Physics-
General
Easy
Question
Lines which represent places of constant angle of dip are called
- Isobaric lines
- Isogonic lines
- Isoclinic lines
- Isodynamic lines
The correct answer is: Isoclinic lines
Related Questions to study
Physics-
At a place, the horizontal and vertical intensities of earth's magnetic field is 0.30 Gauss and 0.173 Gauss respectively. The angle of dip at this place is
At a place, the horizontal and vertical intensities of earth's magnetic field is 0.30 Gauss and 0.173 Gauss respectively. The angle of dip at this place is
Physics-General
Physics-
The angle of dip is the angle
The angle of dip is the angle
Physics-General
Maths-
If the normal at the points Pi (xi, yi), i = 1 to 4 on the hyperbola xy = c2 are concurrent at the point Q(h, k), then  is equal to
is equal to
If the normal at the points Pi (xi, yi), i = 1 to 4 on the hyperbola xy = c2 are concurrent at the point Q(h, k), then  is equal to
is equal to
Maths-General
Maths-
The most general form of the equation of a conic is given by  . Let x and y-axes be respectively tangent and normal to the conic given by equation ((a) at the origin. Then clearly c = 0. Also by putting y = 0, we get
. Let x and y-axes be respectively tangent and normal to the conic given by equation ((a) at the origin. Then clearly c = 0. Also by putting y = 0, we get  = 0. Both roots of the equation are zero. Therefore g = 0.
= 0. Both roots of the equation are zero. Therefore g = 0.
Hence the most general form of the equation of such a conic is given by .
.
Let foci of the conic represented by the equation , where
, where  and
and  be
be  and
and . Then the feet of perpendiculars from F1 and F2 upon x-axis lie on the curve
. Then the feet of perpendiculars from F1 and F2 upon x-axis lie on the curve
The most general form of the equation of a conic is given by  . Let x and y-axes be respectively tangent and normal to the conic given by equation ((a) at the origin. Then clearly c = 0. Also by putting y = 0, we get
. Let x and y-axes be respectively tangent and normal to the conic given by equation ((a) at the origin. Then clearly c = 0. Also by putting y = 0, we get  = 0. Both roots of the equation are zero. Therefore g = 0.
= 0. Both roots of the equation are zero. Therefore g = 0.
Hence the most general form of the equation of such a conic is given by .
.
Let foci of the conic represented by the equation , where
, where  and
and  be
be  and
and . Then the feet of perpendiculars from F1 and F2 upon x-axis lie on the curve
. Then the feet of perpendiculars from F1 and F2 upon x-axis lie on the curve
Maths-General
Chemistry-
According to Huckel’s rule a compound is said to be aromatic if it contains
According to Huckel’s rule a compound is said to be aromatic if it contains
Chemistry-General
Chemistry-
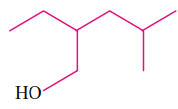 structure is
structure is
 structure is
structure is
Chemistry-General
Chemistry-
Two volatile liquids A and B differ in their boiling points by 0 15 C The process which can be used to separate them is
Two volatile liquids A and B differ in their boiling points by 0 15 C The process which can be used to separate them is
Chemistry-General
Maths-
Consider the ellipse whose equation is  For certain pair of diameters of the above ellipse, the product of their slopes is equal to
For certain pair of diameters of the above ellipse, the product of their slopes is equal to 
The equations of two diameters are  and
and  satisfying the condition mentioned above. Then the eccentricity of the ellipse is
satisfying the condition mentioned above. Then the eccentricity of the ellipse is
Consider the ellipse whose equation is  For certain pair of diameters of the above ellipse, the product of their slopes is equal to
For certain pair of diameters of the above ellipse, the product of their slopes is equal to 
The equations of two diameters are  and
and  satisfying the condition mentioned above. Then the eccentricity of the ellipse is
satisfying the condition mentioned above. Then the eccentricity of the ellipse is
Maths-General
Maths-
The smallest possible value of S where
where  is a permutation of the number 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, and 9 is
is a permutation of the number 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, and 9 is
The smallest possible value of S where
where  is a permutation of the number 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, and 9 is
is a permutation of the number 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, and 9 is
Maths-General
Maths-
Statement 1 : The second degree equation  represents an ellipse Because
represents an ellipse Because
Statement 2 :  represents an ellipse if
represents an ellipse if  and
and 
Statement 1 : The second degree equation  represents an ellipse Because
represents an ellipse Because
Statement 2 :  represents an ellipse if
represents an ellipse if  and
and 
Maths-General
Maths-
Statement-1: P is any point such that the chord of contact of tangents from P to the ellipse  touches
touches  The the tangents from P of
The the tangents from P of  are at right angles and
are at right angles and
Statement-2: The tangent from any point on the director circle of an ellipse are at right angles
Statement-1: P is any point such that the chord of contact of tangents from P to the ellipse  touches
touches  The the tangents from P of
The the tangents from P of  are at right angles and
are at right angles and
Statement-2: The tangent from any point on the director circle of an ellipse are at right angles
Maths-General
Maths-
Statement-1: The distance of the tangent through (0, (d) from a focus of the ellipse  is 5
is 5
and
Statement-2: The locus of the foot of the perpendicular from a focus on any tangent to  is
is 
Statement-1: The distance of the tangent through (0, (d) from a focus of the ellipse  is 5
is 5
and
Statement-2: The locus of the foot of the perpendicular from a focus on any tangent to  is
is 
Maths-General
Maths-
There are ‘n’ numbered seats around a round table. Total number of ways in which n n1 1 () < n persons can sit around the round table is equal to
There are ‘n’ numbered seats around a round table. Total number of ways in which n n1 1 () < n persons can sit around the round table is equal to
Maths-General
Chemistry-
The IUPAC name of  is
is
The IUPAC name of  is
is
Chemistry-General
Maths-
If the normal at any given point P on the ellipse  meets its
meets its
auxiliary circle at Q and R such that QOR = 90, where O is the centre
of ellipse, then
If the normal at any given point P on the ellipse  meets its
meets its
auxiliary circle at Q and R such that QOR = 90, where O is the centre
of ellipse, then
Maths-General





