Physics-
General
Easy
Question
An optical fibre consists of core of  surrounded by a cladding of
surrounded by a cladding of  . A beam of light enters from air at an angle
. A beam of light enters from air at an angle  with axis of fibre. The highest
with axis of fibre. The highest  for which ray can be travelled through fibre is
for which ray can be travelled through fibre is

The correct answer is: 
Here the requirement is that 
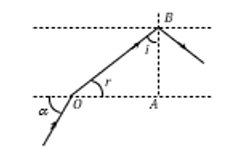
 …..(i)
…..(i)
From Snell’s law  ….(ii)
….(ii)
Also in 


Hence from equation (ii)


 ….(iii)
….(iii)
From equation (i) and (iii) 
Þ  Þ
Þ 

Related Questions to study
physics-
A prism having an apex angle  and refraction index 1.5 is located in front of a vertical plane mirror as shown in figure. Through what total angle is the ray deviated after reflection from the mirror
and refraction index 1.5 is located in front of a vertical plane mirror as shown in figure. Through what total angle is the ray deviated after reflection from the mirror

A prism having an apex angle  and refraction index 1.5 is located in front of a vertical plane mirror as shown in figure. Through what total angle is the ray deviated after reflection from the mirror
and refraction index 1.5 is located in front of a vertical plane mirror as shown in figure. Through what total angle is the ray deviated after reflection from the mirror

physics-General
physics-
In steel the young's modulus and the strain at the breaking point are  and 0.15 respectively the stress at the breaking point for steel is therefore
and 0.15 respectively the stress at the breaking point for steel is therefore
In steel the young's modulus and the strain at the breaking point are  and 0.15 respectively the stress at the breaking point for steel is therefore
and 0.15 respectively the stress at the breaking point for steel is therefore
physics-General
physics-
Hail stones fall from certain height If only 2% of the mass of the hail stone melt on reaching the ground,, the height from which they fall is ( g = 10 ms-2, L = 80 cal/gm and J = 4.2J/cal)
Hail stones fall from certain height If only 2% of the mass of the hail stone melt on reaching the ground,, the height from which they fall is ( g = 10 ms-2, L = 80 cal/gm and J = 4.2J/cal)
physics-General
maths-
 =
=
 =
=
maths-General
physics-
A fish rising vertically up towards the surface of water with speed 3  observes a bird diving vertically down towards it with speed 9
observes a bird diving vertically down towards it with speed 9  . The actual velocity of bird is
. The actual velocity of bird is

A fish rising vertically up towards the surface of water with speed 3  observes a bird diving vertically down towards it with speed 9
observes a bird diving vertically down towards it with speed 9  . The actual velocity of bird is
. The actual velocity of bird is

physics-General
physics-
The image of point P when viewed from top of the slabs will be

The image of point P when viewed from top of the slabs will be

physics-General
physics-
A cube of side 2 m is placed in front of a concave mirror focal length 1m with its face P at a distance of 3 m and face Q at a distance of 5 m from the mirror. The distance between the images of face P and Q and height of images of P and Q are

A cube of side 2 m is placed in front of a concave mirror focal length 1m with its face P at a distance of 3 m and face Q at a distance of 5 m from the mirror. The distance between the images of face P and Q and height of images of P and Q are

physics-General
physics-
Two transparent slabs have the same thickness as shown. One is made of material A of refractive index 1.5. The other is made of two materials B and C with thickness in the ratio 1 : 2. The refractive index of C is 1.6. If a monochromatic parallel beam passing through the slabs has the same number of waves inside both, the refractive index of B is

Two transparent slabs have the same thickness as shown. One is made of material A of refractive index 1.5. The other is made of two materials B and C with thickness in the ratio 1 : 2. The refractive index of C is 1.6. If a monochromatic parallel beam passing through the slabs has the same number of waves inside both, the refractive index of B is

physics-General
Maths-
We can only apply the L’Hospital’s rule if the direct substitution returns an indeterminate form, that means
Maths-General
We can only apply the L’Hospital’s rule if the direct substitution returns an indeterminate form, that means
maths-
If , then
by trapezoidal rule is
If , then
by trapezoidal rule is
maths-General
Maths-
We can only apply the L’Hospital’s rule if the direct substitution returns an indeterminate form, that means
Maths-General
We can only apply the L’Hospital’s rule if the direct substitution returns an indeterminate form, that means
physics-
A wire of length L and radius r is rigidly fixed at one end on stretching the other end of the wire a force F the increase in its lengths is L. If another wire of same material but of length 2 L and radius 2r, is stretched with a force of 2F, the increase in its length will he
A wire of length L and radius r is rigidly fixed at one end on stretching the other end of the wire a force F the increase in its lengths is L. If another wire of same material but of length 2 L and radius 2r, is stretched with a force of 2F, the increase in its length will he
physics-General
physics-
Consider the situation shown in figure. Water  is filled in a breaker upto a height of 10 cm. A plane mirror fixed at a height of 5 cm from the surface of water. Distance of image from the mirror after reflection from it of an object O at the bottom of the beaker is
is filled in a breaker upto a height of 10 cm. A plane mirror fixed at a height of 5 cm from the surface of water. Distance of image from the mirror after reflection from it of an object O at the bottom of the beaker is

Consider the situation shown in figure. Water  is filled in a breaker upto a height of 10 cm. A plane mirror fixed at a height of 5 cm from the surface of water. Distance of image from the mirror after reflection from it of an object O at the bottom of the beaker is
is filled in a breaker upto a height of 10 cm. A plane mirror fixed at a height of 5 cm from the surface of water. Distance of image from the mirror after reflection from it of an object O at the bottom of the beaker is

physics-General
physics-
One side of a glass slab is silvered as shown. A ray of light is incident on the other side at angle of incidence  . Refractive index of glass is given as 1.5. The deviation of the ray of light from its initial path when it comes out of the slab is
. Refractive index of glass is given as 1.5. The deviation of the ray of light from its initial path when it comes out of the slab is

One side of a glass slab is silvered as shown. A ray of light is incident on the other side at angle of incidence  . Refractive index of glass is given as 1.5. The deviation of the ray of light from its initial path when it comes out of the slab is
. Refractive index of glass is given as 1.5. The deviation of the ray of light from its initial path when it comes out of the slab is

physics-General
physics-
A plane mirror is placed at the bottom of the tank containing a liquid of refractive index  . P is a small object at a height h above the mirror. An observer O-vertically above P outside the liquid see P and its image in the mirror. The apparent distance between these two will be
. P is a small object at a height h above the mirror. An observer O-vertically above P outside the liquid see P and its image in the mirror. The apparent distance between these two will be

A plane mirror is placed at the bottom of the tank containing a liquid of refractive index  . P is a small object at a height h above the mirror. An observer O-vertically above P outside the liquid see P and its image in the mirror. The apparent distance between these two will be
. P is a small object at a height h above the mirror. An observer O-vertically above P outside the liquid see P and its image in the mirror. The apparent distance between these two will be

physics-General





