Physics-
General
Easy
Question
If the time period of a pendulum is 1 sec, then what is the length of the pendulum at point of  and
and  intersection of graph
intersection of graph

- 25 cm
- 21 cm
- 22 cm
- 27 cm
The correct answer is: 25 cm
Related Questions to study
physics-
The potential energy of a particle of mass 1kg in motion along x-axis is given by  joule, where ' x' is in meter The period of small oscillations in second is
joule, where ' x' is in meter The period of small oscillations in second is
The potential energy of a particle of mass 1kg in motion along x-axis is given by  joule, where ' x' is in meter The period of small oscillations in second is
joule, where ' x' is in meter The period of small oscillations in second is
physics-General
physics-
For the given figure, calculate zero correction.

For the given figure, calculate zero correction.

physics-General
Maths-
If ABCD is a square as shown in the figure then which of the following are adjacent sides ?

If ABCD is a square as shown in the figure then which of the following are adjacent sides ?

Maths-General
Maths-
In the following figure, a pair of adjacent vertices is

In the following figure, a pair of adjacent vertices is

Maths-General
chemistry-
Kinetic theory of gases is a generalization offered by Maxwell, Boltzmann, Clausius, etc., to explain the behavior of ideal gases. This theory assumes that ideal gas molecules neither attract nor repel each other. Average kinetic energy of gas molecules is directly proportional to the absolute temperature. A gas equation called kinetic gas equation was derived on the basis of kinetic theory
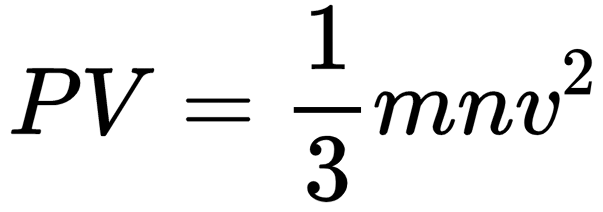

Pick up the correct statement/statements: 1. gas A will tend to lie at the bottom. 2. the number of atoms of various gases A, Band Care same. 3. the gases will diffuse to form homogeneous mixture, 4. average kinetic energy of each gas is same,
Kinetic theory of gases is a generalization offered by Maxwell, Boltzmann, Clausius, etc., to explain the behavior of ideal gases. This theory assumes that ideal gas molecules neither attract nor repel each other. Average kinetic energy of gas molecules is directly proportional to the absolute temperature. A gas equation called kinetic gas equation was derived on the basis of kinetic theory
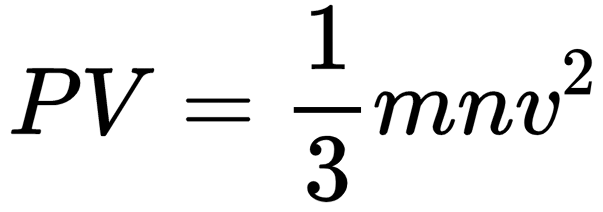

Pick up the correct statement/statements: 1. gas A will tend to lie at the bottom. 2. the number of atoms of various gases A, Band Care same. 3. the gases will diffuse to form homogeneous mixture, 4. average kinetic energy of each gas is same,
chemistry-General
chemistry-
The essential conditions for liquefaction of gases were discovered by Andrews in 1869 as a result of his study of pressure-volume-temperature relationship for  , It was found that above a certain temperature, it was impossible to liquefy a gas whatever the pressure was applied. The temperature below which the gas can be liquefied by the application of pressure alone is called critical temperature
, It was found that above a certain temperature, it was impossible to liquefy a gas whatever the pressure was applied. The temperature below which the gas can be liquefied by the application of pressure alone is called critical temperature  . The pressure required to liquefy a gas at this temperature is called the critical pressure
. The pressure required to liquefy a gas at this temperature is called the critical pressure  The volume occupied by one m91e of the substance at the critical temperature and pressure is called critical volume. Critical constants are related with van der Waals' constant as follows:
The volume occupied by one m91e of the substance at the critical temperature and pressure is called critical volume. Critical constants are related with van der Waals' constant as follows:


Which of the above gases cannot be liquefied at 100 K and 50 - atm?
The essential conditions for liquefaction of gases were discovered by Andrews in 1869 as a result of his study of pressure-volume-temperature relationship for  , It was found that above a certain temperature, it was impossible to liquefy a gas whatever the pressure was applied. The temperature below which the gas can be liquefied by the application of pressure alone is called critical temperature
, It was found that above a certain temperature, it was impossible to liquefy a gas whatever the pressure was applied. The temperature below which the gas can be liquefied by the application of pressure alone is called critical temperature  . The pressure required to liquefy a gas at this temperature is called the critical pressure
. The pressure required to liquefy a gas at this temperature is called the critical pressure  The volume occupied by one m91e of the substance at the critical temperature and pressure is called critical volume. Critical constants are related with van der Waals' constant as follows:
The volume occupied by one m91e of the substance at the critical temperature and pressure is called critical volume. Critical constants are related with van der Waals' constant as follows:


Which of the above gases cannot be liquefied at 100 K and 50 - atm?
chemistry-General
chemistry-
The packing efficiency of the two-dimensional square unit cell shown below is:

The packing efficiency of the two-dimensional square unit cell shown below is:

chemistry-General
chemistry-
The volume-temperature 'graphs of a given mass of an ideal gas at constant pressures are shown below. What is the correct order of pressures?

The volume-temperature 'graphs of a given mass of an ideal gas at constant pressures are shown below. What is the correct order of pressures?

chemistry-General
physics-
For measuring depth of a beaker using verniercallipers observed readings are given as If zero error is - 0.03cm, then mean corrected depth is

For measuring depth of a beaker using verniercallipers observed readings are given as If zero error is - 0.03cm, then mean corrected depth is

physics-General
physics-
The n th division of main scale coincides with  division of vernierscale Given+n one main scale division is equal to 'a' units The least count of vernier is
division of vernierscale Given+n one main scale division is equal to 'a' units The least count of vernier is
The n th division of main scale coincides with  division of vernierscale Given+n one main scale division is equal to 'a' units The least count of vernier is
division of vernierscale Given+n one main scale division is equal to 'a' units The least count of vernier is
physics-General
physics-
The nuclear charge (Ze) is non-uniformly distributed within a nucleus of radius R The (charge per unit volume)  charge density is dependent only on the radial distance r from the centre of the nucleus, as shown The electric field is only along radial direction
charge density is dependent only on the radial distance r from the centre of the nucleus, as shown The electric field is only along radial direction
For a = 0, the value of d(maximum value of  as shown in the figure) is :
as shown in the figure) is :

The nuclear charge (Ze) is non-uniformly distributed within a nucleus of radius R The (charge per unit volume)  charge density is dependent only on the radial distance r from the centre of the nucleus, as shown The electric field is only along radial direction
charge density is dependent only on the radial distance r from the centre of the nucleus, as shown The electric field is only along radial direction
For a = 0, the value of d(maximum value of  as shown in the figure) is :
as shown in the figure) is :

physics-General
physics-
The nuclear charge (Ze) is non-uniformly distributed within a nucleus of radius R The (charge per unit volume)  charge density is dependent only on the radial distance r from the centre of the nucleus, as shown The electric field is only along radial direction
charge density is dependent only on the radial distance r from the centre of the nucleus, as shown The electric field is only along radial direction

The electric field at r = R is :
The nuclear charge (Ze) is non-uniformly distributed within a nucleus of radius R The (charge per unit volume)  charge density is dependent only on the radial distance r from the centre of the nucleus, as shown The electric field is only along radial direction
charge density is dependent only on the radial distance r from the centre of the nucleus, as shown The electric field is only along radial direction

The electric field at r = R is :
physics-General
physics-
Consider radioactive decay of A to B which , further decays either to X or Y, and are decay constants for A to B decay, B to X decay and B to Y decay respectively At t =0, the number of nuclei of A,B,X and Y are
are decay constants for A to B decay, B to X decay and B to Y decay respectively At t =0, the number of nuclei of A,B,X and Y are  ,
,  zero and zero respectively
zero and zero respectively  are the number of nuclei of A,B,X and Y are at any instant t.
are the number of nuclei of A,B,X and Y are at any instant t.

At  , which of following is incorrect?
, which of following is incorrect?
Consider radioactive decay of A to B which , further decays either to X or Y, and are decay constants for A to B decay, B to X decay and B to Y decay respectively At t =0, the number of nuclei of A,B,X and Y are
are decay constants for A to B decay, B to X decay and B to Y decay respectively At t =0, the number of nuclei of A,B,X and Y are  ,
,  zero and zero respectively
zero and zero respectively  are the number of nuclei of A,B,X and Y are at any instant t.
are the number of nuclei of A,B,X and Y are at any instant t.

At  , which of following is incorrect?
, which of following is incorrect?
physics-General
physics-
Consider radioactive decay of A to B which , further decays either to X or Y, and are decay constants for A to B decay, B to X decay and B to Y decay respectively At t =0, the number of nuclei of A,B,X and Y are
are decay constants for A to B decay, B to X decay and B to Y decay respectively At t =0, the number of nuclei of A,B,X and Y are  ,
,  zero and zero respectively
zero and zero respectively  are the number of nuclei of A,B,X and Y are at any instant t.
are the number of nuclei of A,B,X and Y are at any instant t.

The number of nuclei of B will first increase and then after a maximum value, it decreases for
Consider radioactive decay of A to B which , further decays either to X or Y, and are decay constants for A to B decay, B to X decay and B to Y decay respectively At t =0, the number of nuclei of A,B,X and Y are
are decay constants for A to B decay, B to X decay and B to Y decay respectively At t =0, the number of nuclei of A,B,X and Y are  ,
,  zero and zero respectively
zero and zero respectively  are the number of nuclei of A,B,X and Y are at any instant t.
are the number of nuclei of A,B,X and Y are at any instant t.

The number of nuclei of B will first increase and then after a maximum value, it decreases for
physics-General
physics-
Consider radioactive decay of A to B which , further decays either to X or Y, and are decay constants for A to B decay, B to X decay and B to Y decay respectively At t =0, the number of nuclei of A,B,X and Y are
are decay constants for A to B decay, B to X decay and B to Y decay respectively At t =0, the number of nuclei of A,B,X and Y are  ,
,  zero and zero respectively
zero and zero respectively  are the number of nuclei of A,B,X and Y are at any instant t.
are the number of nuclei of A,B,X and Y are at any instant t.

The net rate of accumulation of B at any instant is
Consider radioactive decay of A to B which , further decays either to X or Y, and are decay constants for A to B decay, B to X decay and B to Y decay respectively At t =0, the number of nuclei of A,B,X and Y are
are decay constants for A to B decay, B to X decay and B to Y decay respectively At t =0, the number of nuclei of A,B,X and Y are  ,
,  zero and zero respectively
zero and zero respectively  are the number of nuclei of A,B,X and Y are at any instant t.
are the number of nuclei of A,B,X and Y are at any instant t.

The net rate of accumulation of B at any instant is
physics-General



