Physics-
General
Easy
Question
An ideal spring with spring-constant K is hung from the ceiling and a block of mass M is attached to its lower end. The mass is released with the spring initially un stretched. Then the maximum extension in the spring is

- 4 Mg/K
- 2 Mg/K
- Mg/K
- Mg/2K
The correct answer is: 2 Mg/K
Let x be the maximum extension of the spring. From energy conservation
Loss in gravitational potential energy
= Gain in potential energy of spring


Related Questions to study
Physics-
The bob of a simple pendulum is displaced from its equilibrium position O to a position Q which is at height h above O and the bob is then released. Assuming the mass of the bob to be m and time period of oscillations to be 2.0 sec, the tension in the string when the bob passes through O is

The bob of a simple pendulum is displaced from its equilibrium position O to a position Q which is at height h above O and the bob is then released. Assuming the mass of the bob to be m and time period of oscillations to be 2.0 sec, the tension in the string when the bob passes through O is

Physics-General
Physics-
Two simple pendulums of length 5 m and 20 m respectively are given small linear displacement in one direction at the same time. They will again be in the phase when the pendulum of shorter length has completed .... oscillations.
Two simple pendulums of length 5 m and 20 m respectively are given small linear displacement in one direction at the same time. They will again be in the phase when the pendulum of shorter length has completed .... oscillations.
Physics-General
Physics-
A sphere of radius r is kept on a concave mirror of radius of curvature R. The arrangement is kept on a horizontal table (the surface of concave mirror is frictionless and sliding not rolling). If the sphere is displaced from its equilibrium position and left, then it executes S.H.M. The period of oscillation will be
A sphere of radius r is kept on a concave mirror of radius of curvature R. The arrangement is kept on a horizontal table (the surface of concave mirror is frictionless and sliding not rolling). If the sphere is displaced from its equilibrium position and left, then it executes S.H.M. The period of oscillation will be
Physics-General
Physics-
A cylindrical piston of mass M slides smoothly inside a long cylinder closed at one end, enclosing a certain mass of gas. The cylinder is kept with its axis horizontal. If the piston is disturbed from its equilibrium position, it oscillates simple harmonically. The period of oscillation will be

A cylindrical piston of mass M slides smoothly inside a long cylinder closed at one end, enclosing a certain mass of gas. The cylinder is kept with its axis horizontal. If the piston is disturbed from its equilibrium position, it oscillates simple harmonically. The period of oscillation will be

Physics-General
Physics-
A thin uniform rod of mass M and length L hangs from a frictionless pivot and is connected at the bottom by a spring to the wall as shown. The spring constant is K. The system is allowed to oscillate by pressing end B of the rod and releasing. The period of oscillation will be

A thin uniform rod of mass M and length L hangs from a frictionless pivot and is connected at the bottom by a spring to the wall as shown. The spring constant is K. The system is allowed to oscillate by pressing end B of the rod and releasing. The period of oscillation will be

Physics-General
Physics-
A semi cylindrical shell with negligible thickness oscillates without slipping on a horizontal surface.
The time period of small oscillations is (Hint : centre of mass of the shell lies at  below the centre)
below the centre)

A semi cylindrical shell with negligible thickness oscillates without slipping on a horizontal surface.
The time period of small oscillations is (Hint : centre of mass of the shell lies at  below the centre)
below the centre)

Physics-General
Physics-
Initially spring is compressed by distance  from equilibrium position. At this compression block is given velocity
from equilibrium position. At this compression block is given velocity  so that compression in the spring increases and block start SHM (Spring constant K). Equation of motion of the block is
so that compression in the spring increases and block start SHM (Spring constant K). Equation of motion of the block is

Initially spring is compressed by distance  from equilibrium position. At this compression block is given velocity
from equilibrium position. At this compression block is given velocity  so that compression in the spring increases and block start SHM (Spring constant K). Equation of motion of the block is
so that compression in the spring increases and block start SHM (Spring constant K). Equation of motion of the block is

Physics-General
Physics-
A ball is suspended by a thread of length l at the point O on the wall, forming a small angle  with the vertical (figure) Then the thread with the ball was deviated through 2
with the vertical (figure) Then the thread with the ball was deviated through 2 and set free. Assuming the collision of the ball against the wall to be perfectly elastic, find the oscillation period of such a pendulum.
and set free. Assuming the collision of the ball against the wall to be perfectly elastic, find the oscillation period of such a pendulum.

A ball is suspended by a thread of length l at the point O on the wall, forming a small angle  with the vertical (figure) Then the thread with the ball was deviated through 2
with the vertical (figure) Then the thread with the ball was deviated through 2 and set free. Assuming the collision of the ball against the wall to be perfectly elastic, find the oscillation period of such a pendulum.
and set free. Assuming the collision of the ball against the wall to be perfectly elastic, find the oscillation period of such a pendulum.

Physics-General
Physics-
A mass m attached to a spring A has a frequency of 3 Hz and a spring B has a frequency of 4 Hz. When both the springs are connected as shown, find the frequency (in Hz) of oscillation.

A mass m attached to a spring A has a frequency of 3 Hz and a spring B has a frequency of 4 Hz. When both the springs are connected as shown, find the frequency (in Hz) of oscillation.

Physics-General
Physics-
If we go deep into earth, time period of simple pendulum will:
If we go deep into earth, time period of simple pendulum will:
Physics-General
General
"The sky appears blue. This is due to atmospheric refraction.”
Identify whether the above statement is true or false.
"The sky appears blue. This is due to atmospheric refraction.”
Identify whether the above statement is true or false.
GeneralGeneral
Physics-
A car is moving with a speed of 100 kmh-1 . if the mass of the car is 950 kg, then its kinetic energy is
A car is moving with a speed of 100 kmh-1 . if the mass of the car is 950 kg, then its kinetic energy is
Physics-General
Chemistry-
Acetic acid is a weak electrolyte because:
Acetic acid is a weak electrolyte because:
Chemistry-General
Physics-
A body is projected horizontally from the top of a high tower with a speed of 20 m/s. After 4 sec the displacement of the body is (take g=10m/s2)
A body is projected horizontally from the top of a high tower with a speed of 20 m/s. After 4 sec the displacement of the body is (take g=10m/s2)
Physics-General
Chemistry-
Consider the reaction: The rate equation for this reaction is :
The rate equation for this reaction is :  Which of these mechanisms is/are consistent with this rate equation ?
Which of these mechanisms is/are consistent with this rate equation ?
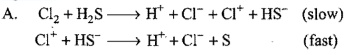

Consider the reaction: The rate equation for this reaction is :
The rate equation for this reaction is :  Which of these mechanisms is/are consistent with this rate equation ?
Which of these mechanisms is/are consistent with this rate equation ?
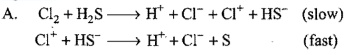

Chemistry-General



