Question
The above is a plot of binding energy per nucleon  against the nuclear mass
against the nuclear mass  correspond to different nuclei. Consider four reactions
correspond to different nuclei. Consider four reactions 


 where
where  is the energy released? In which reaction is
is the energy released? In which reaction is  positive?
positive?

- (i) and (iv)
- (i) and (iii)
- (ii) and (iv)
- (ii) and (iii)
The correct answer is: (i) and (iv)
Energy  is related only when lighter nuclei fuse to form a heavier nucleus such as in reaction (i)
is related only when lighter nuclei fuse to form a heavier nucleus such as in reaction (i)

Again ,energy is released when a heavy nucleus splits into lighter nuclei as in(iv)

Related Questions to study
Fe(OH)3 can be separated from Al(OH)3 by addition of
Fe(OH)3 can be separated from Al(OH)3 by addition of
Which of the following elements (M) reacts with HNO3 to form MO2?
Which of the following elements (M) reacts with HNO3 to form MO2?
An acidic solution contains Cu2+, Pb2+ and Zn2+. If H2S(g) is passed through the solution the precipitate will contain
An acidic solution contains Cu2+, Pb2+ and Zn2+. If H2S(g) is passed through the solution the precipitate will contain
In all the oxyacids of phosphorus, each phosphorus atom is in sp3 hybrid state, i.e., it is tetrahedrally bonded to neighbouring four atoms. All these acids contain P - OH bonds, the hydrogen atom of which are ionisable imparting acidic nature to the compound. The ous acids (oxidation state of P = +1 or +3) also have P - H bonds in which hydrogens are not ionisable (P and hydrogen have nearly same electronegativity). The presence of P - H group in these acids imparts reducing properties. The structure of the various acids are drawn below (note that the tetrahedral shape of phosphorus is not shown only for convenience of representation).
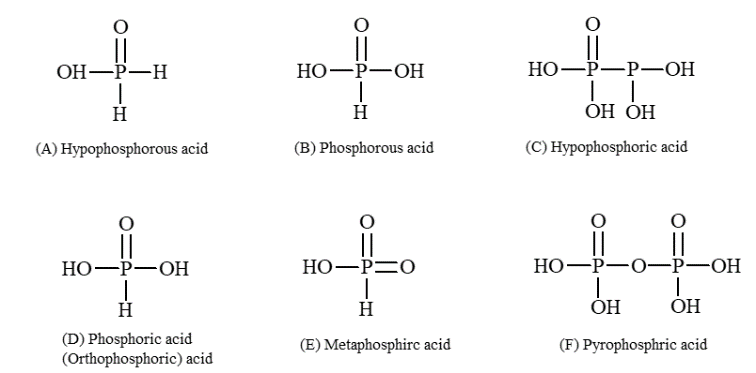
There is very little difference in acid strength in the series H3PO4, H3PO3 and H3PO2 because
In all the oxyacids of phosphorus, each phosphorus atom is in sp3 hybrid state, i.e., it is tetrahedrally bonded to neighbouring four atoms. All these acids contain P - OH bonds, the hydrogen atom of which are ionisable imparting acidic nature to the compound. The ous acids (oxidation state of P = +1 or +3) also have P - H bonds in which hydrogens are not ionisable (P and hydrogen have nearly same electronegativity). The presence of P - H group in these acids imparts reducing properties. The structure of the various acids are drawn below (note that the tetrahedral shape of phosphorus is not shown only for convenience of representation).

There is very little difference in acid strength in the series H3PO4, H3PO3 and H3PO2 because
If  where r = 1, 2, 3 and
where r = 1, 2, 3 and  = 0 …etc, then,
= 0 …etc, then,  is equal to
is equal to
If  where r = 1, 2, 3 and
where r = 1, 2, 3 and  = 0 …etc, then,
= 0 …etc, then,  is equal to
is equal to
If A and B are two non-singular square matrices of the same order, the adjoint of AB is equal to
If A and B are two non-singular square matrices of the same order, the adjoint of AB is equal to
If I = , J =
, J =  and B =
and B =  , then B equals
, then B equals
If I = , J =
, J =  and B =
and B =  , then B equals
, then B equals
If A′ is the transpose of a square matrix A, then
If A′ is the transpose of a square matrix A, then
If  = 72, then n is equal to
= 72, then n is equal to
If  = 72, then n is equal to
= 72, then n is equal to
The determinant  is equal to zero if
is equal to zero if
The determinant  is equal to zero if
is equal to zero if
Equation of the line passing though the point of intersection of the lines x + 2y – 3 = 0 and x
+ y –2 = 0 and also through the point (2, 1) is
For such questions, we should know different formulas to find equation of line.
Equation of the line passing though the point of intersection of the lines x + 2y – 3 = 0 and x
+ y –2 = 0 and also through the point (2, 1) is
For such questions, we should know different formulas to find equation of line.
The locus of the point which moves so that the square of its distance from the point (3, 0) is
equal to 7 is
Locus of a point means path traced by the given point while satisfying the given conditions. For such questions, we should know distance formula.
The locus of the point which moves so that the square of its distance from the point (3, 0) is
equal to 7 is
Locus of a point means path traced by the given point while satisfying the given conditions. For such questions, we should know distance formula.
The area of triangle with vertices at (–4, –1) , (1, 2), (4, –3)
Here, the area of a triangle cannot be negative. Hence only the numerical value is considered.
The area of triangle with vertices at (–4, –1) , (1, 2), (4, –3)
Here, the area of a triangle cannot be negative. Hence only the numerical value is considered.



