Physics-
General
Easy
Question
A block of mass 1 kg is placed on a rough horizontal surface. A spring is attached to the block whose other end is joined to a rigid wall,as shown in the figure. A horizontal force is applied on the block so that it remains at rest while the spring is elongated by x. Let
Let  be the maximum and minimum values of force F for which the block remains in equilibrium. For a particular x,
be the maximum and minimum values of force F for which the block remains in equilibrium. For a particular x,  = 2 N. Also shown is the variation of
= 2 N. Also shown is the variation of  , the elongation of the spring The value of
, the elongation of the spring The value of  , if x = 3 cm is :
, if x = 3 cm is :


- 0
- 0.2

- 5

- 1

The correct answer is: 0
When  , which is less than
, which is less than 
 The block will be at rest, without applying force F.
The block will be at rest, without applying force F.
Related Questions to study
physics-
A block of mass 1 kg is placed on a rough horizontal surface. A spring is attached to the block whose other end is joined to a rigid wall,as shown in the figure. A horizontal force is applied on the block so that it remains at rest while the spring is elongated by x. Let
Let  be the maximum and minimum values of force F for which the block remains in equilibrium. For a particular x,
be the maximum and minimum values of force F for which the block remains in equilibrium. For a particular x,  = 2 N. Also shown is the variation of
= 2 N. Also shown is the variation of  , the elongation of the spring The spring constant of the spring is:
, the elongation of the spring The spring constant of the spring is:


A block of mass 1 kg is placed on a rough horizontal surface. A spring is attached to the block whose other end is joined to a rigid wall,as shown in the figure. A horizontal force is applied on the block so that it remains at rest while the spring is elongated by x. Let
Let  be the maximum and minimum values of force F for which the block remains in equilibrium. For a particular x,
be the maximum and minimum values of force F for which the block remains in equilibrium. For a particular x,  = 2 N. Also shown is the variation of
= 2 N. Also shown is the variation of  , the elongation of the spring The spring constant of the spring is:
, the elongation of the spring The spring constant of the spring is:


physics-General
physics-
A block of mass 1 kg is placed on a rough horizontal surface. A spring is attached to the block whose other end is joined to a rigid wall,as shown in the figure. A horizontal force is applied on the block so that it remains at rest while the spring is elongated by x  be the maximum and minimum values of force F for which the block remains in equilibrium. For a particular x,
be the maximum and minimum values of force F for which the block remains in equilibrium. For a particular x,  . Also shown is the variation of Fmax+ Fmin versus x, the elongation of the spring The coefficient of friction between the block and the horizontal surface is :
. Also shown is the variation of Fmax+ Fmin versus x, the elongation of the spring The coefficient of friction between the block and the horizontal surface is :


A block of mass 1 kg is placed on a rough horizontal surface. A spring is attached to the block whose other end is joined to a rigid wall,as shown in the figure. A horizontal force is applied on the block so that it remains at rest while the spring is elongated by x  be the maximum and minimum values of force F for which the block remains in equilibrium. For a particular x,
be the maximum and minimum values of force F for which the block remains in equilibrium. For a particular x,  . Also shown is the variation of Fmax+ Fmin versus x, the elongation of the spring The coefficient of friction between the block and the horizontal surface is :
. Also shown is the variation of Fmax+ Fmin versus x, the elongation of the spring The coefficient of friction between the block and the horizontal surface is :


physics-General
physics-
Two bodies A and B of masses 10 kg and 5 kg are placed very slightly separated as shown in figure. The coefficients of friction between the floor and the blocks are as  . Block A is pushed by an external force F. The value of F can be changed. When the welding between block A and ground breaks, block A will start pressing block B and when welding of B also breaks, block B will start pressing the vertical wall If F = 50 N, the friction force acting between block B and ground will be :
. Block A is pushed by an external force F. The value of F can be changed. When the welding between block A and ground breaks, block A will start pressing block B and when welding of B also breaks, block B will start pressing the vertical wall If F = 50 N, the friction force acting between block B and ground will be :

Two bodies A and B of masses 10 kg and 5 kg are placed very slightly separated as shown in figure. The coefficients of friction between the floor and the blocks are as  . Block A is pushed by an external force F. The value of F can be changed. When the welding between block A and ground breaks, block A will start pressing block B and when welding of B also breaks, block B will start pressing the vertical wall If F = 50 N, the friction force acting between block B and ground will be :
. Block A is pushed by an external force F. The value of F can be changed. When the welding between block A and ground breaks, block A will start pressing block B and when welding of B also breaks, block B will start pressing the vertical wall If F = 50 N, the friction force acting between block B and ground will be :

physics-General
physics-
Two bodies A and B of masses 10 kg and 5 kg are placed very slightly separated as shown in figure. The coefficients of friction between the floor and the blocks are as  . Block A is pushed by an external force F. The value of F can be changed. When the welding between block A and ground breaks, block A will start pressing block B and when welding of B also breaks, block B will start pressing the vertical wall
. Block A is pushed by an external force F. The value of F can be changed. When the welding between block A and ground breaks, block A will start pressing block B and when welding of B also breaks, block B will start pressing the vertical wall  If
If  , with how much force does block A presses the block B
, with how much force does block A presses the block B

Two bodies A and B of masses 10 kg and 5 kg are placed very slightly separated as shown in figure. The coefficients of friction between the floor and the blocks are as  . Block A is pushed by an external force F. The value of F can be changed. When the welding between block A and ground breaks, block A will start pressing block B and when welding of B also breaks, block B will start pressing the vertical wall
. Block A is pushed by an external force F. The value of F can be changed. When the welding between block A and ground breaks, block A will start pressing block B and when welding of B also breaks, block B will start pressing the vertical wall  If
If  , with how much force does block A presses the block B
, with how much force does block A presses the block B

physics-General
physics-
STATEMENT-1 : A fixed wedge of inclination  lies on horizontal table. x and y axes are drawn on inclined surface as shown, such that x axis is horizontal and y-axis is along line of greatest slope. A block of mass m is placed (at rest) on inclined surface at origin. The coefficient of friction between block and wedge is
lies on horizontal table. x and y axes are drawn on inclined surface as shown, such that x axis is horizontal and y-axis is along line of greatest slope. A block of mass m is placed (at rest) on inclined surface at origin. The coefficient of friction between block and wedge is  , such that
, such that  . Then a force
. Then a force  applied to block parallel to inclined surface and along x-axis can move the block along x-axis
applied to block parallel to inclined surface and along x-axis can move the block along x-axis
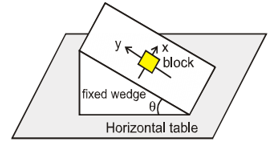
STATEMENT-2 : To move the block placed at rest on rough inclined surface along the inclined surface, the net force on block (except frictional force) should be greater than  . (N = normal reaction on block).
. (N = normal reaction on block).
STATEMENT-1 : A fixed wedge of inclination  lies on horizontal table. x and y axes are drawn on inclined surface as shown, such that x axis is horizontal and y-axis is along line of greatest slope. A block of mass m is placed (at rest) on inclined surface at origin. The coefficient of friction between block and wedge is
lies on horizontal table. x and y axes are drawn on inclined surface as shown, such that x axis is horizontal and y-axis is along line of greatest slope. A block of mass m is placed (at rest) on inclined surface at origin. The coefficient of friction between block and wedge is  , such that
, such that  . Then a force
. Then a force  applied to block parallel to inclined surface and along x-axis can move the block along x-axis
applied to block parallel to inclined surface and along x-axis can move the block along x-axis

STATEMENT-2 : To move the block placed at rest on rough inclined surface along the inclined surface, the net force on block (except frictional force) should be greater than  . (N = normal reaction on block).
. (N = normal reaction on block).
physics-General
chemistry-
Borax is converted into B by steps Borax I and II reagents are
Borax is converted into B by steps Borax I and II reagents are
chemistry-General
chemistry-
The following diagram shows the arrangement of lattice points with  and
and  . Choose the correct options
. Choose the correct options

The following diagram shows the arrangement of lattice points with  and
and  . Choose the correct options
. Choose the correct options

chemistry-General
chemistry-
In the cubic lattice given below, the three distances between the atoms  , and
, and  are, respectively,
are, respectively,

In the cubic lattice given below, the three distances between the atoms  , and
, and  are, respectively,
are, respectively,

chemistry-General
chemistry-
In an f cc unit cell, atoms are numbered as shown below. The atoms not touching each other are (Atom numbered 3 is face center of front face)

In an f cc unit cell, atoms are numbered as shown below. The atoms not touching each other are (Atom numbered 3 is face center of front face)

chemistry-General
chemistry-
In body-centered cubic lattice given below, the three distances AB, AC, and AA'' are

In body-centered cubic lattice given below, the three distances AB, AC, and AA'' are

chemistry-General
chemistry-
The packing efficiency of the two-dimensional square unit cell shown below is

The packing efficiency of the two-dimensional square unit cell shown below is

chemistry-General
physics-
A particle A of mass  kg is moving in the positive direction of x. Its initial position is x = 0 & initial velocity is 1
kg is moving in the positive direction of x. Its initial position is x = 0 & initial velocity is 1  . The velocity at x = 10 is in
. The velocity at x = 10 is in  (use the graph given)
(use the graph given)

A particle A of mass  kg is moving in the positive direction of x. Its initial position is x = 0 & initial velocity is 1
kg is moving in the positive direction of x. Its initial position is x = 0 & initial velocity is 1  . The velocity at x = 10 is in
. The velocity at x = 10 is in  (use the graph given)
(use the graph given)

physics-General
physics-
STATEMENT-1 : A block of mass m is placed at rest on rough horizontal surface. The coefficient of friction between the block and horizontal surface is  . The minimum force F applied at angle
. The minimum force F applied at angle  (as shown in figure) to pull the block horizontally is not equal to mmg. (Take
(as shown in figure) to pull the block horizontally is not equal to mmg. (Take  )
)

STATEMENT-2 : For a block of mass m placed on rough horizontal surface, the minimum horizontal force required to pull the block is  . The minimum force F applied at angle
. The minimum force F applied at angle  (as shown in figure) to pull the block horizontally may be less than mmg. (Where
(as shown in figure) to pull the block horizontally may be less than mmg. (Where  is co-efficient of friction)
is co-efficient of friction)

STATEMENT-1 : A block of mass m is placed at rest on rough horizontal surface. The coefficient of friction between the block and horizontal surface is  . The minimum force F applied at angle
. The minimum force F applied at angle  (as shown in figure) to pull the block horizontally is not equal to mmg. (Take
(as shown in figure) to pull the block horizontally is not equal to mmg. (Take  )
)

STATEMENT-2 : For a block of mass m placed on rough horizontal surface, the minimum horizontal force required to pull the block is  . The minimum force F applied at angle
. The minimum force F applied at angle  (as shown in figure) to pull the block horizontally may be less than mmg. (Where
(as shown in figure) to pull the block horizontally may be less than mmg. (Where  is co-efficient of friction)
is co-efficient of friction)

physics-General
physics-
In the following figure, find the direction of friction on the blocks and ground respectively

In the following figure, find the direction of friction on the blocks and ground respectively

physics-General
physics-
A mass m is supported as shown in the figure by ideal strings connected to a rigid wall and to a mass 3m at rest on a fixed horizontal surface. The string connected to larger mass is horizontal, that connected to smaller mass is vertical and the one connected to wall makes an angle  with horizontal. Then the minimum coefficient of static friction between the larger mass and the horizontal surface that permits the system to remain in equilibrium in the situation shown is:
with horizontal. Then the minimum coefficient of static friction between the larger mass and the horizontal surface that permits the system to remain in equilibrium in the situation shown is:

A mass m is supported as shown in the figure by ideal strings connected to a rigid wall and to a mass 3m at rest on a fixed horizontal surface. The string connected to larger mass is horizontal, that connected to smaller mass is vertical and the one connected to wall makes an angle  with horizontal. Then the minimum coefficient of static friction between the larger mass and the horizontal surface that permits the system to remain in equilibrium in the situation shown is:
with horizontal. Then the minimum coefficient of static friction between the larger mass and the horizontal surface that permits the system to remain in equilibrium in the situation shown is:

physics-General





