Physics-
General
Easy
Question
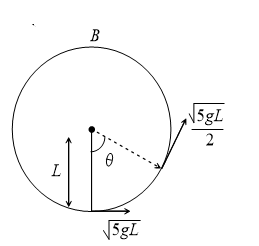
A bob of mass  is suspended by a massless string of length
is suspended by a massless string of length  . The horizontal velocity
. The horizontal velocity  at position
at position  is just sufficient to make it reach the point
is just sufficient to make it reach the point  . The angle
. The angle  at which the speed of the bob is half of that at
at which the speed of the bob is half of that at  , satisfies
, satisfies

The correct answer is: 
Related Questions to study
maths-
The foot of the perpendicular on the line drown from the origin is C if the line cuts the x-axis and y-axis at A and B respectively then BC : CA is
The foot of the perpendicular on the line drown from the origin is C if the line cuts the x-axis and y-axis at A and B respectively then BC : CA is
maths-General
maths-
(where a, b are integers) =
(where a, b are integers) =
maths-General
maths-
maths-General
maths-
is equal to
is equal to
maths-General
maths-
Let denotes greatest integer function, then is equal to
Let denotes greatest integer function, then is equal to
maths-General
maths-
The value of is equal to
The value of is equal to
maths-General
Maths-
The value of  (where {x} is the fractional part of x) is
(where {x} is the fractional part of x) is
The value of  (where {x} is the fractional part of x) is
(where {x} is the fractional part of x) is
Maths-General
Maths-
The shortest distance between the two straight line and
and  is
is
The shortest distance between the two straight line and
and  is
is
Maths-General
physics-
A bob of mass M is suspended by a massless string of length L. The horizontal velocity at position A is just sufficient to make it reach the point B. The angle at which the speed of the bob is half of that at A, satisfies

A bob of mass M is suspended by a massless string of length L. The horizontal velocity at position A is just sufficient to make it reach the point B. The angle at which the speed of the bob is half of that at A, satisfies

physics-General
Physics-
A piece of wire is bent in the shape of a parabola  -axis vertical) with a bead of mass
-axis vertical) with a bead of mass  on it. The bead can side on the wire without friction. It stays at the lowest point of the parabola when the wire is at rest. The wire is now accelerated parallel to the
on it. The bead can side on the wire without friction. It stays at the lowest point of the parabola when the wire is at rest. The wire is now accelerated parallel to the  -axis with a constant acceleration
-axis with a constant acceleration  . The distance of the new equilibrium position of the bead, where the bead can stay at rest with respect to the wire, from the
. The distance of the new equilibrium position of the bead, where the bead can stay at rest with respect to the wire, from the  -axis is
-axis is

A piece of wire is bent in the shape of a parabola  -axis vertical) with a bead of mass
-axis vertical) with a bead of mass  on it. The bead can side on the wire without friction. It stays at the lowest point of the parabola when the wire is at rest. The wire is now accelerated parallel to the
on it. The bead can side on the wire without friction. It stays at the lowest point of the parabola when the wire is at rest. The wire is now accelerated parallel to the  -axis with a constant acceleration
-axis with a constant acceleration  . The distance of the new equilibrium position of the bead, where the bead can stay at rest with respect to the wire, from the
. The distance of the new equilibrium position of the bead, where the bead can stay at rest with respect to the wire, from the  -axis is
-axis is

Physics-General
physics-
A point P moves in counter-clockwise direction on a circular path as shown in the figure. The movement of P is such that it sweeps out length  where
where  is in metre and t is in second. The radius of the path is 20 m. The acceleration of P when t =2s is nearly
is in metre and t is in second. The radius of the path is 20 m. The acceleration of P when t =2s is nearly

A point P moves in counter-clockwise direction on a circular path as shown in the figure. The movement of P is such that it sweeps out length  where
where  is in metre and t is in second. The radius of the path is 20 m. The acceleration of P when t =2s is nearly
is in metre and t is in second. The radius of the path is 20 m. The acceleration of P when t =2s is nearly

physics-General
maths-
The equation of the plane containing the line  where al + bm + cn is equal to
where al + bm + cn is equal to
The equation of the plane containing the line  where al + bm + cn is equal to
where al + bm + cn is equal to
maths-General
physics-
A small body of mass  slides down from the top of a hemisphere of radius
slides down from the top of a hemisphere of radius  . The surface of block and hemisphere are frictionless. The height at which the body lose contact with the surface of the sphere is
. The surface of block and hemisphere are frictionless. The height at which the body lose contact with the surface of the sphere is

A small body of mass  slides down from the top of a hemisphere of radius
slides down from the top of a hemisphere of radius  . The surface of block and hemisphere are frictionless. The height at which the body lose contact with the surface of the sphere is
. The surface of block and hemisphere are frictionless. The height at which the body lose contact with the surface of the sphere is

physics-General
physics-
Average torque on a projectile of mass  , initial speed
, initial speed  and angles of projection
and angles of projection  , between initial and final position
, between initial and final position  and
and  as shown in figure about the point of projection is
as shown in figure about the point of projection is

Average torque on a projectile of mass  , initial speed
, initial speed  and angles of projection
and angles of projection  , between initial and final position
, between initial and final position  and
and  as shown in figure about the point of projection is
as shown in figure about the point of projection is

physics-General
physics-
A string of length  is fixed at one end and the string makes
is fixed at one end and the string makes  rev/s around the vertical axis through, the fixed and as shown in the figure, then tension in the string is
rev/s around the vertical axis through, the fixed and as shown in the figure, then tension in the string is

A string of length  is fixed at one end and the string makes
is fixed at one end and the string makes  rev/s around the vertical axis through, the fixed and as shown in the figure, then tension in the string is
rev/s around the vertical axis through, the fixed and as shown in the figure, then tension in the string is

physics-General