Physics-
General
Easy
Question
From the adjacent figure, the correct observation is

- The pressure on the bottom of tank(a) is greater than at the bottom of (b).
- The pressure on the bottom of the tank(a) is smaller than at the bottom of(b)
- The pressure depend on the shape of the container
- The pressure on the bottom of(a) and(b) is the same
The correct answer is: The pressure on the bottom of(a) and(b) is the same
Pressure = hrg i.e. pressure at the bottom is independent of the area of the bottom of the tank. It depends on the height of water upto which the tank is filled with water. As in both the tanks, the levels of water are the same, pressure at the bottom is also the same.
Related Questions to study
Physics-
A vertical U-tube of uniform inner cross section contains mercury in both sides of its arms. A glycerin (density = 1.3 g/cm3) column of length 10 cm is introduced into one of its arms. Oil of density 0.8 gm/cm3 is poured into the other arm until the upper surfaces of the oil and glycerin are in the same horizontal level. Find the length of the oil column, Density of mercury = 13.6 g/cm3

A vertical U-tube of uniform inner cross section contains mercury in both sides of its arms. A glycerin (density = 1.3 g/cm3) column of length 10 cm is introduced into one of its arms. Oil of density 0.8 gm/cm3 is poured into the other arm until the upper surfaces of the oil and glycerin are in the same horizontal level. Find the length of the oil column, Density of mercury = 13.6 g/cm3

Physics-General
Physics-
A closed rectangular tank is completely filled with water and is accelerated horizontally with an acceleration a towards right. Pressure is (i) maximum at, and (ii) minimum at

A closed rectangular tank is completely filled with water and is accelerated horizontally with an acceleration a towards right. Pressure is (i) maximum at, and (ii) minimum at

Physics-General
Physics-
A siphon in use is demonstrated in the following figure. The density of the liquid flowing in siphon is 1.5 gm/cc. The pressure difference between the point P and S will be

A siphon in use is demonstrated in the following figure. The density of the liquid flowing in siphon is 1.5 gm/cc. The pressure difference between the point P and S will be

Physics-General
Chemistry-
Acetylene on treatment with dilute. having
having  gives:
gives:
Acetylene on treatment with dilute. having
having  gives:
gives:
Chemistry-General
Chemistry-
In the given reaction,
 X will be:
X will be:
In the given reaction,
 X will be:
X will be:
Chemistry-General
Chemistry-
 (isomeric products),
(isomeric products),  (isomeric products) Give the number of N and M:
(isomeric products) Give the number of N and M:
 (isomeric products),
(isomeric products),  (isomeric products) Give the number of N and M:
(isomeric products) Give the number of N and M:
Chemistry-General
Chemistry-
Free radical halogenation takes place in tile presence of light or at high temperature (above 500 C). Formation of halogen free radical intermediate takes place in first step called chain initiation •.
C). Formation of halogen free radical intermediate takes place in first step called chain initiation •.
 This reaction is mainly given by those compounds which have at least one hydrogen atom present at sp3 -hybrid carbon. Reactivity of
This reaction is mainly given by those compounds which have at least one hydrogen atom present at sp3 -hybrid carbon. Reactivity of  -hybrid carbon depends on' the reactivity of reaction intermediate.
-hybrid carbon depends on' the reactivity of reaction intermediate.
The relative rate of formation of alkyl radicals by a chlorine radical is:

Relative amount =
Relative amount = Number of hydrogen atoms on the respective carbon x relative reactivity. NBS (N-Bromo succinimide) is used for bromination at allylic and benzylic carbon, whereas  gives bromination at benzylic, allylic and alkyl carbons Which one of the following compounds will react with NBS?
gives bromination at benzylic, allylic and alkyl carbons Which one of the following compounds will react with NBS?
Free radical halogenation takes place in tile presence of light or at high temperature (above 500 C). Formation of halogen free radical intermediate takes place in first step called chain initiation •.
C). Formation of halogen free radical intermediate takes place in first step called chain initiation •.
 This reaction is mainly given by those compounds which have at least one hydrogen atom present at sp3 -hybrid carbon. Reactivity of
This reaction is mainly given by those compounds which have at least one hydrogen atom present at sp3 -hybrid carbon. Reactivity of  -hybrid carbon depends on' the reactivity of reaction intermediate.
-hybrid carbon depends on' the reactivity of reaction intermediate.
The relative rate of formation of alkyl radicals by a chlorine radical is:

Relative amount =
Relative amount = Number of hydrogen atoms on the respective carbon x relative reactivity. NBS (N-Bromo succinimide) is used for bromination at allylic and benzylic carbon, whereas  gives bromination at benzylic, allylic and alkyl carbons Which one of the following compounds will react with NBS?
gives bromination at benzylic, allylic and alkyl carbons Which one of the following compounds will react with NBS?
Chemistry-General
Chemistry-
Nucleophilic substitution reaction" is given by those compounds which have nucleophilic. groups as leaving groups. The weaker the basicity of a group of the substrate, the better is its leaving ability. In nucleophilic substitution reactions, the basicity of leaving group should be less than the incoming nucleophilic group. Nucleophilic substitution reaction at sp3-hybridised carbon is either bimolecular  or 1lIlim0lecular:
or 1lIlim0lecular:  Bimolecular reaction takes place in single step, involving transition state intermediate. In
Bimolecular reaction takes place in single step, involving transition state intermediate. In  reaction, inversion in configuration takes place. In case of optically active alkyl halides, the inversion in configuration is called Walden "inversion.
reaction, inversion in configuration takes place. In case of optically active alkyl halides, the inversion in configuration is called Walden "inversion.  reaction is preferred if the compound has less steric hindrance. " Unimolecular (
reaction is preferred if the compound has less steric hindrance. " Unimolecular ( ) reaction" involves two steps and" carbonium ion intermediate. Optically active" substrates give racemic mixture in these" reactions.
) reaction" involves two steps and" carbonium ion intermediate. Optically active" substrates give racemic mixture in these" reactions.
Which among the following will give  reaction?
reaction?
I) 
II) 
III) 
IV) 
Nucleophilic substitution reaction" is given by those compounds which have nucleophilic. groups as leaving groups. The weaker the basicity of a group of the substrate, the better is its leaving ability. In nucleophilic substitution reactions, the basicity of leaving group should be less than the incoming nucleophilic group. Nucleophilic substitution reaction at sp3-hybridised carbon is either bimolecular  or 1lIlim0lecular:
or 1lIlim0lecular:  Bimolecular reaction takes place in single step, involving transition state intermediate. In
Bimolecular reaction takes place in single step, involving transition state intermediate. In  reaction, inversion in configuration takes place. In case of optically active alkyl halides, the inversion in configuration is called Walden "inversion.
reaction, inversion in configuration takes place. In case of optically active alkyl halides, the inversion in configuration is called Walden "inversion.  reaction is preferred if the compound has less steric hindrance. " Unimolecular (
reaction is preferred if the compound has less steric hindrance. " Unimolecular ( ) reaction" involves two steps and" carbonium ion intermediate. Optically active" substrates give racemic mixture in these" reactions.
) reaction" involves two steps and" carbonium ion intermediate. Optically active" substrates give racemic mixture in these" reactions.
Which among the following will give  reaction?
reaction?
I) 
II) 
III) 
IV) 
Chemistry-General
Chemistry-
Identify the correct order of reactivity in electrophilic substitution reactions of the following compounds:
I) 
II) 
III) 
IV) 
Identify the correct order of reactivity in electrophilic substitution reactions of the following compounds:
I) 
II) 
III) 
IV) 
Chemistry-General
Chemistry-
Dehydrobromination (HBr-) of the following in increasing order will be:
I) 
II) 
III) 
Dehydrobromination (HBr-) of the following in increasing order will be:
I) 
II) 
III) 
Chemistry-General
Chemistry-
 by the reaction is:
by the reaction is:
 by the reaction is:
by the reaction is:
Chemistry-General
Chemistry-
Oxidation of alkenes by cleavage with acidic or alkaline KMn04 or acidic K2Cr2O7 at higher temperature yields products depending upon the nature of aIkene. A hot solution ofKMnO4 is a strong oxidising agent which gives only ketones and carboxylic . acids and not aldehydes (as they cannot be isolated).
Oxidation of alkenes with OsO4 followed by alcoholic NaHSO3 or Na2SO4 yields glycols.
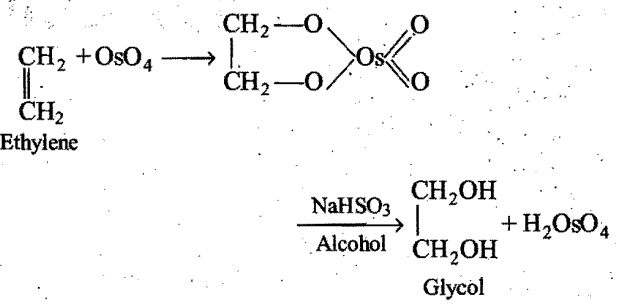
An alkene 1,2-dimethyl cyclobutene on oxidation With. hot KMnO4 gives:
Oxidation of alkenes by cleavage with acidic or alkaline KMn04 or acidic K2Cr2O7 at higher temperature yields products depending upon the nature of aIkene. A hot solution ofKMnO4 is a strong oxidising agent which gives only ketones and carboxylic . acids and not aldehydes (as they cannot be isolated).
Oxidation of alkenes with OsO4 followed by alcoholic NaHSO3 or Na2SO4 yields glycols.

An alkene 1,2-dimethyl cyclobutene on oxidation With. hot KMnO4 gives:
Chemistry-General
Chemistry-
Oxidation of alkenes by cleavage with acidic or alkaline KMn04 or acidic K2Cr2O7 at higher temperature yields products depending upon the nature of aIkene. A hot solution ofKMnO4 is a strong oxidising agent which gives only ketones and carboxylic . acids and not aldehydes (as they cannot be isolated).

Oxidation of alkenes with OsO4 followed by alcoholic NaHSO3 or Na2SO4 yields glycols.

An alkene 1,2-dimethyl cyclobutene on oxidation With. hot KMnO4 gives:
Oxidation of alkenes by cleavage with acidic or alkaline KMn04 or acidic K2Cr2O7 at higher temperature yields products depending upon the nature of aIkene. A hot solution ofKMnO4 is a strong oxidising agent which gives only ketones and carboxylic . acids and not aldehydes (as they cannot be isolated).

Oxidation of alkenes with OsO4 followed by alcoholic NaHSO3 or Na2SO4 yields glycols.

An alkene 1,2-dimethyl cyclobutene on oxidation With. hot KMnO4 gives:
Chemistry-General
Chemistry-
Oxidation of alkenes by cleavage with acidic or alkaline KMn04 or acidic K2Cr2O7 at higher temperature yields products depending upon the nature of aIkene. A hot solution ofKMnO4 is a strong oxidising agent which gives only ketones and carboxylic . acids and not aldehydes (as they cannot be isolated).

Oxidation of alkenes with OsO4 followed by alcoholic NaHSO3 or Na2SO4 yields glycols.

An alkene 1,2-dimethyl cyclobutene on oxidation With. hot KMnO4 gives:
Oxidation of alkenes by cleavage with acidic or alkaline KMn04 or acidic K2Cr2O7 at higher temperature yields products depending upon the nature of aIkene. A hot solution ofKMnO4 is a strong oxidising agent which gives only ketones and carboxylic . acids and not aldehydes (as they cannot be isolated).

Oxidation of alkenes with OsO4 followed by alcoholic NaHSO3 or Na2SO4 yields glycols.

An alkene 1,2-dimethyl cyclobutene on oxidation With. hot KMnO4 gives:
Chemistry-General
Maths-
Out of 21 tickets marked with numbers from 1 to 21, three are drawn at random. The chance that the numbers on them are in A.P., is
Out of 21 tickets marked with numbers from 1 to 21, three are drawn at random. The chance that the numbers on them are in A.P., is
Maths-General



