Maths-
General
Easy
Question
Statement I : Trace of matrix A =  is equal to a11 + a22 + a33
is equal to a11 + a22 + a33
Statement II : Trace of a matrix is equal to sum of its diagonal elements.
- If both (A) and (R) are true, and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
- If both (A) and (R) are true but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
- If (A) is true but (R) is false.
- If (A) is false but (R) is true.
The correct answer is: If both (A) and (R) are true, and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
Statement I : Trace of matrix A =  is equal to a11 + a22 + a33
is equal to a11 + a22 + a33
Statement II : Trace of a matrix is equal to sum of its diagonal elements.
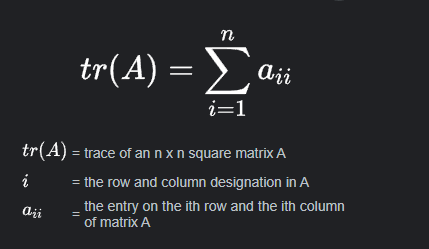
The trace of a square matrix is the sum of its diagonal entries.
Therefore, both Statement I and Statement Il are true, and Statement Il is the correct explanation of Statement I.
The trace has several properties that are used to prove important results in matrix algebra and its applications.
Let A and B be two K X K matrices. Then,![]()
Related Questions to study
Maths-
Statement I : The inverse of the matrix A  does not exist.
does not exist.
Statement II : |A| .
Statement I : The inverse of the matrix A  does not exist.
does not exist.
Statement II : |A| .
Maths-General
Maths-
the focus of parabola (y – k)2 = 4 (x – h) always lies between the line x + y = 1 and x + y = 3 then -
the focus of parabola (y – k)2 = 4 (x – h) always lies between the line x + y = 1 and x + y = 3 then -
Maths-General
Maths-
If the parabola y2 = 4ax passes through (3, 2), then length of latus rectum of the parabola is
If the parabola y2 = 4ax passes through (3, 2), then length of latus rectum of the parabola is
Maths-General
Maths-
The value of 'λ' such that vertex of parabola y = x2 + 2λx + 13 is 4 unit above x axis & lies in first quadrant is
The value of 'λ' such that vertex of parabola y = x2 + 2λx + 13 is 4 unit above x axis & lies in first quadrant is
Maths-General
Maths-
PSQ is a focal chord of a parabola whose focus is S & vertex A . PA and QA are produced to meet the directrix in R and T respectively then 
PSQ is a focal chord of a parabola whose focus is S & vertex A . PA and QA are produced to meet the directrix in R and T respectively then 
Maths-General
physics-
In the figure shown initially spring is in unstretched state & blocks are at rest. Now 100 N force is applied on block A & B as shown in the figure. After some time velocity of 'A' becomes 2 m/s & that of 'B' is 4 m/s & block A displaced by amount 10 cm and spring is stretched by amount 30 cm. Then work done by spring (in joule) force on A will be

In the figure shown initially spring is in unstretched state & blocks are at rest. Now 100 N force is applied on block A & B as shown in the figure. After some time velocity of 'A' becomes 2 m/s & that of 'B' is 4 m/s & block A displaced by amount 10 cm and spring is stretched by amount 30 cm. Then work done by spring (in joule) force on A will be

physics-General
physics-
In the figure, the ball A is released from rest when the spring is at its natural length. For the block B, of mass M to leave contact with the ground at some stage, the minimum mass of A must be:

In the figure, the ball A is released from rest when the spring is at its natural length. For the block B, of mass M to leave contact with the ground at some stage, the minimum mass of A must be:

physics-General
physics-
In the track shown in figure section AB is a quadrant of a circle of 1 metre radius. A block is released at A and slides without friction until it reaches B. After B it moves on a rough horizontal floor and comes to rest at distance 3 metres from B. What is the coefficient of friction between floor and body ?

In the track shown in figure section AB is a quadrant of a circle of 1 metre radius. A block is released at A and slides without friction until it reaches B. After B it moves on a rough horizontal floor and comes to rest at distance 3 metres from B. What is the coefficient of friction between floor and body ?

physics-General
physics-
A particle of mass m moving along a straight line experiences force F which varies with the distance x travelled as shown in the figure. If the velocity of the particle at x0 is  , then velocity at 4
, then velocity at 4  is:-
is:-

A particle of mass m moving along a straight line experiences force F which varies with the distance x travelled as shown in the figure. If the velocity of the particle at x0 is  , then velocity at 4
, then velocity at 4  is:-
is:-

physics-General
physics-
Power versus time graph for a given force is given below. Work done by the force up to time t(£ t0 )

Power versus time graph for a given force is given below. Work done by the force up to time t(£ t0 )

physics-General
physics-
A particle A of mass  is moving in the positive direction of x. Its initial position is x = 0 & initial velocity is 1 m/s. The velocity at x = 10 is in m/s (use the graph given)
is moving in the positive direction of x. Its initial position is x = 0 & initial velocity is 1 m/s. The velocity at x = 10 is in m/s (use the graph given)

A particle A of mass  is moving in the positive direction of x. Its initial position is x = 0 & initial velocity is 1 m/s. The velocity at x = 10 is in m/s (use the graph given)
is moving in the positive direction of x. Its initial position is x = 0 & initial velocity is 1 m/s. The velocity at x = 10 is in m/s (use the graph given)

physics-General
physics-
Block ‘A‘ is hanging from a vertical spring and is at rest. Block ‘B‘ strikes the block ‘A’ with velocity ‘v‘ and sticks to it. Then the value of ‘ v ‘ for which the spring just attains natural length is

Block ‘A‘ is hanging from a vertical spring and is at rest. Block ‘B‘ strikes the block ‘A’ with velocity ‘v‘ and sticks to it. Then the value of ‘ v ‘ for which the spring just attains natural length is

physics-General
physics-
Statement 1:Sound waves cannot propagate through vacuum but light waves can
Statement 2:Sound waves cannot be polarised but light waves can be polarized
Statement 1:Sound waves cannot propagate through vacuum but light waves can
Statement 2:Sound waves cannot be polarised but light waves can be polarized
physics-General
Maths-
Straight line  x + my + n = 0 touches parabola y2 = 4ax if
x + my + n = 0 touches parabola y2 = 4ax if  n = amk then k =
n = amk then k =
Straight line  x + my + n = 0 touches parabola y2 = 4ax if
x + my + n = 0 touches parabola y2 = 4ax if  n = amk then k =
n = amk then k =
Maths-General
Maths-
If  1 &
1 &  2 are length of segments of focal chord of parabola y2 = 4ax than harmonic mean of
2 are length of segments of focal chord of parabola y2 = 4ax than harmonic mean of  1 &
1 &  2 is equal to
2 is equal to
If  1 &
1 &  2 are length of segments of focal chord of parabola y2 = 4ax than harmonic mean of
2 are length of segments of focal chord of parabola y2 = 4ax than harmonic mean of  1 &
1 &  2 is equal to
2 is equal to
Maths-General





