Question
If  then
then

The angles of the triangle ABC are denoted by A, B, C and the corresponding opposite sides by a, b, c. solve If  then angle.
then angle.
The correct answer is: 
If  then
then

All three sides are equal. All three angles are congruent and are equal to 60 degrees. It is a regular polygon with three sides. The perpendicular drawn from vertex of the equilateral triangle to the opposite side bisects it into equal halves.
Related Questions to study
Two bodies of mass 1 kg and 3 kg have position vector  respectively the center of mass of this system has a position vector.
respectively the center of mass of this system has a position vector.
Two bodies of mass 1 kg and 3 kg have position vector  respectively the center of mass of this system has a position vector.
respectively the center of mass of this system has a position vector.
In 
In 
In HCl macule the separation between the nuclei of the two atoms is about The approximate location of the center of mass of the molecule is - -A,i with respect of Hydrogen atom ( mass of is 35.5 times of mass of Hydrogen)
In HCl macule the separation between the nuclei of the two atoms is about The approximate location of the center of mass of the molecule is - -A,i with respect of Hydrogen atom ( mass of is 35.5 times of mass of Hydrogen)
Concrete is produced from a mixture of cement, water and small stones. Small amount of gypsum,  is added in cement production to improve the subsequent hardening of concrete. The elevated temperature during the production of cement may lead to the formation of unwanted hemihydrate
is added in cement production to improve the subsequent hardening of concrete. The elevated temperature during the production of cement may lead to the formation of unwanted hemihydrate
 according to reaction,
according to reaction,

The  of
of are
are  and
and  respectively. The respective values of their standard entropies are 194.0, 130.0 and
respectively. The respective values of their standard entropies are 194.0, 130.0 and  . The values of
. The values of 
Answer the following questions on the basis of above information
Heat change occurring during conversion of 1 kg of  (molar mass 172 g
(molar mass 172 g  ) of
) of  is equal to
is equal to
Concrete is produced from a mixture of cement, water and small stones. Small amount of gypsum,  is added in cement production to improve the subsequent hardening of concrete. The elevated temperature during the production of cement may lead to the formation of unwanted hemihydrate
is added in cement production to improve the subsequent hardening of concrete. The elevated temperature during the production of cement may lead to the formation of unwanted hemihydrate
 according to reaction,
according to reaction,

The  of
of are
are  and
and  respectively. The respective values of their standard entropies are 194.0, 130.0 and
respectively. The respective values of their standard entropies are 194.0, 130.0 and  . The values of
. The values of 
Answer the following questions on the basis of above information
Heat change occurring during conversion of 1 kg of  (molar mass 172 g
(molar mass 172 g  ) of
) of  is equal to
is equal to
For an ideal gas, an illustration of three different paths  and
and  from an initial state
from an initial state  to a final state
to a final state  is shown in the given figure
is shown in the given figure
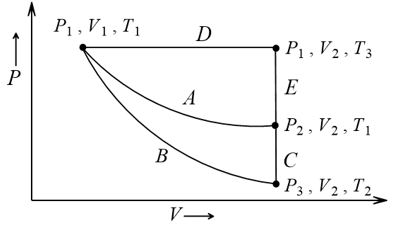
Path A represents a reversible isothermal expansion from  to
to  . Path
. Path  represents a reversible adiabatic expansion (
represents a reversible adiabatic expansion ( ) from
) from  to
to followed by reversible heating the gas at constant volume (
followed by reversible heating the gas at constant volume ( ) from
) from  to
to  . Path
. Path  represents a reversible expansion at constant pressure
represents a reversible expansion at constant pressure  from
from  to
to  followed by a reversible cooling at constant volume
followed by a reversible cooling at constant volume  from
from  to
to 
What is  , for path
, for path  ?
?
For an ideal gas, an illustration of three different paths  and
and  from an initial state
from an initial state  to a final state
to a final state  is shown in the given figure
is shown in the given figure

Path A represents a reversible isothermal expansion from  to
to  . Path
. Path  represents a reversible adiabatic expansion (
represents a reversible adiabatic expansion ( ) from
) from  to
to followed by reversible heating the gas at constant volume (
followed by reversible heating the gas at constant volume ( ) from
) from  to
to  . Path
. Path  represents a reversible expansion at constant pressure
represents a reversible expansion at constant pressure  from
from  to
to  followed by a reversible cooling at constant volume
followed by a reversible cooling at constant volume  from
from  to
to 
What is  , for path
, for path  ?
?
If t is parameter, A = (aSec t, bTan t) and B = (-aTan t, bSec t), O = (0, 0) then the locus of the centroid of  OAB is
OAB is
If t is parameter, A = (aSec t, bTan t) and B = (-aTan t, bSec t), O = (0, 0) then the locus of the centroid of  OAB is
OAB is
A straight line of length 9 units slides with its ends A, B always on x and y axes respectively. Locus of centroid of  OAB is
OAB is
A straight line of length 9 units slides with its ends A, B always on x and y axes respectively. Locus of centroid of  OAB is
OAB is
If the earth were to suddenly contract so that its radius become half of it present radius, without any change in its mass, the duration of the new day will be....
If the earth were to suddenly contract so that its radius become half of it present radius, without any change in its mass, the duration of the new day will be....
If the angles of the Δ ABC are in A.P then 3R2=1
s denotes the semi-perimeter of the triangle ABC, ∆ its area and R the radius of the circle circumscribing the triangle ABC i.e., R is the circum-radius.
If the angles of the Δ ABC are in A.P then 3R2=1
s denotes the semi-perimeter of the triangle ABC, ∆ its area and R the radius of the circle circumscribing the triangle ABC i.e., R is the circum-radius.
Two circular loop A & B of radius rA and rB respectively are made from a uniform wire. The ratio of their moment of inertia about axes passing through their center and perpendicular to their planes is  is equal to...
is equal to...
Two circular loop A & B of radius rA and rB respectively are made from a uniform wire. The ratio of their moment of inertia about axes passing through their center and perpendicular to their planes is  is equal to...
is equal to...
In 
s denotes the semi-perimeter of the triangle ABC, ∆ its area and R the radius of the circle circumscribing the triangle ABC i.e., R is the circum-radius.
In 
s denotes the semi-perimeter of the triangle ABC, ∆ its area and R the radius of the circle circumscribing the triangle ABC i.e., R is the circum-radius.





