Physics-
General
Easy
Question
Two mirrors are inclined at an angle  as shown in the figure. Light ray is incident parallel to one of the mirrors. The ray will start retracting its path after third reflection if:
as shown in the figure. Light ray is incident parallel to one of the mirrors. The ray will start retracting its path after third reflection if:




- all three
The correct answer is: 
Related Questions to study
physics-
Two plane mirror AB and AC are inclined at an angle  . A ray of light starting from point P is incident at point Q on the mirror AB, then at R on mirror AC and again at S on AB, finally the ray ST goes parallel to the mirror AC. The angle i which the ray makes with the normal at point Q on mirror AB is
. A ray of light starting from point P is incident at point Q on the mirror AB, then at R on mirror AC and again at S on AB, finally the ray ST goes parallel to the mirror AC. The angle i which the ray makes with the normal at point Q on mirror AB is

Two plane mirror AB and AC are inclined at an angle  . A ray of light starting from point P is incident at point Q on the mirror AB, then at R on mirror AC and again at S on AB, finally the ray ST goes parallel to the mirror AC. The angle i which the ray makes with the normal at point Q on mirror AB is
. A ray of light starting from point P is incident at point Q on the mirror AB, then at R on mirror AC and again at S on AB, finally the ray ST goes parallel to the mirror AC. The angle i which the ray makes with the normal at point Q on mirror AB is

physics-General
physics-
In the figure, the angle between two reflected rays is

In the figure, the angle between two reflected rays is

physics-General
physics-
A ray of light is to travel from point A to point B in figure in the shortest possible time after reflecting from P. Find  .
.

A ray of light is to travel from point A to point B in figure in the shortest possible time after reflecting from P. Find  .
.

physics-General
physics-
Three identical plane mirrors AB, BC, AC are arranged as shown in the figure. Find the total number of images of a point object ' S ' formed by the three mirrors. ( S is at the centre of the system)

Three identical plane mirrors AB, BC, AC are arranged as shown in the figure. Find the total number of images of a point object ' S ' formed by the three mirrors. ( S is at the centre of the system)

physics-General
physics-
A transparent solid sphere of radius 2 cm and density  floats in a transparent liquid of density
floats in a transparent liquid of density  kept in a beaker. The bottom of the beaker is spherical in shape with its radius of anvature 8 cm and is silvered to make it a concave mirror as shown in Fig. When an abject is placed at a distance of 10 cm directly above the centre of the sphere its final image coincide with it. If ' h ' is the height of liquid surface from the apex of the bottom as shown in figure. Consider paraxial rays only for image formation. The refractive index of the sphere is
kept in a beaker. The bottom of the beaker is spherical in shape with its radius of anvature 8 cm and is silvered to make it a concave mirror as shown in Fig. When an abject is placed at a distance of 10 cm directly above the centre of the sphere its final image coincide with it. If ' h ' is the height of liquid surface from the apex of the bottom as shown in figure. Consider paraxial rays only for image formation. The refractive index of the sphere is  and that of the liquid is
and that of the liquid is  .
.
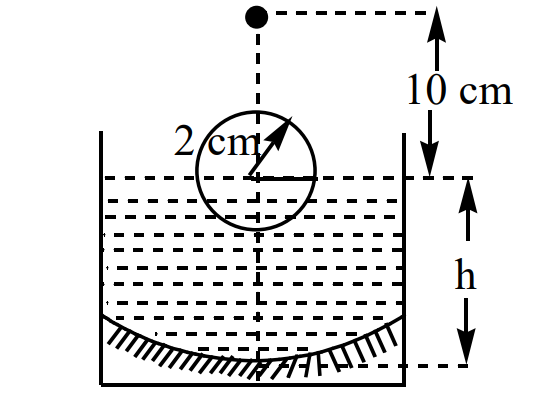
The value of  is (nearly equal to)
is (nearly equal to)
A transparent solid sphere of radius 2 cm and density  floats in a transparent liquid of density
floats in a transparent liquid of density  kept in a beaker. The bottom of the beaker is spherical in shape with its radius of anvature 8 cm and is silvered to make it a concave mirror as shown in Fig. When an abject is placed at a distance of 10 cm directly above the centre of the sphere its final image coincide with it. If ' h ' is the height of liquid surface from the apex of the bottom as shown in figure. Consider paraxial rays only for image formation. The refractive index of the sphere is
kept in a beaker. The bottom of the beaker is spherical in shape with its radius of anvature 8 cm and is silvered to make it a concave mirror as shown in Fig. When an abject is placed at a distance of 10 cm directly above the centre of the sphere its final image coincide with it. If ' h ' is the height of liquid surface from the apex of the bottom as shown in figure. Consider paraxial rays only for image formation. The refractive index of the sphere is  and that of the liquid is
and that of the liquid is  .
.

The value of  is (nearly equal to)
is (nearly equal to)
physics-General
physics-
A transparent solid sphere of radius 2 cm and density  floats in a transparent liquid of density
floats in a transparent liquid of density  kept in a beaker. The bottom of the beaker is spherical in shape with its radius of anvature 8 cm and is silvered to make it a concave mirror as shown in Fig. When an abject is placed at a distance of 10 cm directly above the centre of the sphere its final image coincide with it. If ' h ' is the height of liquid surface from the apex of the bottom as shown in figure. Consider paraxial rays only for image formation. The refractive index of the sphere is
kept in a beaker. The bottom of the beaker is spherical in shape with its radius of anvature 8 cm and is silvered to make it a concave mirror as shown in Fig. When an abject is placed at a distance of 10 cm directly above the centre of the sphere its final image coincide with it. If ' h ' is the height of liquid surface from the apex of the bottom as shown in figure. Consider paraxial rays only for image formation. The refractive index of the sphere is  and that of the liquid is
and that of the liquid is  .
.
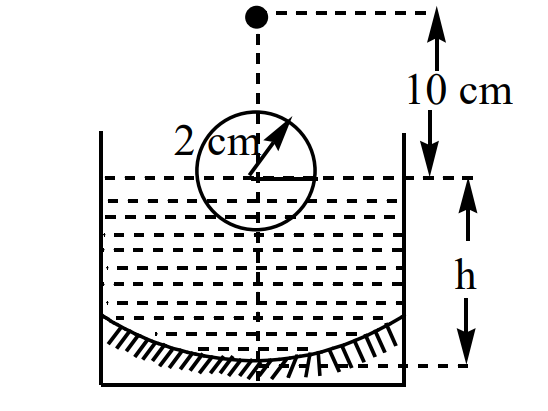
The image formed by the top spherical portion of sphere is (as measured from top of spherical ball)
A transparent solid sphere of radius 2 cm and density  floats in a transparent liquid of density
floats in a transparent liquid of density  kept in a beaker. The bottom of the beaker is spherical in shape with its radius of anvature 8 cm and is silvered to make it a concave mirror as shown in Fig. When an abject is placed at a distance of 10 cm directly above the centre of the sphere its final image coincide with it. If ' h ' is the height of liquid surface from the apex of the bottom as shown in figure. Consider paraxial rays only for image formation. The refractive index of the sphere is
kept in a beaker. The bottom of the beaker is spherical in shape with its radius of anvature 8 cm and is silvered to make it a concave mirror as shown in Fig. When an abject is placed at a distance of 10 cm directly above the centre of the sphere its final image coincide with it. If ' h ' is the height of liquid surface from the apex of the bottom as shown in figure. Consider paraxial rays only for image formation. The refractive index of the sphere is  and that of the liquid is
and that of the liquid is  .
.

The image formed by the top spherical portion of sphere is (as measured from top of spherical ball)
physics-General
physics-
A ray of light is incident normally on one face of  prism of refractive index 5/3 immersed in water of refractive index
prism of refractive index 5/3 immersed in water of refractive index  as shown in figure.
as shown in figure.

A ray of light is incident normally on one face of  prism of refractive index 5/3 immersed in water of refractive index
prism of refractive index 5/3 immersed in water of refractive index  as shown in figure.
as shown in figure.

physics-General
physics-
Two identical thin isosceles prisms of prism angle each A and refractive index  are placed with their bases touching each other. This system acts as a converging lens. What is the focal length of this system for parallel rays at a distance h from the base of the prism ?
are placed with their bases touching each other. This system acts as a converging lens. What is the focal length of this system for parallel rays at a distance h from the base of the prism ?

Two identical thin isosceles prisms of prism angle each A and refractive index  are placed with their bases touching each other. This system acts as a converging lens. What is the focal length of this system for parallel rays at a distance h from the base of the prism ?
are placed with their bases touching each other. This system acts as a converging lens. What is the focal length of this system for parallel rays at a distance h from the base of the prism ?

physics-General
physics-
In the given figure, there are two thin lenses of same focal length  arranged with their principal axes inclined at angle
arranged with their principal axes inclined at angle  . The separation between the optical centers of the lenses is 2f. A point object lies on the principal axis of the convex lens at a large distance to the left of the convex lens. Find the co-ordinates of the final image formed by the system of lenses taking 'O' as the origin of co-ordinate axes.
. The separation between the optical centers of the lenses is 2f. A point object lies on the principal axis of the convex lens at a large distance to the left of the convex lens. Find the co-ordinates of the final image formed by the system of lenses taking 'O' as the origin of co-ordinate axes.

In the given figure, there are two thin lenses of same focal length  arranged with their principal axes inclined at angle
arranged with their principal axes inclined at angle  . The separation between the optical centers of the lenses is 2f. A point object lies on the principal axis of the convex lens at a large distance to the left of the convex lens. Find the co-ordinates of the final image formed by the system of lenses taking 'O' as the origin of co-ordinate axes.
. The separation between the optical centers of the lenses is 2f. A point object lies on the principal axis of the convex lens at a large distance to the left of the convex lens. Find the co-ordinates of the final image formed by the system of lenses taking 'O' as the origin of co-ordinate axes.

physics-General
physics-
An equiconvex lens  of focal length 20 cm is cut into two equal parts and one part
of focal length 20 cm is cut into two equal parts and one part  is silvered. Another concavo-convex lens
is silvered. Another concavo-convex lens  (radii 10 cm and 20 cm, μ=1.5 ) is placed with its principle axis 2 mm above the principle axis of
(radii 10 cm and 20 cm, μ=1.5 ) is placed with its principle axis 2 mm above the principle axis of  A point object ' O ' is placed at a distance of 80 cm from the lens on its principal axis as shown in figure. Find the position of final image.
A point object ' O ' is placed at a distance of 80 cm from the lens on its principal axis as shown in figure. Find the position of final image.

An equiconvex lens  of focal length 20 cm is cut into two equal parts and one part
of focal length 20 cm is cut into two equal parts and one part  is silvered. Another concavo-convex lens
is silvered. Another concavo-convex lens  (radii 10 cm and 20 cm, μ=1.5 ) is placed with its principle axis 2 mm above the principle axis of
(radii 10 cm and 20 cm, μ=1.5 ) is placed with its principle axis 2 mm above the principle axis of  A point object ' O ' is placed at a distance of 80 cm from the lens on its principal axis as shown in figure. Find the position of final image.
A point object ' O ' is placed at a distance of 80 cm from the lens on its principal axis as shown in figure. Find the position of final image.

physics-General
physics-
A point object 'O' is placed at a distance of 30 cm from a convex lens ( f=20 cm ) cut into two equal haves each of which is displaced by 0.05 cm as shown in figure. Find the position of image? If more than one image is formed, find their number and distance between them.

A point object 'O' is placed at a distance of 30 cm from a convex lens ( f=20 cm ) cut into two equal haves each of which is displaced by 0.05 cm as shown in figure. Find the position of image? If more than one image is formed, find their number and distance between them.

physics-General
physics-
Figure shows an arrangement of an equiconvex lens ( f=20 cm in air) and a concave mirror (R=80 cm). A point object ' O ' is placed on the principal axis at a distance 40 cm from the lens such that the final image is also formed at the position of object. Find d.

Figure shows an arrangement of an equiconvex lens ( f=20 cm in air) and a concave mirror (R=80 cm). A point object ' O ' is placed on the principal axis at a distance 40 cm from the lens such that the final image is also formed at the position of object. Find d.

physics-General
physics-
A thin biconvex lens of refractive index  is placed an a horizontal plane mirror as shown in mirror. The space between the lens and the mirror is filled with water of refractive index
is placed an a horizontal plane mirror as shown in mirror. The space between the lens and the mirror is filled with water of refractive index  . It is found that when a point object is placed
. It is found that when a point object is placed  above the lens on its principal axis, the object coincides with its Onn image. On repeating with another liquid, the object and the image again coincide at a distance of
above the lens on its principal axis, the object coincides with its Onn image. On repeating with another liquid, the object and the image again coincide at a distance of  from the lens. Calculate refractive index of the liquid.
from the lens. Calculate refractive index of the liquid.

A thin biconvex lens of refractive index  is placed an a horizontal plane mirror as shown in mirror. The space between the lens and the mirror is filled with water of refractive index
is placed an a horizontal plane mirror as shown in mirror. The space between the lens and the mirror is filled with water of refractive index  . It is found that when a point object is placed
. It is found that when a point object is placed  above the lens on its principal axis, the object coincides with its Onn image. On repeating with another liquid, the object and the image again coincide at a distance of
above the lens on its principal axis, the object coincides with its Onn image. On repeating with another liquid, the object and the image again coincide at a distance of  from the lens. Calculate refractive index of the liquid.
from the lens. Calculate refractive index of the liquid.

physics-General
physics-
An object is placed at a distance of  from a thin plano convex lens of focal length
from a thin plano convex lens of focal length  . The plane surface of lens is now silvered. What is the position of image?
. The plane surface of lens is now silvered. What is the position of image?

An object is placed at a distance of  from a thin plano convex lens of focal length
from a thin plano convex lens of focal length  . The plane surface of lens is now silvered. What is the position of image?
. The plane surface of lens is now silvered. What is the position of image?

physics-General
physics-
A glass slab of thickness 3 cm and refractive index 1.5 is placed 12 cm from concave lens of focal length 20 cm. A convex lens of focal length 10 cm is placed on the same axis at a distance of 5 cm from the concave lens. An object is located 6 cm in front of glass slab and an observer looks it from the other end of optical train. Where will the object appear to be? What is the magnification of the object?

A glass slab of thickness 3 cm and refractive index 1.5 is placed 12 cm from concave lens of focal length 20 cm. A convex lens of focal length 10 cm is placed on the same axis at a distance of 5 cm from the concave lens. An object is located 6 cm in front of glass slab and an observer looks it from the other end of optical train. Where will the object appear to be? What is the magnification of the object?

physics-General





