Chemistry-
General
Easy
Question
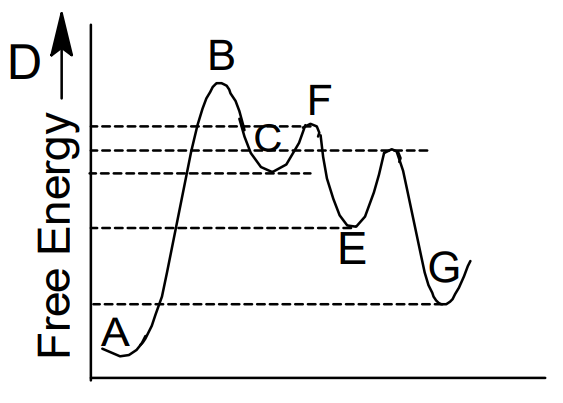
The free energy profile for the transformation of A in to G is shown below.

The slowest step in the forward direction:
- A to C
- C to E
- E to G
- C to F
The correct answer is: A to C
Related Questions to study
chemistry-
The free energy profile for the transformation of A in to G is shown below.
The overall reaction is :
The free energy profile for the transformation of A in to G is shown below.

The overall reaction is :
chemistry-General
chemistry-
The reaction  is of first order both with respect to the persulphate and iodide ions. Taking the initial concentration as ' a ' and 'b' respectively and taking x as the concentration of the triodide at time t a differential rate equation can be written. Two suggested mechanisms for the reaction are
is of first order both with respect to the persulphate and iodide ions. Taking the initial concentration as ' a ' and 'b' respectively and taking x as the concentration of the triodide at time t a differential rate equation can be written. Two suggested mechanisms for the reaction are

The general differential equation for the above reaction is
The reaction  is of first order both with respect to the persulphate and iodide ions. Taking the initial concentration as ' a ' and 'b' respectively and taking x as the concentration of the triodide at time t a differential rate equation can be written. Two suggested mechanisms for the reaction are
is of first order both with respect to the persulphate and iodide ions. Taking the initial concentration as ' a ' and 'b' respectively and taking x as the concentration of the triodide at time t a differential rate equation can be written. Two suggested mechanisms for the reaction are

The general differential equation for the above reaction is
chemistry-General
chemistry-
Figure shows a graph in  where K is rate constant and T is temperature. The straight line BC has slope,
where K is rate constant and T is temperature. The straight line BC has slope,  and an intercept of 5 on y-axis. Thus
and an intercept of 5 on y-axis. Thus  , the energy of activation is:
, the energy of activation is:

Figure shows a graph in  where K is rate constant and T is temperature. The straight line BC has slope,
where K is rate constant and T is temperature. The straight line BC has slope,  and an intercept of 5 on y-axis. Thus
and an intercept of 5 on y-axis. Thus  , the energy of activation is:
, the energy of activation is:

chemistry-General
chemistry-
For an exothermic chemical process occurring in two steps as :
i) A+B→X (slow)
ii) X→AB( fast 
The progress of the reaction can be best described by :
For an exothermic chemical process occurring in two steps as :
i) A+B→X (slow)
ii) X→AB( fast 
The progress of the reaction can be best described by :
chemistry-General
chemistry-
With respect to the figure given below which of the following statement is correct

With respect to the figure given below which of the following statement is correct

chemistry-General
chemistry-
Mark correct statement about given graph:

Mark correct statement about given graph:

chemistry-General
chemistry-
The heats of combustion of carbon, hydrogen and acetylene are -394K.J, -286K.J and -1301 K.J respectively. Calculate heat of formation of 
The heats of combustion of carbon, hydrogen and acetylene are -394K.J, -286K.J and -1301 K.J respectively. Calculate heat of formation of 
chemistry-General
chemistry-
For the adsorption of solution on a solid surface  Adsorption isotherm of
Adsorption isotherm of  was found of the type (Fig) This is when
was found of the type (Fig) This is when

For the adsorption of solution on a solid surface  Adsorption isotherm of
Adsorption isotherm of  was found of the type (Fig) This is when
was found of the type (Fig) This is when

chemistry-General
physics-
For the same total mass which of the following will have the largest moment of inertia about an axis passing through its centre of mass and perpendicular to the plane of the body
For the same total mass which of the following will have the largest moment of inertia about an axis passing through its centre of mass and perpendicular to the plane of the body
physics-General
chemistry-
The change in the state of hybridization of asterisked carbon in the following reaction is-

The change in the state of hybridization of asterisked carbon in the following reaction is-

chemistry-General
chemistry-
The geometrical arrangement and shape of I3 are respectively
The geometrical arrangement and shape of I3 are respectively
chemistry-General
physics-
A rigid lamina is rotating about an axis passing Perpendiuclar to its plane through point O as shown in figure. The angular velocity of point B w.r.t. A is

A rigid lamina is rotating about an axis passing Perpendiuclar to its plane through point O as shown in figure. The angular velocity of point B w.r.t. A is

physics-General
chemistry-
The correct statement for the reaction NH +H+→NH+
The correct statement for the reaction NH +H+→NH+
chemistry-General
chemistry-
Correct statement regarding this reaction BF3+NH3¾→[F3B¬NH3]
Correct statement regarding this reaction BF3+NH3¾→[F3B¬NH3]
chemistry-General
physics-
STATEMENT-1 : No external force acts on system of two spheres which undergo a perfectly elastic head on collision. The minimum kinetic energy of this system is zero if the net momentum of this system is zero
STATEMENT-2 : In any two body system undergoing perfectly elastic head on collision, at the instant of maximum deformation, the complete kinetic energy of the system is converted to deformation potential energy of the system.
STATEMENT-1 : No external force acts on system of two spheres which undergo a perfectly elastic head on collision. The minimum kinetic energy of this system is zero if the net momentum of this system is zero
STATEMENT-2 : In any two body system undergoing perfectly elastic head on collision, at the instant of maximum deformation, the complete kinetic energy of the system is converted to deformation potential energy of the system.
physics-General



