Physics-
General
Easy
Question
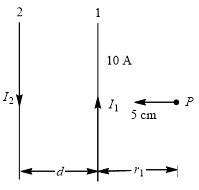
Two long parallel conductors carry currents in opposite directions as shown. One conductor carries a current of 10 A and the distance between the wires is d=10cm Current I is adjusted, so that the magnetic field at P is zero. P is at a distance of 5 cm to the right of the 10 A current. Value of I is

- 40 A
- 30 A
- 20 A
- 10 A
The correct answer is: 30 A
From Biot-Savart’s law the magnetic field  due to a conductor carrying current
due to a conductor carrying current  at a distance
at a distance  is
is

Magnetic field at  due to current in second conductor is
due to current in second conductor is

From Fleming’s right hands rule the fields at  are directed opposite.
are directed opposite.


Given, 


Related Questions to study
physics-
Two long straight wires are set parallel to each other. Each carries a current  in the opposite direction and the separation between them is 2R. The intensity of the magnetic field midway between them is
in the opposite direction and the separation between them is 2R. The intensity of the magnetic field midway between them is

Two long straight wires are set parallel to each other. Each carries a current  in the opposite direction and the separation between them is 2R. The intensity of the magnetic field midway between them is
in the opposite direction and the separation between them is 2R. The intensity of the magnetic field midway between them is

physics-General
physics-
A current of 10 A is passing through a long wire which has semicircular loop of the radius 20 cm as shown in the figure. Magnetic field produced at the centre of the loop is

A current of 10 A is passing through a long wire which has semicircular loop of the radius 20 cm as shown in the figure. Magnetic field produced at the centre of the loop is

physics-General
physics-
In the figure shown, the magnetic field induction at the point  will be
will be

In the figure shown, the magnetic field induction at the point  will be
will be

physics-General
physics-
PQ and RS are long parallel conductors separated by certain distance. M is the mid-point between them (see the figure). The net magnetic field at M is B. Now, the current 2A is switched off. The field at M now becomes

PQ and RS are long parallel conductors separated by certain distance. M is the mid-point between them (see the figure). The net magnetic field at M is B. Now, the current 2A is switched off. The field at M now becomes

physics-General
physics-
Current through ABC and A’ B’ C’ is I. What is the magnetic field at P?  (Here C’ B’ PBC are collinear)
(Here C’ B’ PBC are collinear)

Current through ABC and A’ B’ C’ is I. What is the magnetic field at P?  (Here C’ B’ PBC are collinear)
(Here C’ B’ PBC are collinear)

physics-General
physics
The ratio of pathlength and the respective time interval is
The ratio of pathlength and the respective time interval is
physicsGeneral
physics
A particle is thrown in upward direction with initial velocity of 60 m/s. Find average speed and average velocity after 10 seconds. [g =10 MS2]
A particle is thrown in upward direction with initial velocity of 60 m/s. Find average speed and average velocity after 10 seconds. [g =10 MS2]
physicsGeneral
physics-
The work done in deforming body is given by
The work done in deforming body is given by
physics-General
physics-
A wire of length  and radius
and radius  is stretched between
is stretched between  and
and  without the application of any tension. If
without the application of any tension. If  is the Young’s modulus of the wire and it is stretched like
is the Young’s modulus of the wire and it is stretched like  , then the tension in the wire will be
, then the tension in the wire will be

A wire of length  and radius
and radius  is stretched between
is stretched between  and
and  without the application of any tension. If
without the application of any tension. If  is the Young’s modulus of the wire and it is stretched like
is the Young’s modulus of the wire and it is stretched like  , then the tension in the wire will be
, then the tension in the wire will be

physics-General
physics-
A cube of aluminium of sides 0.1 m is subjected to a sharing force of 100 N. The top face of the cube is displaced through 0.02 cm with respect to the bottom face. The shearing strain would be
A cube of aluminium of sides 0.1 m is subjected to a sharing force of 100 N. The top face of the cube is displaced through 0.02 cm with respect to the bottom face. The shearing strain would be
physics-General
physics-
A uniform slender rod of length L, cross-sectional area A and Young’s modulus Y is acted upon by the forces shown in the figure. The elongation of the rod is

A uniform slender rod of length L, cross-sectional area A and Young’s modulus Y is acted upon by the forces shown in the figure. The elongation of the rod is

physics-General
physics-
The graph shows the behaviour of a length of wire in the region for which the substance obeys Hooke’s law.  and
and  represent
represent
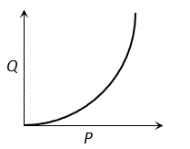
The graph shows the behaviour of a length of wire in the region for which the substance obeys Hooke’s law.  and
and  represent
represent

physics-General
physics-
If the shear modulus of a wire material is 5.9 then the potential energy of a wire of
then the potential energy of a wire of  in diameter and 5 cm long twisted through an angle of 10’ , is
in diameter and 5 cm long twisted through an angle of 10’ , is
If the shear modulus of a wire material is 5.9 then the potential energy of a wire of
then the potential energy of a wire of  in diameter and 5 cm long twisted through an angle of 10’ , is
in diameter and 5 cm long twisted through an angle of 10’ , is
physics-General
physics-
The Young’s modulus of the material of a wire is equal to the
The Young’s modulus of the material of a wire is equal to the
physics-General
Maths-
Maths-General



