Physics-
General
Easy
Question
Two small particles of equal masses start moving in opposite directions from a point  in a horizontal circular orbit. Their tangential velocities are
in a horizontal circular orbit. Their tangential velocities are  and
and  , respectively, as shown in the figure. Between collisions, the particles move with constant speeds. After making how many elastic collisions, other than that at
, respectively, as shown in the figure. Between collisions, the particles move with constant speeds. After making how many elastic collisions, other than that at  , these two particles will again reach the point
, these two particles will again reach the point 

- 4
- 3
- 2
- 1
The correct answer is: 2
Let initially particle  is moving in anticlockwise direction and
is moving in anticlockwise direction and  in clockwise direction
in clockwise direction
As the ratio of velocities of  and
and  particles are
particles are  , therefore ratio of their distance covered will be in the ratio of
, therefore ratio of their distance covered will be in the ratio of  . It means they collide at point B
. It means they collide at point B
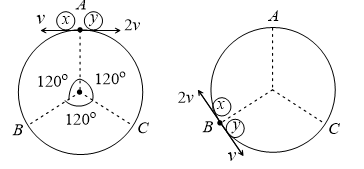
After first collision at B, velocities of particles get interchanged,  .,
.,  will move with
will move with  and particle
and particle  with
with 
Second collision will take place at point C. Again at this point velocities get interchanged and third collision take place at point A
So, after two collision these two particles will again reach the point A
Related Questions to study
maths-
In a model, it is shown that an arch of abridge is semi-elliptical with major axis horizontal. If the length of the base is 9 m and the highest part of the bridge is 3 m from the horizontal, the best approximation of the height of the arch, 2 m from the centre of the base is
In a model, it is shown that an arch of abridge is semi-elliptical with major axis horizontal. If the length of the base is 9 m and the highest part of the bridge is 3 m from the horizontal, the best approximation of the height of the arch, 2 m from the centre of the base is
maths-General
maths-
The number of non-negative integral solutions of x + y + z n, where n N is -
The number of non-negative integral solutions of x + y + z n, where n N is -
maths-General
maths-
Between two junction stations A and B there are 12 intermediate stations. The number of ways in which a train can be made to stop at 4 of these stations so that no two of these halting stations are consecutive is -
Between two junction stations A and B there are 12 intermediate stations. The number of ways in which a train can be made to stop at 4 of these stations so that no two of these halting stations are consecutive is -
maths-General
maths-
If n objects are arranged in a row, then the number of ways of selecting three of these objects so that no two of them are next to each other is -
If n objects are arranged in a row, then the number of ways of selecting three of these objects so that no two of them are next to each other is -
maths-General
Maths-
The number of numbers between 1 and 1010 which contain the digit 1 is -
The number of numbers between 1 and 1010 which contain the digit 1 is -
Maths-General
Maths-
The number of rectangles in the adjoining figure is –

The number of rectangles in the adjoining figure is –

Maths-General
chemistry-
Assertion :this equilibrium favours backward direction.
Reason :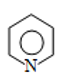 is stronger base than
is stronger base than 
Assertion :this equilibrium favours backward direction.
Reason : is stronger base than
is stronger base than 
chemistry-General
Physics-
A 0.098 kg block slides down a frictionless track as shown. The vertical component of the velocity of block at  is
is
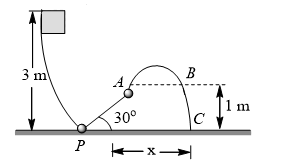
A 0.098 kg block slides down a frictionless track as shown. The vertical component of the velocity of block at  is
is

Physics-General
physics-
Two small particles of equal masses start moving in opposite directions from a point A in a horizontal circular orbit. Their tangential velocities are  respectively, as shown in the figure. Between collisions, the particles move with constant speeds. After making how many elastic collisions, other than that at
respectively, as shown in the figure. Between collisions, the particles move with constant speeds. After making how many elastic collisions, other than that at  ,these two particles will again reach The point
,these two particles will again reach The point 

Two small particles of equal masses start moving in opposite directions from a point A in a horizontal circular orbit. Their tangential velocities are  respectively, as shown in the figure. Between collisions, the particles move with constant speeds. After making how many elastic collisions, other than that at
respectively, as shown in the figure. Between collisions, the particles move with constant speeds. After making how many elastic collisions, other than that at  ,these two particles will again reach The point
,these two particles will again reach The point 

physics-General
physics-
The trajectory of a particle moving in vast maidan is as shown in the figure. The coordinates of a position  are
are  The coordinates of another point at which the instantaneous velocity is same as the average velocity between the points are
The coordinates of another point at which the instantaneous velocity is same as the average velocity between the points are
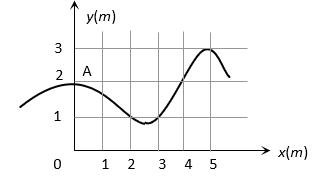
The trajectory of a particle moving in vast maidan is as shown in the figure. The coordinates of a position  are
are  The coordinates of another point at which the instantaneous velocity is same as the average velocity between the points are
The coordinates of another point at which the instantaneous velocity is same as the average velocity between the points are

physics-General
physics-
The potential energy of a particle varies with distance  as shown in the graph.
as shown in the graph.
The force acting on the particle is zero at

The potential energy of a particle varies with distance  as shown in the graph.
as shown in the graph.
The force acting on the particle is zero at

physics-General
physics-
A  mass moves along
mass moves along  -axis. Its acceleration as a function of its position is shown in the figure. What is the total work done on the mass by the force as the mass moves from
-axis. Its acceleration as a function of its position is shown in the figure. What is the total work done on the mass by the force as the mass moves from  to
to 

A  mass moves along
mass moves along  -axis. Its acceleration as a function of its position is shown in the figure. What is the total work done on the mass by the force as the mass moves from
-axis. Its acceleration as a function of its position is shown in the figure. What is the total work done on the mass by the force as the mass moves from  to
to 

physics-General
physics-
A mass  slips along the wall of a semispherical surface of radius
slips along the wall of a semispherical surface of radius  . The velocity at the bottom of the surface is
. The velocity at the bottom of the surface is

A mass  slips along the wall of a semispherical surface of radius
slips along the wall of a semispherical surface of radius  . The velocity at the bottom of the surface is
. The velocity at the bottom of the surface is

physics-General
physics-
Three forces of magnitudes 6N, 6N and  N at a corner of a cube along three sides as shown in figure. Resultant of these forces is
N at a corner of a cube along three sides as shown in figure. Resultant of these forces is

Three forces of magnitudes 6N, 6N and  N at a corner of a cube along three sides as shown in figure. Resultant of these forces is
N at a corner of a cube along three sides as shown in figure. Resultant of these forces is

physics-General
physics-
A man standing on a hill top projects a stone horizontally with speed  as shown in figure. Taking the coordinate system as given in the figure. The coordinates of the point where the stone will hit the hill surface
as shown in figure. Taking the coordinate system as given in the figure. The coordinates of the point where the stone will hit the hill surface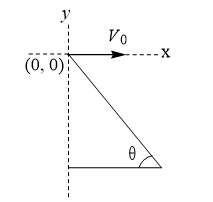
A man standing on a hill top projects a stone horizontally with speed  as shown in figure. Taking the coordinate system as given in the figure. The coordinates of the point where the stone will hit the hill surface
as shown in figure. Taking the coordinate system as given in the figure. The coordinates of the point where the stone will hit the hill surface
physics-General





