of the gas respectively. Then

Physics-General
Physics-
For an ideal gas V-T curves as constant pressures  are shown in figure - from the figure
are shown in figure - from the figure

For an ideal gas V-T curves as constant pressures  are shown in figure - from the figure
are shown in figure - from the figure

Physics-General
Physics-
Two gases A and B having the same pressure, P, volume V and temperature T are mixed. If the mixture has volume and temperature as V and T respectively the pressure of the mixture is
Two gases A and B having the same pressure, P, volume V and temperature T are mixed. If the mixture has volume and temperature as V and T respectively the pressure of the mixture is
Physics-General
Physics-
The volume of agas at  is 100CC at normal pressure when it is heated to
is 100CC at normal pressure when it is heated to  , its volume is 125CC at the same pressure the volume coeficient of the gas is
, its volume is 125CC at the same pressure the volume coeficient of the gas is
The volume of agas at  is 100CC at normal pressure when it is heated to
is 100CC at normal pressure when it is heated to  , its volume is 125CC at the same pressure the volume coeficient of the gas is
, its volume is 125CC at the same pressure the volume coeficient of the gas is
Physics-General
chemistry-
Compressibility factor (Z): Real gases deviate from ideal behavior due to the following two faulty assumptions of kinetic theory of gases.
i)Actual volume occupied by the gas molecule is negligible as compared to the total volume of the gases.
ii)Forces of attraction and repulsion among the gas molecules are negligible.
the, extent of deviation of the real gas from ideal behaviour, is explained in terms of compressibility factor (Z), which is function of pressure and temperature for real gas.
For ideal gas, Z = 1
For real gases, Z > 1 or Z < 1
When Z > 1, then it is less compressible because force of repulsion dominates over force of attraction when Z < 1, force of attraction dominates over the force repulsion.
Graph in between Z & P is shown as under
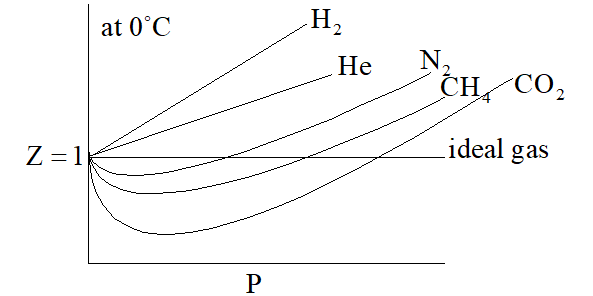
On increasing temperature, Z increases and approaches to unity. Graph between
Z and P at different temperature for the same gas is shown as under:
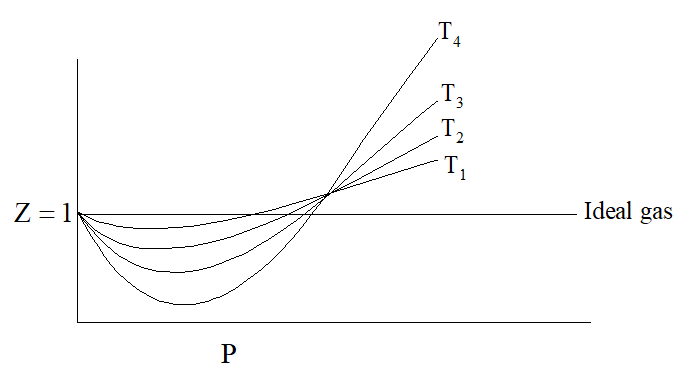
The van der Waal’s equation of state for 1 mole of gas is as under:
 …(1)
…(1)
Where a and b are van der Waal’s constants.
van der Waal’s constant “a” measures the amount of the force of attraction among the gas molecules. Higher the value of “a”, higher will be the ease of liquefaction.
Case (1)For H2 and He then equation into –I will reduce P(V – b) = RTCase (2) When pressure is too low i.e. for N2 or CH4 or, CO2 then equation (–I) reduces into 
Which of the following statement is correct as shown in the above graph?
Compressibility factor (Z): Real gases deviate from ideal behavior due to the following two faulty assumptions of kinetic theory of gases.
i)Actual volume occupied by the gas molecule is negligible as compared to the total volume of the gases.
ii)Forces of attraction and repulsion among the gas molecules are negligible.
the, extent of deviation of the real gas from ideal behaviour, is explained in terms of compressibility factor (Z), which is function of pressure and temperature for real gas.
For ideal gas, Z = 1
For real gases, Z > 1 or Z < 1
When Z > 1, then it is less compressible because force of repulsion dominates over force of attraction when Z < 1, force of attraction dominates over the force repulsion.
Graph in between Z & P is shown as under

On increasing temperature, Z increases and approaches to unity. Graph between
Z and P at different temperature for the same gas is shown as under:

The van der Waal’s equation of state for 1 mole of gas is as under:
 …(1)
…(1)
Where a and b are van der Waal’s constants.
van der Waal’s constant “a” measures the amount of the force of attraction among the gas molecules. Higher the value of “a”, higher will be the ease of liquefaction.
Case (1)For H2 and He then equation into –I will reduce P(V – b) = RTCase (2) When pressure is too low i.e. for N2 or CH4 or, CO2 then equation (–I) reduces into 
Which of the following statement is correct as shown in the above graph?
chemistry-General
chemistry-
I, II, III are three isotherm respectively at T1, T2 & T3 temperatures will be in order

I, II, III are three isotherm respectively at T1, T2 & T3 temperatures will be in order

chemistry-General
maths-
In the figure shown, PT and PAB are the tangent and the secant drawn to a circle. If PT = 12 cm and PB = 8 cm then AB is

In the figure shown, PT and PAB are the tangent and the secant drawn to a circle. If PT = 12 cm and PB = 8 cm then AB is

maths-General
maths-
Find the value of ‘x’ in the given figure

Find the value of ‘x’ in the given figure

maths-General





